Q. What are the protein making sites of the cell?
Ribosomes are the sites in a cell in which protein synthesis takes place. Cells have many ribosomes, and the exact number depends on how active a particular cell is in synthesizing proteins. For example, rapidly growing cells usually have a large number of ribosomes (Figure 5).
Q. How is a protein made?
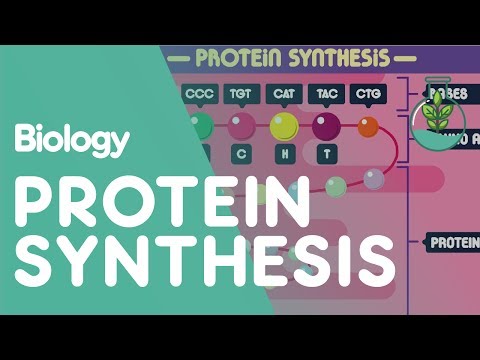
Protein from your diet is broken down into individual amino acids which are reassembled by your ribosomes into proteins that your cells need. The information to produce a protein is encoded in the cell’s DNA. When a protein is produced, a copy of the DNA is made (called mRNA) and this copy is transported to a ribosome.
Table of Contents
Q. What does DNA do in protein synthesis?
DNA is the primary genetic material contained within your cells and in nearly all organisms. It’s used to create proteins during protein synthesis, which is a multi-step process that takes the coded message of DNA and converts it into a usable protein molecule.
Q. What is the major role of protein in the body?
Protein has many roles in your body. It helps repair and build your body’s tissues, allows metabolic reactions to take place and coordinates bodily functions. In addition to providing your body with a structural framework, proteins also maintain proper pH and fluid balance.
Q. How does DNA turn into protein?
The type of RNA that contains the information for making a protein is called messenger RNA (mRNA) because it carries the information, or message, from the DNA out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm. A type of RNA called transfer RNA (tRNA) assembles the protein, one amino acid at a time.
Q. What is the role of proteins in our cells?
Proteins are large, complex molecules that play many critical roles in the body. They do most of the work in cells and are required for the structure, function, and regulation of the body’s tissues and organs. These proteins provide structure and support for cells. On a larger scale, they also allow the body to move.