A major effect of sedimentation is the loss of storage capacity, which can have a serious impact on water resources development by reducing water supply, hydropower production, the supply of irrigation water, and the effectiveness of flood control schemes.
Q. Why is sediment a problem?
Sediment in stream beds disrupts the natural food chain by destroying the habitat where the smallest stream organisms live and causing massive declines in fish populations. Sediment increases the cost of treating drinking water and can result in odor and taste problems.
Table of Contents
- Q. Why is sediment a problem?
- Q. What is sedimentation and sedimentation problems in India?
- Q. What are examples of sediment?
- Q. What are the 4 types of sediments?
- Q. What is the settling out of the sediment called?
- Q. What pulls the sediment down?
- Q. When boiling water Liquifies sediment what can form?
- Q. What bacteria survives boiling?
- Q. Is boiling water an example of conduction?
- Q. Can you get water hotter than boiling?
- Q. Can boiling water go above 100?
- Q. What is hotter boiling water or steam?
- Q. Is boiling water always 100?
- Q. Does salt help water boil?
Q. What is sedimentation and sedimentation problems in India?
Soil erosion, sediment transport and sediment deposition also cause major problems for the numerous hydropower projects which are found in the Indian sub–Himalayan region. Furthermore, reservoir storage can be greatly reduced by reservoir sedimentation.
Q. What are examples of sediment?
Common sedimentary rocks include sandstone, limestone, and shale. These rocks often start as sediments carried in rivers and deposited in lakes and oceans. When buried, the sediments lose water and become cemented to form rock.
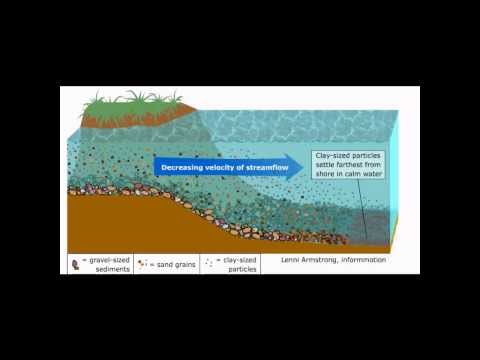
Q. What are the 4 types of sediments?
Sediments are also classified by origin. There are four types: lithogenous, hydrogenous, biogenous and cosmogenous. Lithogenous sediments come from land via rivers, ice, wind and other processes. Biogenous sediments come from organisms like plankton when their exoskeletons break down.
Q. What is the settling out of the sediment called?
The particles that settle out from the suspension become sediment, and in water treatment is known as sludge. When a thick layer of sediment continues to settle, this is known as consolidation.
Q. What pulls the sediment down?
The sediments are transported away from the place where they form. There are several agents of erosion. Flowing water moves and deposits sediments. Water erodes far more material than any other erosional agent. Gravity as a force of erosion pulls material downhill.
Q. When boiling water Liquifies sediment what can form?
(2016) described for the first time how boiling water provokes ejection of sand particles while the liquid flow percolates downslope. The combination of these transport mechanisms triggers the formation of arcuate sand ridges perpendicular to the flow direction and dry sand avalanches.
Q. What bacteria survives boiling?
Although, some bacterial spores not typically associated with water borne disease are capable of surviving boiling conditions (e.g. clostridium and bacillus spores), research shows that water borne pathogens are inactivated or killed at temperatures below boiling (212°F or 100°C).
Q. Is boiling water an example of conduction?
Conduction is probably the most basic and intuitive way of achieving heat transfer. Something hot touches something cool and the cool thing heats up. For instance, the water in a pot boils when the flame from the stovetop heats the pan, and the heat from the pan is transferred to the water via conduction.
Q. Can you get water hotter than boiling?
Superheated water is liquid water under pressure at temperatures between the usual boiling point, 100 °C (212 °F) and the critical temperature, 374 °C (705 °F).
Q. Can boiling water go above 100?
Water Hotter Than Boiling Point and Colder Than Freezing Point. Liquid water can be hotter than 100 °C (212 °F) and colder than 0 °C (32 °F). Heating water above its boiling point without boiling is called superheating. If water is superheated, it can exceed its boiling point without boiling.
Q. What is hotter boiling water or steam?
Boiling water is a saturated liquid vapor mixture but steam is either a saturated vapor or a superheated vapor. Steam can be superheated only when the applied temperature is greater than the saturated temperature for a given pressure. Hence steam is always hotter than boiling water.
Q. Is boiling water always 100?
The simple answer to this question is that the boiling point of water is 100 °C or 212 °F at 1 atmosphere of pressure (sea level). However, the value is not a constant. The boiling point of water depends on the atmospheric pressure, which changes according to elevation.
Q. Does salt help water boil?
Adding salt to water is going to do two things to water’s physical properties: it will raise the boiling point and it will lower the specific heat. These two changes actually work against each other. Raising the boiling point will make the water boil slower.