Q. What are the organs protected by the thoracic cage?
The thoracic cage protects the heart and lungs. It is composed of 12 pairs of ribs with their costal cartilages and the sternum.
Q. What 2 organs do the ribs protect?
The ribs are connected to the sternum with a strong, somewhat flexible material called cartilage. The rib cage help protects the organs in the chest, such as the heart and lungs, from damage.
Q. What two primary functions are performed by the thoracic cage?
The ribs are attached posteriorly to the 12 thoracic vertebrae and most are anchored anteriorly either directly or indirectly to the sternum. The thoracic cage functions to protect the heart and lungs.
Q. What are the components of the thoracic cage?
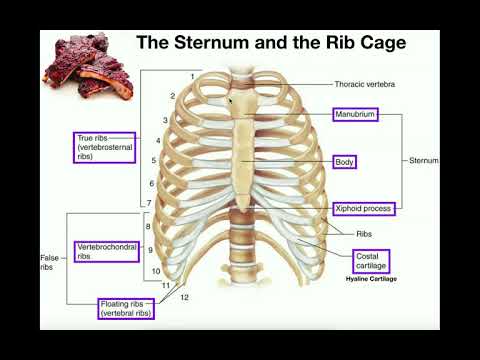
The thoracic cage (human rib cage) is a bony and cartilaginous structure which surrounds the thoracic cavity and supports the pectoral girdle, forming a core portion of the human skeleton. A typical human rib cage consists of 24 ribs, the sternum (with xiphoid process), costal cartilages, and the 12 thoracic vertebrae.
Q. What are the 4 parts of the thoracic cage?
It is formed by the 12 pairs of ribs, the sternum (breast bone), costal cartilages, and the 12 thoracic vertebrae. These bony and cartilagenous structures form the thoracic cage (rib cage) which surrounds the thoracic cavity and supports the shoulder girdle.
Q. What does thoracic cage mean?
Thoracic cage: The structure formed by the thoracic vertebrae and ribs, the sternum (breastbone), and the costal cartilages (that attach the ribs to the sternum). A cage is an enclosure made of “open work” that usually houses animals. The thoracic cage is also called the rib cage.
Q. Does the thoracic cage protect the liver?
The liver is partly protected by the rib cage. In fact, it is so tightly packed into the ribcage that a slight impression is often left on the top of the liver. The liver is the largest organ in the body.
Q. Is liver under rib cage?
Your liver is a football-sized organ that sits under your ribs. It works as your body’s processing plant. Among its more than 500 jobs are to convert food from the small intestine into substances that help you absorb fat and fight off diseases, stockpile energy, and filter and clean your blood.
Q. Can a doctor feel if your liver is enlarged?
You may have an enlarged liver if your doctor can feel it during a physical exam. A typical liver can’t be felt with your fingers. The size and weight of your liver increases naturally with age.
Q. How do you check your pancreas?
Blood tests to look for elevated levels of pancreatic enzymes. Stool tests in chronic pancreatitis to measure levels of fat that could suggest your digestive system isn’t absorbing nutrients adequately. Computerized tomography (CT) scan to look for gallstones and assess the extent of pancreas inflammation.
Q. What triggers pancreatitis?
The most common cause of acute pancreatitis is having gallstones. Gallstones cause inflammation of your pancreas as stones pass through and get stuck in a bile or pancreatic duct. This condition is called gallstone pancreatitis.