Q. What are the functions of nerve cells?
Neurons (also known as neurones, nerve cells and nerve fibers) are electrically excitable cells in the nervous system that function to process and transmit information. In vertebrate animals, neurons are the core components of the brain, spinal cord and peripheral nerves.
Q. Is the nerve cell a cell?
Cells of the nervous system, called nerve cells or neurons, are specialized to carry “messages” through an electrochemical process. Neurons are similar to other cells in the body because: Neurons are surrounded by a cell membrane. Neurons have a nucleus that contains genes.
Table of Contents
- Q. What are the functions of nerve cells?
- Q. Is the nerve cell a cell?
- Q. Where can you find the nerve cell?
- Q. What are the two nerve cells?
- Q. What is another name for a nerve cell?
- Q. What is the main part of the nerve cell?
- Q. What are the types of nerve cell?
- Q. Which organ is part of our nervous system?
- Q. What part of your nervous system does logical thinking?
- Q. What are 5 components of nervous system anatomy?
- Q. What does nerve pain feel like?
- Q. What color is a nerve?
- Q. What runs through nerves?
- Q. Where are most of your nerves located?
- Q. Do you have nerves in your brain?
- Q. How do you treat nerve inflammation?
- Q. Will an MRI show nerve damage?
- Q. How do you prove you have nerve damage?
- Q. What happens if you have nerve damage?
- Q. Can I sue for nerve damage?
Q. Where can you find the nerve cell?
The target cells of neurons include other nerve cells in the brain, spinal cord, and autonomic ganglia, and the cells of muscles and glands throughout the body.
Q. What are the two nerve cells?
There are two broad classes of cells in the nervous system: neurons, which process information, and glia, which provide the neurons with mechanical and metabolic support. Three general categories of neurons are commonly recognized (Peters, Palay, & Webster, 1976).
Q. What is another name for a nerve cell?
Nerve cell (neuron)
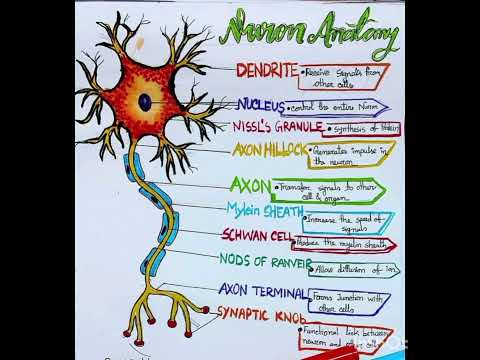
Q. What is the main part of the nerve cell?
A neuron has three main parts: dendrites, an axon, and a cell body or soma (see image below), which can be represented as the branches, roots and trunk of a tree, respectively. A dendrite (tree branch) is where a neuron receives input from other cells.
Q. What are the types of nerve cell?
For the spinal cord though, we can say that there are three types of neurons: sensory, motor, and interneurons.
- Sensory neurons.
- Motor neurons.
- Interneurons.
- Neurons in the brain.
Q. Which organ is part of our nervous system?
The central nervous system is made up of the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system is made up of nerves that branch off from the spinal cord and extend to all parts of the body.
Q. What part of your nervous system does logical thinking?
Cerebrum. The largest part of the brain is divided into two halves called hemispheres. The left one, which controls the right side of your body, handles speech for most people. It also controls logic, math calculations, and pulling facts from your memory.
Q. What are 5 components of nervous system anatomy?
The nervous system consists of the brain, spinal cord, sensory organs, and all of the nerves that connect these organs with the rest of the body. Together, these organs are responsible for the control of the body and communication among its parts.
Q. What does nerve pain feel like?
Nerve pain often feels like a shooting, stabbing or burning sensation. Sometimes it can be as sharp and sudden as an electric shock. People with neuropathic pain are often very sensitive to touch or cold and can experience pain as a result of stimuli that would not normally be painful, such as brushing the skin.
Q. What color is a nerve?
Color is both symbolic and practical Arteries and nerves appear white, and veins appear whitish-blue.
Q. What runs through nerves?
Nervous system messages travel through neurons as electrical signals. When these signals reach the end of a neuron, they stimulate the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters travel across synapses, spaces between neurons or between neurons and other body tissues and cells.
Q. Where are most of your nerves located?
The central nervous system (CNS) includes the nerves in the brain and spinal cord. It is safely contained within the skull and vertebral canal of the spine. All of the other nerves in the body are part of the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
Q. Do you have nerves in your brain?
Nerves that directly connect the brain and the brain stem with the eyes, ears, nose, and throat and with various parts of the head, neck, and trunk are called cranial nerves. There are 12 pairs of them (see Overview of the Cranial Nerves).
Q. How do you treat nerve inflammation?
Treating Nerve Pain
- Topical treatments. Some over-the-counter and prescription topical treatments — like creams, lotions, gels, and patches — can ease nerve pain.
- Anticonvulsants.
- Antidepressants .
- Painkillers.
- Electrical stimulation.
- Other techniques.
- Complementary treatments.
- Lifestyle changes.
Q. Will an MRI show nerve damage?
MRI is sensitive to changes in cartilage and bone structure resulting from injury, disease, or aging. It can detect herniated discs, pinched nerves, spinal tumors, spinal cord compression, and fractures.
Q. How do you prove you have nerve damage?
The signs of nerve damage Numbness or tingling in the hands and feet. Feeling like you’re wearing a tight glove or sock. Muscle weakness, especially in your arms or legs. Regularly dropping objects that you’re holding.
Q. What happens if you have nerve damage?
A nerve injury can affect your brain’s ability to communicate with your muscles and organs. Damage to the peripheral nerves is called peripheral neuropathy. It’s important to get medical care for a peripheral nerve injury as soon as possible. Early diagnosis and treatment may prevent complications and permanent damage.
Q. Can I sue for nerve damage?
Can I Sue If My Nerve Damage was Caused by a Botched Surgery? If your nerve damage was caused by a botched or failed surgery, you may be able to file a medical malpractice lawsuit. Oftentimes nerve problems after surgery resolve on their own, but sometimes the damage is more severe and will cause lifelong issues.