Q. What are the three natural forces?
If you remember any of the physics you learned in school, it’s possible you may remember that there are four fundamental forces of nature. They are in no particular order gravity, electromagnetism, the weak nuclear force and the strong nuclear force.
Q. How many forces are there on Earth?
four forces
Table of Contents
- Q. What are the three natural forces?
- Q. How many forces are there on Earth?
- Q. What are the four natural forces?
- Q. What are the five forces of nature?
- Q. What is the strongest force in the universe?
- Q. What are 2 types of forces?
- Q. Which force is the strongest DC?
- Q. What is a balanced force?
- Q. Is gravity a balanced force?
- Q. What are 3 examples of unbalanced forces?
- Q. What happens when two equal forces collide?
- Q. Do forces always act in pairs?
- Q. How do things move if forces are equal and opposite?
- Q. How is energy lost in a collision?
- Q. What is collision Class 11?
- Q. What are the 2 types of collision?
- Q. What is collision formula?
- Q. What are the types of collision Class 11?
- Q. What is Torque class 11?
- Q. What is meant by one dimensional elastic collision?
- Q. What is head on collision in physics class 11?
- Q. What causes death in head on collision?
- Q. What is the force of a head on collision?
- Q. What is the value of E for head on collision?
- Q. When two bodies stick together after the collision is said to be?
- Q. When two balls of same temperature collide what is conserved?
- Q. Do objects stick together in an elastic collision?
- Q. What are the 7 forces?
- Q. What are 3 types of collisions?
- Q. Is kinetic energy conserved in an explosion?
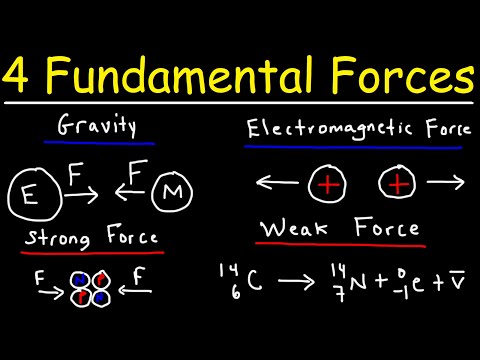
Q. What are the four natural forces?
Fundamental force, also called fundamental interaction, in physics, any of the four basic forces—gravitational, electromagnetic, strong, and weak—that govern how objects or particles interact and how certain particles decay. All the known forces of nature can be traced to these fundamental forces.
Q. What are the five forces of nature?
The forces controlling the world, and by extension, the visible universe, are gravity, electromagnetism, weak nuclear forces, and strong nuclear forces.
Q. What is the strongest force in the universe?
The strong nuclear force
Q. What are 2 types of forces?
There are 2 types of forces, contact forces and act at a distance force. Every day you are using forces. Force is basically push and pull. When you push and pull you are applying a force to an object.
Q. Which force is the strongest DC?
the Forever Force
Q. What is a balanced force?
When two forces acting on an object are equal in size but act in opposite directions, we say that they are balanced forces . a moving object continues to move at the same speed and in the same direction. …
Q. Is gravity a balanced force?
Forces acting on an object may be balanced or unbalanced. When the forces acting on an object have equal strength and act in opposite directions, they are balanced. Gravity is a force that pulls objects toward one another. For example, Earth pulls all objects toward it.
Q. What are 3 examples of unbalanced forces?
The gravitational force, air resistance, friction, and other forces acting on the ball have kept it at rest. But when an external force acts on the ball in the form of muscular force, the force system is unbalanced.
Q. What happens when two equal forces collide?
In a collision between two objects, both objects experience forces that are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. Such forces often cause one object to speed up (gain momentum) and the other object to slow down (lose momentum).
Q. Do forces always act in pairs?
Forces always occur in ‘Newton pairs’ and are made up from an action force and an equal reaction force in the opposite direction.
Q. How do things move if forces are equal and opposite?
According to Newton’s third law of motion, forces always act in equal but opposite pairs. Another way of saying this is for every action, there is an equal but opposite reaction. This means that when you push on a wall, the wall pushes back on you with a force equal in strength to the force you exerted.
