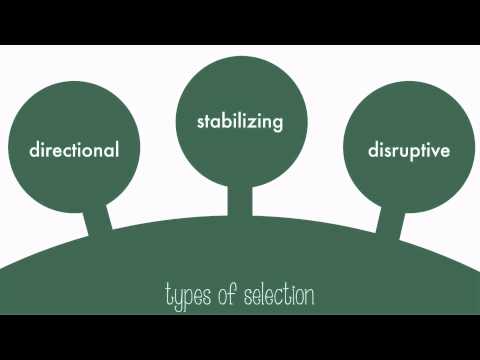
Q. What are the three types of natural selection on polygenic traits?
Natural selection on polygenic traits can affect the distributions of phenotypes in three ways: directional selection, stabilizing selection, or disruptive selection.
Q. What are 3 ways nature can select for individuals?
There are three conditions for natural selection: 1. Variation: Individuals within a population have different characteristics/traits (or phenotypes). 2. Inheritance: Offspring inherit traits from their parents.
Table of Contents
- Q. What are the three types of natural selection on polygenic traits?
- Q. What are 3 ways nature can select for individuals?
- Q. What are three types of selection pressures?
- Q. What are some examples of selection pressures?
- Q. What are the four main types of selection pressures?
- Q. What are some examples of disruptive selection?
- Q. What are the two main drivers of evolution?
- Q. How do mutations affect natural selection?
- Q. What are the 5 steps of natural selection?
- Q. What are the four requirements of natural selection?
- Q. Which is a requirement for natural selection to occur quizlet?
- Q. What is the first step in natural selection?
- Q. What are the 4 processes of natural selection?
Q. What are three types of selection pressures?
Types of selection pressures include:
- Resource availability – Presence of sufficient food, habitat (shelter / territory) and mates.
- Environmental conditions – Temperature, weather conditions or geographical access.
- Biological factors – Predators and pathogens (diseases)
Q. What are some examples of selection pressures?
Examples of selective pressures include competition, predation, land clearance, pollutants, diseases and illnesses, climate change and parasitism. A famous example of selective pressure is the long neck and legs of giraffes.
Q. What are the four main types of selection pressures?
Stabilizing selection, directional selection, diversifying selection, frequency -dependent selection, and sexual selection all contribute to the way natural selection can affect variation within a population.
Q. What are some examples of disruptive selection?
Disruptive Selection Examples: Color
- Peppered moths: One of the most studied examples of disruptive selection is the case of London’s peppered moths.
- Oysters: Light- and dark-colored oysters could also have a camouflage advantage as opposed to their medium-colored relatives.
Q. What are the two main drivers of evolution?
The developing research area on how the vast biodiversity on Earth evolves accepts natural selection and three other established forces of evolution as its basis. These include: mutation, random genetic drift and gene flow.
Q. How do mutations affect natural selection?
As mutations occur, natural selection decides which mutations will live on and which ones will die out. If the mutation is beneficial, the mutated organism survives to reproduce, and the mutation gets passed on to its offspring.
Q. What are the 5 steps of natural selection?
Natural selection is a simple mechanism that causes populations of living things to change over time. In fact, it is so simple that it can be broken down into five basic steps, abbreviated here as VISTA: Variation, Inheritance, Selection, Time and Adaptation.
Q. What are the four requirements of natural selection?
Only the successful competitors will reproduce, mortality is very high. Four (4) conditions for natural selection. Four conditions are needed for natural selection to occur: reproduction, heredity, variation in fitness or organisms, variation in individual characters among members of the population.
Q. Which is a requirement for natural selection to occur quizlet?
In order for natural selection to occur, three conditions must be met: There must be variation for the particular trait within a population. The variation must be inheritable (that is, it must be capable of being passed on from the parents to their offspring).
Q. What is the first step in natural selection?
The first step, the production of variation, is under the control of chance; the second step, selection proper, is an anti-chance process, but subject to many constraints.
Q. What are the 4 processes of natural selection?
Darwin’s process of natural selection has four components.
- Variation. Organisms (within populations) exhibit individual variation in appearance and behavior.
- Inheritance. Some traits are consistently passed on from parent to offspring.
- High rate of population growth.
- Differential survival and reproduction.