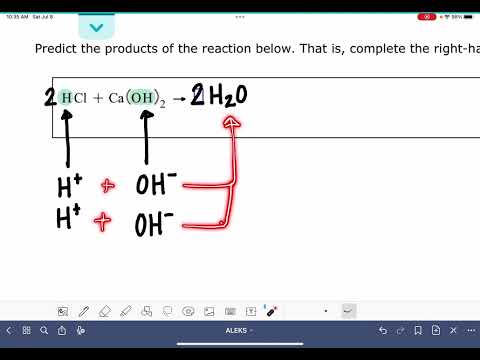
Q. What are the products of neutralization?
Neutralization reactions occur when two reactants, an acid and a base, combine to form the products salt and water.
Q. What are the three products of a neutralization reaction?
In the neutralisation reaction between an acid and a metal carbonate, there are three products. The hydrogen ions (H +) from the acid react with the carbonate ions (CO 3 2-) to form water and carbon dioxide gas. A salt is also produced.
Table of Contents
- Q. What are the products of neutralization?
- Q. What are the three products of a neutralization reaction?
- Q. What is Neutralisation in chemistry?
- Q. Which best describes the pH scale?
- Q. What is Neutralisation give two examples?
- Q. What is a real life example of neutralization reaction?
- Q. What happens when acid or base is mixed with water?
- Q. What happens when bases are mixed with water?
- Q. What happens when an acid or base is?
- Q. How strong are acid or base solutions?
- Q. Is chloric acid strong or weak?
- Q. What is the pH of most soils?
- Q. How can the strength of basic solution be increased?
- Q. Which solution is more basic?
- Q. What is the strength of solution?
- Q. What is the difference between concentration and strength in chemistry?
- Q. What are the similarities and differences between acid or base strength and concentration?
- Q. What is the relation between pH and concentration?
- Q. How is pH related to acidity?
- Q. Why pH is not more than 14?
- Q. How is pH calculated?
- Q. What is pH full form?
- Q. How is pH important in our daily lives?
- Q. What is the pH for 1.5 m NaOH?
- Q. What is the pH of 1’m NaOH?
- Q. What is the pH of a 2m solution of HCl?
- Q. What is the pH of 4m NaOH?
Q. What is Neutralisation in chemistry?
Neutralisation is the reaction between an acid and a base. Acids react with metals, bases and carbonates to produce salts.
Q. Which best describes the pH scale?
Answer: The correct answer is Acids measure below 7. pH ( Potential of hydrogen) is used to measure the basicity ( alkalinity) or acidity of water soluble substances. The value on pH scales lies from 0 to 14 where 7 indicates a neutral pH that corresponding to neutral solutions like water.
Q. What is Neutralisation give two examples?
Hint: The neutralization reaction is the one in which an acid reacts with an equimolar amount of base to give salt and water. The example could be a reaction between any strong acid and a base. The sodium chloride formed is a result of neutralization reaction.
Q. What is a real life example of neutralization reaction?
Using neutralisation Antacid tablets contain bases such as magnesium hydroxide and magnesium carbonate to neutralise the extra acid. Bee stings are acidic. They can be neutralised using baking powder, which contains sodium hydrogen carbonate.
Q. What happens when acid or base is mixed with water?
Diluting acids and bases Adding water to an acid or base will change its pH. Water is mostly water molecules so adding water to an acid or base reduces the concentration of ions in the solution. The acid is becoming less acidic. Similarly, when an alkali is diluted with water the concentration of OH – ions decreases.
Q. What happens when bases are mixed with water?
Bases, on the other hand, mixed with water yield hydroxide ions (OH-). If a solution has a high concentration of H+ ions, then it is acidic. The H+ ions in the acid join with and are neutralized by the OH- ions of the base to form H2O.
Q. What happens when an acid or base is?
When an acid and a base are placed together, they react to neutralize the acid and base properties, producing a salt. The H(+) cation of the acid combines with the OH(-) anion of the base to form water. The compound formed by the cation of the base and the anion of the acid is called a salt.