Q. How is energy lost in a collision?
In a perfectly inelastic collision, i.e., a zero coefficient of restitution, the colliding particles stick together. In such a collision, kinetic energy is lost by bonding the two bodies together. This bonding energy usually results in a maximum kinetic energy loss of the system.
Q. What is collision Class 11?
Collision means two objects coming into contact with each other for a very short period. In other words, collision is a reciprocative interaction between two masses for a very short interval wherein the momentum and energy of the colliding masses changes.
Q. What are the 2 types of collision?
There are two types of collisions: Inelastic collisions: momentum is conserved, Elastic collisions: momentum is conserved and kinetic energy is conserved.
Q. What is collision formula?
An elastic collision is a collision where both the Kinetic Energy, KE, and momentum, p are conserved. In other words, it means that KE0 = KEf and po = pf. Moreover, as p = linear momentum = mv, then we will write m1v1i + m2v2i = m1v1f + m2v2f. …
Q. What are the types of collision Class 11?
Difference between Elastic and Inelastic Collision
| Elastic Collision | Inelastic Collision |
|---|---|
| The total kinetic energy is conserved. | The total kinetic energy of the bodies at the beginning and the end of the collision is different. |
| Momentum is conserved. | Momentum is conserved. |
Q. What is Torque class 11?
Torque is the measure of the force that can cause an object to rotate about an axis. Hence, torque can be defined as the rotational equivalent of linear force. The point where the object rotates is called the axis of rotation. In physics, torque is simply the tendency of a force to turn or twist.
Q. What is meant by one dimensional elastic collision?
We start with the elastic collision of two objects moving along the same line—a one-dimensional problem. An elastic collision is one that also conserves internal kinetic energy. Internal kinetic energy is the sum of the kinetic energies of the objects in the system.
Q. What is head on collision in physics class 11?
Head-on collision- A collision is said to be head-on collision when the colliding objects move along a straight line joining their centres.
Q. What causes death in head on collision?
Some of the most tragic head-on collisions are caused when a motorist gets confused and drives the wrong way on a one-way street, highway entrance or exit ramp, or highway. Intoxicated drivers whose vision and judgment are impaired cause many of these accidents late at night or in the early morning hours.
Q. What is the force of a head on collision?
In a head-on collision: Newton’s third law dictates that the forces on the trucks are equal but opposite in direction. Impulse is force multiplied by time, and time of contact is the same for both, so the impulse is the same in magnitude for the two trucks.
Q. What is the value of E for head on collision?
e is usually a positive, real number between 0 and 1: e = 0: This is a perfectly inelastic collision. This means kinetic energy along the common normal is 0. Kinetic energy is converted to heat or work done in deforming the objects.
Q. When two bodies stick together after the collision is said to be?
If two bodies stick together after collision and move as a single body, the collision is said to be inelastic.
Q. When two balls of same temperature collide what is conserved?
When two balls at the same temprature collide, some fraction of their KE appears in other forms of energy, like heat energy , second energy. Hence neither temparture, nor velocity or KE will remain conserved. The only quantity which will remain conserved.
Q. Do objects stick together in an elastic collision?
– An elastic collision is one in which no energy is lost. – A partially inelastic collision is one in which some energy is lost, but the objects do not stick together. – The greatest portion of energy is lost in the perfectly inelastic collision, when the objects stick.
Q. What are the 7 forces?
Types of Forces
| Contact Forces | Action-at-a-Distance Forces |
|---|---|
| Frictional Force | Gravitational Force |
| Tension Force | Electrical Force |
| Normal Force | Magnetic Force |
| Air Resistance Force |
Q. What are 3 types of collisions?
Collisions are of three types:
- perfectly elastic collision.
- inelastic collision.
- perfectly inelastic collision.
Q. Is kinetic energy conserved in an explosion?
So, like in inelastic collisions, total kinetic energy is not conserved in explosions. But total momentum is always conserved. Thus if the momenta of some of the parts of the exploding object are measured, we can use momentum conservation to solve the problem!