Q. What are the four groups of silicate minerals?
Silicate minerals are the most common of Earth’s minerals and include quartz, feldspar, mica, amphibole, pyroxene, and olivine.
Q. What is the most common group of silicates?
Feldspar and quartz are the two most common silicate minerals. Both are extremely common rock-forming minerals. The basic building block for all silicate minerals is the silica tetrahedron, which is illustrated in Figure below.
Table of Contents
- Q. What are the four groups of silicate minerals?
- Q. What is the most common group of silicates?
- Q. What are the two classes of silicate minerals?
- Q. What is silicates and its types?
- Q. What is the basic building block of silicate minerals?
- Q. Why are minerals classified?
- Q. What are the different kind of minerals?
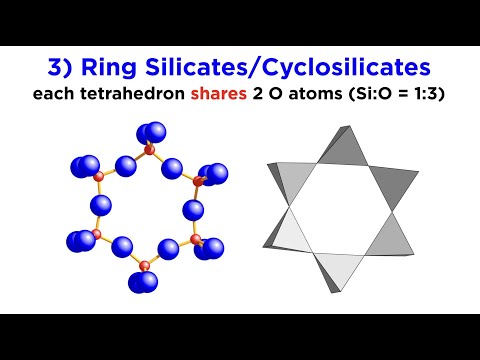
Q. What are the two classes of silicate minerals?
For example, nesosilicates are minerals whose structure are made up of independent silicate tetrahedrons. Sorosilicates are silicate minerals consisting of double tetrahedral groups in which one oxygen atom is shared by two tetrahedrons.
Q. What is silicates and its types?
TYPES & CLASSIFICATION OF SILICATES Ortho silicates (or Nesosilicates) Pyro silicate (or Sorosilicates) Cyclic silicates (or Ring silicates) Chain silicates (or pyroxenes) Double chain silicate (or amphiboles)
Q. What is the basic building block of silicate minerals?
The basic building block of the silicate structure is the silicate tetrahedron–a pyramid-shaped unit with one Si at the center surrounded by four oxygen atoms. These tetrahedra link together and combine with additional elements such as Fe, Al, Ca etc. to form the different silicate minerals.
Q. Why are minerals classified?
Minerals are classified on the basis of their chemical composition, which is expressed in their physical properties. This module, the second in a series on minerals, describes the physical properties that are commonly used to identify minerals. These include color, crystal form, hardness, density, luster, and cleavage.
Q. What are the different kind of minerals?
Types of minerals
- Native elements. eg. Gold, Silver, Mercury, graphite, diamond.
- Oxides. eg corundum (incl. sapphire), hematite, spinel.
- Hydroxides. eg. Goethite, brucite.
- Sulfides. eg. Pyrite, galena, sphalerite.
- Sulfates. eg. Baryte, gypsum.
- Carbonates. eg. Calcite, magnesite, dolomite.
- Phosphates. eg. Apatite, monazite.
- Halides. eg.