Q. How strong are acid or base solutions?
The strength of an acid or base is measured on a scale of numbers called pH scale (0-14). More acidic a solution is lesser will be its pH. Solution with pH=0,1,2,3 are strong acids. Solution with pH=4,5,6 are weak acids.
Q. Is chloric acid strong or weak?
The strong acids are hydrochloric acid, nitric acid, sulfuric acid, hydrobromic acid, hydroiodic acid, perchloric acid, and chloric acid. The only weak acid formed by the reaction between hydrogen and a halogen is hydrofluoric acid (HF).
Q. What is the pH of most soils?
Most soils have pH values between 3.5 and 10. In higher rainfall areas the natural pH of soils typically ranges from 5 to 7, while in drier areas the range is 6.5 to 9. Soils can be classified according to their pH value: 6.5 to 7.5—neutral.
Q. How can the strength of basic solution be increased?
We can increase the strength of the basic solution by adding more concentration of ions or by adding more basic solution to it.
Q. Which solution is more basic?
Now there are more hydrogen ions than hydroxide ions in the solution. This kind of solution is acidic. A base is a substance that accepts hydrogen ions….What does it mean for a solution to be acidic or basic (alkaline)?
| pH Value | H+ Concentration Relative to Pure Water | Example |
|---|---|---|
| 11 | 0.000 1 | ammonia solution |
Q. What is the strength of solution?
Strength of the solution is defined as the amount of solute in grams that is present in one litre solution. There are many quantities that represent the strength of the solution which is normality, molarity and molality.
Q. What is the difference between concentration and strength in chemistry?
Strength: The strength of an acid or base refers to how much of the acid or bases ions are released in a solution. Concentration: Concentration refers to the number of moles per volume are contained within the solution. It also applies to how much of the acid or base is contained within the solution.
Q. What are the similarities and differences between acid or base strength and concentration?
The strength of an acid relates to the number of free ions in solution while the concentration of an acid relates to the number of ions that it contributes to a solution.
Q. What is the relation between pH and concentration?
As a solution gets more basic (higher [OH-]), the pH increases. As the pH of a solution decreases by one pH unit, the concentration of H+ increases by ten times. As the pH of a solution increases by one pH unit, the concentration of OH- increases by ten times….
| [H+] | [OH-] | pH |
|---|---|---|
| 1.0 × 10-14 | 1.0 | 14.00 |
Q. How is pH related to acidity?
If you add acid to a solution the concentration of hydrogen ions (acidity) increases and the pH decreases. Frequently people confuse pH with acidity—pH is the scale on which acidity is expressed, but it is not synonymous with acidity.
Q. Why pH is not more than 14?
One far end is not more than 1M of hydrogen ions, which results in a pH value of not more than 0. While on the other end is not more than 1M of hydroxide ions which results in a pH value of not more than 14. The pH value goes out of the 0-14 range when the concentration of the solution exceeds 1M.
Q. How is pH calculated?
To calculate the pH of an aqueous solution you need to know the concentration of the hydronium ion in moles per liter (molarity). The pH is then calculated using the expression: pH = – log [H3O+]. Example: What is the pOH of a solution that has a hydroxide ion concentration of 4.82 x 10-5 M?
Q. What is pH full form?
In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/, denoting ‘potential of hydrogen’ or ‘power of hydrogen’) is a scale used to specify the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution.
Q. How is pH important in our daily lives?
pH is very important in our digestive system. In the stomach, hydrochloric acid is secreted as food enters the stomach. It turns the pH of the stomach between 1 and 3. This pH is important for the activation of the enzyme pepsin, which helps in the digestion of protein in food.
Q. What is the pH for 1.5 m NaOH?
Calculating pH Next, apply the formula pH + pOH = 14. To isolate the pH, work out 14 – 1 = 13. The pH of your NaOH solution is 13.
Q. What is the pH of 1’m NaOH?
13
Q. What is the pH of a 2m solution of HCl?
3
Q. What is the pH of 4m NaOH?
Specifications
| Appearance | Liquid |
|---|---|
| Odor | Odorless |
| Solubility | Completely miscible |
| Vapor Pressure | 3mmHg (37°C) |
| pH | Alkaline |