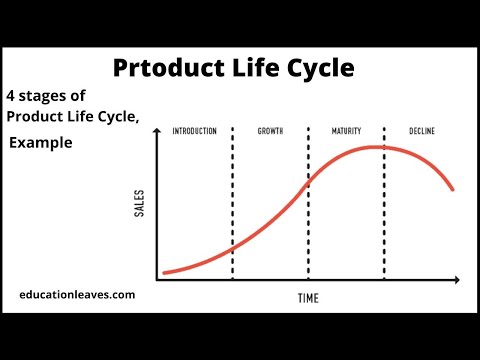
After a product reaches the marketplace, it enters the product life cycle. This cycle typically has four stages: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline (and possibly death). Profit margins are usually small in the introductory phase, reach a peak at the end of the growth phase, and then decline.
Q. What is the introduction stage of the product life cycle?
Definition: Introduction stage is the first stage in the product life cycle. The highlighting factor of this stage is that the product is new in the market, sales are slow and to push it higher the company has to incur heavy expenditure on advertisement to make it appealing to customers.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the introduction stage of the product life cycle?
- Q. Which phase of the product life cycle includes sales?
- Q. What are the 4 phases of the product lifecycle?
- Q. What are 4 possible extension strategies?
- Q. Is it possible to continually extend a brand to increase the life cycle of a product?
- Q. What is brand extension and example?
- Q. When is brand extension a good strategy?
- Q. Is brand extension a good strategy?
- Q. What makes a successful brand extension?
- Q. When is brand extension a bad strategy?
- Q. What is brand extension strategies?
- Q. Why is brand extension bad?
- Q. What possible mistakes can a company make when pursuing a brand extension?
- Q. What are common branding mistakes?
- Q. What is bad branding?
- Q. How do you avoid branding mistakes?
- Q. Why does brand strategy matter?
- Q. What are the effects of unsuccessful branding?
- Q. What brands are bad?
- Q. What makes a brand weak?
- Q. What is a weak market image?
- Q. What makes a good brand?
- Q. What are the five key features of a brand?
- Q. How do you develop your brand?
Q. Which phase of the product life cycle includes sales?
The diagram at the top of the page illustrates that the marketing product cycle consists of four phases: introduction, growth, maturity and decline. When a product has reached the maturity stage, its sales figures are up and it generates a profit.
Q. What are the 4 phases of the product lifecycle?
As mentioned earlier, the product life cycle is separated into four different stages, namely introduction, growth, maturity and in some cases decline.
- Introduction. The introduction phase is the period where a new product is first introduced into the market.
- Growth.
- Maturity.
- Decline.
Q. What are 4 possible extension strategies?
Extension strategies include rebranding, price discounting and seeking new markets.
Q. Is it possible to continually extend a brand to increase the life cycle of a product?
A branded good can enjoy continuous growth, such as Microsoft, because the product is being constantly improved and advertised, and maintains a strong brand loyalty. Extension strategies extend the life of the product before it goes into decline. Again businesses use marketing techniques to improve sales.
Q. What is brand extension and example?
Brand extension or brand stretching is a marketing strategy in which a firm marketing a product with a well-developed image uses the same brand name in a different product category. The new product is called a spin-off. An example of a brand extension is Jello-gelatin creating Jello pudding pops.
Q. When is brand extension a good strategy?
Companies may implement a brand-extension strategy when they have new products to launch but don’t want to set up a new brand. Brand extensions also have real potential for businesses who have a solid following and loyal customer base, but also want to diversify products and reach a wider audience.
Q. Is brand extension a good strategy?
A brand extension strategy can be a great way to tap into the full potential of your business, by exploring new niches, products, and services. When used correctly, your brand extension solution can improve your reputation, give you ways to connect with new audiences, and even strengthen your global image.
Q. What makes a successful brand extension?
What is the recipe for a successful brand extension? Simply put, companies must expand their reach, demonstrate their value, and grow their business with products that capitalize on logic and leverage.
