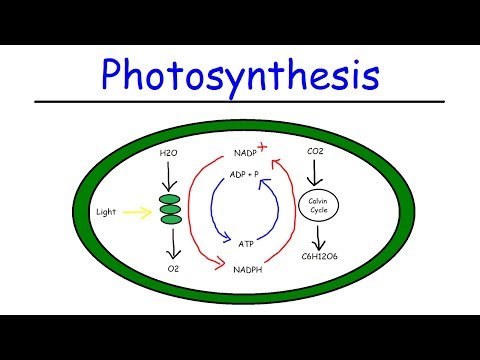
Q. What are the reactants and products of the Calvin cycle?
The Calvin Cycle You’ve learned that the first, light-dependent stage of photosynthesis uses two of the three reactants, water and light, and produces one of the products, oxygen gas (a waste product of this process).
Q. What are the end products of the Calvin cycle?
The Calvin cycle reactions use chemical energy from NADPH and ATP that were produced in the light reactions. The final product of the Calvin cycle is glucose.
Table of Contents
- Q. What are the reactants and products of the Calvin cycle?
- Q. What are the end products of the Calvin cycle?
- Q. What is the product of the Calvin cycle quizlet?
- Q. What are the major products of the Calvin cycle and why are they important?
- Q. What is the main goal of Calvin cycle?
- Q. How does Calvin cycle work?
- Q. What is the main output of the Calvin cycle?
- Q. How much ATP is produced in the Calvin cycle?
- Q. Is Calvin cycle light dependent?
- Q. Why does the Calvin cycle have 6 turns?
- Q. Where does the Calvin cycle RuBP come from?
- Q. Is RuBisCO and RuBP the same thing?
- Q. What are the inputs to the Calvin cycle where do they come from?
- Q. What is Calvin cycle Rubisco?
- Q. Is Rubisco a carb?
Q. What is the product of the Calvin cycle quizlet?
The product of the Calvin cycle is a triose-phosphate sugar that is either exported from the chloroplast or used to regenerate RUBP.
Q. What are the major products of the Calvin cycle and why are they important?
Converting Carbon Dioxide and Water Into Glucose In the most general sense, the primary function of the Calvin cycle is to make organic products that plants need using the products from the light reactions of photosynthesis (ATP and NADPH).
Q. What is the main goal of Calvin cycle?
The function of the Calvin cycle is to create three-carbon sugars, which can then be used to build other sugars such as glucose, starch, and cellulose that is used by plants as a structural building material.
Q. How does Calvin cycle work?
The Calvin cycle is a process that plants and algae use to turn carbon dioxide from the air into sugar, the food autotrophs need to grow. Energy to fuel chemical reactions in this sugar-generating process is provided by ATP and NADPH, chemical compounds which contain the energy plants have captured from sunlight.
Q. What is the main output of the Calvin cycle?
Outputs of the Calvin cycle are ADP, P, and NADP+, which go into the light reactions, and sugar, which is used by the plant. 2.
Q. How much ATP is produced in the Calvin cycle?
18 ATP
Q. Is Calvin cycle light dependent?
The Calvin cycle refers to the light-independent reactions in photosynthesis that take place in three key steps. Although the Calvin Cycle is not directly dependent on light, it is indirectly dependent on light since the necessary energy carriers ( ATP and NADPH) are products of light-dependent reactions.
Q. Why does the Calvin cycle have 6 turns?
Because the carbohydrate molecule has six carbon atoms, it takes six turns of the Calvin cycle to make one carbohydrate molecule (one for each carbon dioxide molecule fixed). The remaining G3P molecules regenerate RuBP, which enables the system to prepare for the carbon-fixation step.
Q. Where does the Calvin cycle RuBP come from?
In the Calvin-Benson cycle, RuBP is a product of the phosphorylation of ribulose-5-phosphate (produced by glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate) by ATP.
Q. Is RuBisCO and RuBP the same thing?
I. Introduction. Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (Rubisco; EC 4.1. 1.39) catalyzes the addition of gaseous carbon dioxide to ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (RuBP), generating two molecules of 3-phosphoglyceric acid (3-PGA), and is thus the key enzyme in CO2 assimilation.
Q. What are the inputs to the Calvin cycle where do they come from?
The inputs to the Calvin cycle are CO₂, ATP, and NADPH. The CO₂ comes from the atmosphere around the plant, and the ATP and NADPH come from the light-dependent reaction.
Q. What is Calvin cycle Rubisco?
The enzyme ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase, most commonly known by the shorter name RuBisCO or just rubisco is used in the Calvin cycle to catalyze the first major step of carbon fixation. They estimate that every person on Earth is supported by about 44 kg of rubisco! …
Q. Is Rubisco a carb?
The key event in carbohydrate storage is the capture of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. That task is carried out by ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase (usually abbreviated as rubisco).