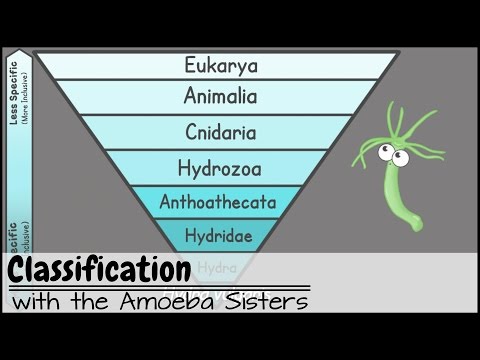
Taxonomic entities are classified in three ways. They are artificial classification, natural classification and phylogenetic classification.
Q. What are the two types of classification?
Classification by Attributes or Qualitative classification Classification according to attributes is of two kinds: simple classification and manifold classification.
Table of Contents
- Q. What are the two types of classification?
- Q. What is classification example?
- Q. What is classification mean?
- Q. What is basic classification?
- Q. What are the 8 levels of classification?
- Q. What are the aims of classification?
- Q. What is need and importance of classification?
- Q. What are advantages of classification?
- Q. What is the Six Kingdom classification?
- Q. What are the 7 kingdoms of classification?
- Q. Who is the father of classification?
- Q. What are the 5 kingdoms and 3 domains?
- Q. What are the 3 domains and 6 kingdoms of life?
- Q. What are the 3 domains and examples?
- Q. What are the 5 kingdoms and examples of each?
- Q. What is the basis of 5 kingdom classification?
- Q. What are the 5 kingdoms GCSE?
- Q. Are there 5 or 6 kingdoms?
- Q. What are the six kingdoms used for?
- Q. What are the 6 kingdoms and their characteristics?
- Q. Who gave the 6 kingdom classification?
- Q. How many kingdoms are there?
- Q. Who proposed 7 kingdom classification?
- Q. Who is the father of five kingdom classification?
Q. What is classification example?
In many cases, standards include a classification system such as a standard vocabulary and set of definitions that can be used to classify things….Standards.
| Overview: Classification | |
|---|---|
| Type | Generalization |
| Definition | The process of grouping things according to shared properties, structure and characteristics. |
Q. What is classification mean?
1 : the act or process of classifying. 2a : systematic arrangement in groups or categories according to established criteria specifically : taxonomy. b : class, category. Other Words from classification Synonyms Example Sentences Learn More about classification.
Q. What is basic classification?
Basis of Classification. Species is the basic unit of classification. Organisms that share many features in common and can breed with each other and produce fertile offspring are members of the same species. Related species are grouped into a genus (plural- genera).
Q. What are the 8 levels of classification?
The major levels of classification are: Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, Species.
Q. What are the aims of classification?
Ranks. The goal of classifying is to place an organism into an already existing group or to create a new group for it, based on its resemblances to and differences from known forms. To this end, a hierarchy of categories is recognized.
Q. What is need and importance of classification?
Three importance of classification are: It helps in the identification of living organisms as well as in understanding the diversity of living organisms. To understand and study the features, similarities and differences between different living organisms and how they are grouped under different categories.
Q. What are advantages of classification?
The advantages of classifying organisms are as follows: (i) Classification facilitates the identification of organisms. (ii) helps to establish the relationship among various groups of organisms. (iii) helps to study the phylogeny and evolutionary history of organisms.
Q. What is the Six Kingdom classification?
Plants, Animals, Protists, Fungi, Archaebacteria, Eubacteria. How are organism placed into their kingdoms? You are probably quite familiar with the members of this kingdom as it contains all the plants that you have come to know – flowering plants, mosses, and ferns.
Q. What are the 7 kingdoms of classification?
7 Major Levels of Classification There are seven major levels of classification: Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, and Species. The two main kingdoms we think about are plants and animals. Scientists also list four other kingdoms including bacteria, archaebacteria, fungi, and protozoa.
Q. Who is the father of classification?
Carolus Linnaeus
Q. What are the 5 kingdoms and 3 domains?
Ribosomal RNA is a molecular building block for ribosomes . Under this system, organisms are classified into three domains and six kingdoms . The domains are Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya. The kingdoms are Archaebacteria (ancient bacteria), Eubacteria (true bacteria), Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia.
Q. What are the 3 domains and 6 kingdoms of life?
Comparison of Classification Systems
| Archaea Domain | Bacteria Domain | Eukarya Domain |
|---|---|---|
| Archaebacteria Kingdom | Eubacteria Kingdom | Protista Kingdom |
| Fungi Kingdom | ||
| Plantae Kingdom | ||
| Animalia Kingdom |
Q. What are the 3 domains and examples?
According to this system, the tree of life consists of three domains: Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya. The first two are all prokaryotic microorganisms, or mostly single-celled organisms whose cells have no nucleus. All life that has a cell nucleus and eukaryotic membrane-bound organelles is included in Eukarya.
Q. What are the 5 kingdoms and examples of each?
The Five Kingdoms of Life
- Kingdom Monera (Prokaryotic bacteria and blue green algae).
- Kingdom Protista (Unicellular Eukaryotic organisms- protozoans, fungi and algae).
- Kingdom Fungi (Multinucleate higher fungi).
- Kingdom Plantae (Multicellular green plants and advanced algae).
- Kingdom Animalia (Multicellular animals).
Q. What is the basis of 5 kingdom classification?
On what basis are the living organisms divided in the five-kingdom classification? The living organisms are divided into five different kingdoms – Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Animalia, and Monera on the basis of their characteristics such as cell structure, mode of nutrition, mode of reproduction and body organization.
Q. What are the 5 kingdoms GCSE?
The five kingdoms are:
- animals (all multicellular animals)
- plants (all green plants)
- fungi (moulds, mushrooms, yeast)
- protists (Amoeba, Chlorella and Plasmodium)
- prokaryotes (bacteria, blue-green algae)
Q. Are there 5 or 6 kingdoms?
Whittaker’s classification scheme recognizes five kingdoms: Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. 6 Kingdoms? Based on RNA studies Carl Woese divided the prokaryotes (Kingdom Monera) into two kingdoms, called Eubacteria and Archaebacteria. The Eubacteria and Archaebacteria made up the other two urkingdoms.
Q. What are the six kingdoms used for?
The Six Kingdoms of Life Organisms are placed into these categories based on similarities or common characteristics. Some of the characteristics that are used to determine placement are cell type, nutrient acquisition, and reproduction. The two main cell types are prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Q. What are the 6 kingdoms and their characteristics?
The six kingdoms are:Animal, Plant, Protist, Fungi, Bacteria, Archaea . Bacteria is both a domain and a kingdom. Archaea is also both a domain and a kingdom. Within the Eukarya domain, there are four more kingdoms: Animal, Plant, Fungi, and Protist.
Q. Who gave the 6 kingdom classification?
Carl Woese
Q. How many kingdoms are there?
Five kingdoms
| Empire Prokaryota | Kingdom Monera |
|---|---|
| Empire Eukaryota | Kingdom Protista or Protoctista Kingdom Plantae Kingdom Fungi Kingdom Animalia |
Q. Who proposed 7 kingdom classification?
Thomas Cavalier-Smith
Q. Who is the father of five kingdom classification?
Whittaker