Q. When is brand extension a bad strategy?
Brand extension in unrelated markets may lead to loss of reliability if a brand name is extended too far. An organization must research the product categories in which the established brand name will work. There is a risk that the new product may generate implications that damage the image of the core/original brand.
Q. What is brand extension strategies?
A brand extension is when a company uses one of its established brand names on a new product or new product category. It’s sometimes known as brand stretching. The strategy behind a brand extension is to use the company’s already established brand equity to help it launch its newest product.
Q. Why is brand extension bad?
Having the extension fail is usually not nearly so bad as having it “succeed” and damage the brand name by creating undesirable attribute associations, damaging the brand’s perceived quality, or altering existing associations.
Q. What possible mistakes can a company make when pursuing a brand extension?
Brand Cannibalism: There is the potential for brand cannibalism where the extensions don’t enhance the parent brand but rather shift market share from it or damage its reputation. Brand Dilution: The brand could become a victim of brand dilution, which is a common result of a over-extending a brand.
Q. What are common branding mistakes?
Top Ten Branding Mistakes
- INCONSISTENT CORPORATE IDENTITY.
- POOR VISUALS (or no visuals)
- NOT TRAINING EMPLOYEES.
- FAILURE TO TRACK BRANDING EFFORTS.
- NOT USING EXISTING CONSUMERS, CLIENTS, PATIENTS FOR BRANDING.
- LETTING MARKETING MATERIALS GET STALE.
- FAILING TO FOCUS BRANDING ON THE CORE SERVICE.
- NOT HAVING A TAG LINE THAT IS BELIEVABLE.
Q. What is bad branding?
A “bad brand” is a brand that, for one reason or another, doesn’t resonate with audiences. The values may be weak or lacking, and the messaging may be all over the place. People want to associate with these brands because of their values and/or mission.
Q. How do you avoid branding mistakes?
9 Crucial Branding Mistakes to Avoid
- Not Having Brand Guidelines.
- Underestimating the Importance of a Logo.
- Using Vague or Inaccurate Copy.
- Not Proofreading Before Publishing Content.
- Jumping on the Bandwagon for the Sake of Relevance.
- Neglecting Customer Experience.
- Disengaging from the Community.
- Not Having a Crisis Management Plan.
Q. Why does brand strategy matter?
If you can’t clearly express what your business does, the unique value it brings to the market and what it stands for, no one will understand what your brand is about. Makes it easier for prospects to recognize your brand among competitors. Improves marketing efforts.
Q. What are the effects of unsuccessful branding?
The effects of poor branding design can run deep in your business. At their worst, they can negate the advantage of having a stellar product or service. Poor branding design ultimately gives consumers an inaccurate representation of your business, which then prevents you from developing relationships.
Q. What brands are bad?
Here are the 10 brands with the worst corporate reputations in America in 2019:
- Trump Org.
- Sears.
- Wells Fargo.
- Dish.
- 7. Facebook.
- Goldman Sachs. Reuters/ Lucas Jackson.
- Bank of America. AP Photo.
- Comcast. Lucas Jackson/Reuters.
Q. What makes a brand weak?
A brand is weak when it cannot communicate its values – or when it is incapable of asserting a price premium for the added value it offers. Brand weakness is often a mark of those brands that consumers consider to be interchangeable.
Q. What is a weak market image?
A technically weak market reflects the fragile signals or negative data points from money flow or technical analysis that contribute to the overall fragility of the market. Typically, technically weak markets are considered to be bearish markets, in which the market shows declining trading volume and prices.
Q. What makes a good brand?
A good brand has a clear focus, knows their target audience, has a defined mission, knows their competition and USP, can identify their key values, tell their story and have a brand identity reflective of these goals, and does all of this consistently. …
Q. What are the five key features of a brand?
The process of branding is complete only when you have carefully defined and considered these five key elements: promise, position, personality traits, story and associations.
Q. How do you develop your brand?
A 10-Step Brand Development Strategy
- Consider your overall business strategy.
- Identify your target clients.
- Research your target client group.
- Develop your brand positioning.
- Develop your messaging strategy.
- Develop your name, logo and tagline.
- Develop your content marketing strategy.
- Develop your website.