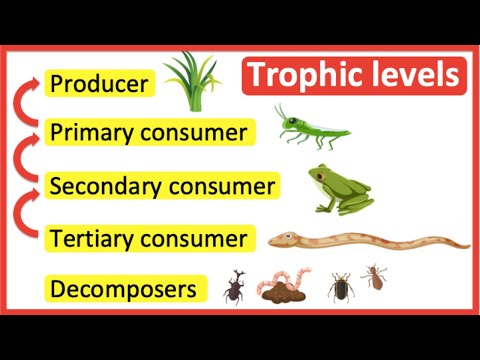
Q. What are the main Autotrophs on land?
Plants
Q. What is an Autotroph primary producer?
Autotroph, in ecology, an organism that serves as a primary producer in a food chain. Autotrophs obtain energy and nutrients by harnessing sunlight through photosynthesis (photoautotrophs) or, more rarely, obtain chemical energy through oxidation (chemoautotrophs) to make organic substances from inorganic ones.
Table of Contents
- Q. What are the main Autotrophs on land?
- Q. What is an Autotroph primary producer?
- Q. What is the main producer?
- Q. What are the examples of Autotroph?
- Q. What are the 4 types of Autotrophs?
- Q. Can humans fix carbon?
- Q. Is algae a bacteria or plant?
- Q. Is algae toxic to humans?
- Q. Why is algae so bad?
- Q. Is algae a prokaryote?
- Q. What are 2 examples of prokaryotes?
- Q. Is virus a prokaryote?
- Q. Is microalgae a prokaryote?
- Q. Is microalgae a seaweed?
- Q. Is algae a microalgae?
- Q. Why is microalgae important to life?
- Q. Is algae the future?
- Q. What is the difference between algae and microalgae?
Q. What is the main producer?
The producer also supervises the pre-production, production, and post-production stages of filmmaking. In this case, the main producer or executive producer may hire and delegate work to associate producers, assistant producers, line producers or unit production managers.
Q. What are the examples of Autotroph?
Autotrophs are any organisms that are capable of producing their own food….Some examples include:
- Algae.
- Cyanobacteria.
- Maize plant.
- Grass.
- Wheat.
- Seaweed.
- Phytoplankton.
Q. What are the 4 types of Autotrophs?
Types of Autotrophs
- Photoautotrophs. Photoautotrophs are organisms who get the energy to make organic materials from sunlight.
- Chemoautotrophs. Chemoautotrophs are organisms that obtain energy from inorganic chemical processes.
- Plants.
- Green Algae.
- ”Iron Bacteria” – Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans.
Q. Can humans fix carbon?
Carbon is primarily fixed through photosynthesis, but some organisms use a process called chemosynthesis in the absence of sunlight. Heterotrophs are not themselves capable of carbon fixation but are able to grow by consuming the carbon fixed by autotrophs or other heterotrophs.
Q. Is algae a bacteria or plant?
Algae are sometimes considered plants and sometimes considered “protists” (a grab-bag category of generally distantly related organisms that are grouped on the basis of not being animals, plants, fungi, bacteria, or archaeans).
Q. Is algae toxic to humans?
Harmful algae and cyanobacteria (sometimes called blue-green algae) can produce toxins (poisons) that can make people and animals sick and affect the environment.
Q. Why is algae so bad?
Harmful effects. As algal blooms grow, they deplete the oxygen in the water and block sunlight from reaching fish and plants. And when the algae eventually die off, the microbes which decompose the dead algae use up even more oxygen, which in turn causes more fish to die or leave the area.
Q. Is algae a prokaryote?
Algae are eukaryotic organisms, which are organisms whose cells contain a nucleus and other structures (organelles) enclosed within membranes. Cyanobacteria are prokaryotes, which lack membrane-bound organelles and have a single circular chromosome.
Q. What are 2 examples of prokaryotes?
Examples of prokaryotes are bacteria, archaea, and cyanobacteria (blue-green algae).
Q. Is virus a prokaryote?
Viruses are neither prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Viruses are not made of cells. Viruses cannot replicate on their own. Most scientists do not consider viruses to be living.
Q. Is microalgae a prokaryote?
Microalgae are prokaryotic and eukaryotic micro-organisms that can fix organic (autotrophic) and inorganic (heterotrophic) carbon. The example of prokaryotic microalgae includes Cyanobacteria, and eukaryotic microalgae include diatoms and green algae.
Q. Is microalgae a seaweed?
Summary – Macroalgae vs Microalgae Macroalgae are commonly known as seaweeds while microalgae are commonly known as phytoplankton. Macroalgae are large and multicellular aquatic photosynthetic plant-like organisms. Hence, they are visible to our naked eye.
Q. Is algae a microalgae?
What are Algae? Algae are simple plants that can range from the microscopic (microalgae), to large seaweeds (macroalgae), such as giant kelp more than one hundred feet in length. Microalgae include both cyanobacteria, (similar to bacteria, and formerly called “blue-green algae”) as well as green, brown and red algae.
Q. Why is microalgae important to life?
Microalgae, capable of performing photosynthesis, are important for life on earth; they produce approximately half of the atmospheric oxygen and use simultaneously the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide to grow photoautotrophically. The biodiversity of microalgae is enormous and they represent an almost untapped resource.
Q. Is algae the future?
Experts say algae could be a possible solution. Unlike most crops, it doesn’t require fresh water to flourish. About 70% of the planet’s available fresh water goes toward crops and raising livestock. Meat uses up a lot of our finite resources, like water and land, not just for the animals but to grow their food, too.
Q. What is the difference between algae and microalgae?
Algae and microalgae are photosynthetic organisms that serve as an excellent food source in aquatic ecosystems. The main difference between algae and microalgae is that algae are simple, autotrophic organisms, consisting of a huge diversity among them whereas microalgae are the microscopic type of algae.