There are two main types of metamorphic rocks: those that are foliated because they have formed in an environment with either directed pressure or shear stress, and those that are not foliated because they have formed in an environment without directed pressure or relatively near the surface with very little pressure …
Q. What are 5 examples of igneous?
These rocks include: andesite, basalt, dacite, obsidian, pumice, rhyolite, scoria, and tuff. Pictures and brief descriptions of some common igneous rock types are shown on this page.
Table of Contents
- Q. What are 5 examples of igneous?
- Q. What is another name for an igneous rock?
- Q. What are the three main groups of igneous rocks?
- Q. What are three types of metamorphic rock?
- Q. Where can you find shale rock?
- Q. What type of rock is siltstone?
- Q. Is siltstone well sorted?
- Q. Is Sandstone poorly sorted?
- Q. Is Gravel well sorted or poorly sorted?
- Q. Is siltstone well rounded?
Q. What is another name for an igneous rock?
Igneous rocks are also known as magmatic rocks. Igneous rocks are divided into two types: plutonic and volcanic rock. Plutonic rock is another name…
Q. What are the three main groups of igneous rocks?
Igneous rocks may be simply classified according to their chemical/mineral composition as felsic, intermediate, mafic, and ultramafic, and by texture or grain size: intrusive rocks are course grained (all crystals are visible to the naked eye) while extrusive rocks may be fine-grained (microscopic crystals) or glass ( …
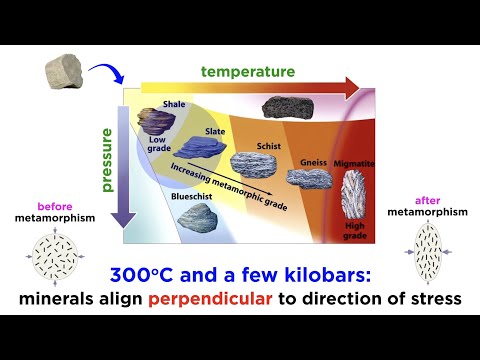
Q. What are three types of metamorphic rock?
Common metamorphic rocks include phyllite, schist, gneiss, quartzite and marble. Foliated Metamorphic Rocks: Some kinds of metamorphic rocks — granite gneiss and biotite schist are two examples — are strongly banded or foliated.
Q. Where can you find shale rock?
Shales are often found with layers of sandstone or limestone. They typically form in environments where muds, silts, and other sediments were deposited by gentle transporting currents and became compacted, as, for example, the deep-ocean floor, basins of shallow seas, river floodplains, and playas.
Q. What type of rock is siltstone?
Siltstone, hardened sedimentary rock that is composed primarily of angular silt-sized particles (0.0039 to 0.063 mm [0.00015 to 0.0025 inch] in diameter) and is not laminated or easily split into thin layers.
Q. Is siltstone well sorted?
*Characteristics – fine-grained siltstone and shale, which are well stratified (layered) commonly, form in the central portion, whereas some well-sorted sandstone is also formed along the margins.
Q. Is Sandstone poorly sorted?
Poorly-sorted sediments have grains of varying sizes, and are evidence of sediments that have been deposited fairly close to the source area, i.e., have not undergone much transport. Other examples of angular, poorly-sorted rocks are breccia and arkose sandstone.
Q. Is Gravel well sorted or poorly sorted?
If the grains, however, are poorly sorted, the spaces between larger grains may be filled with smaller grains instead of water. Sand and gravel aquifers having well-sorted grains, therefore, hold and transmit larger quantities of water than such aquifers with poorly sorted grains.
Q. Is siltstone well rounded?
Grains are usually angular through well rounded. Minerals include all the immature minerals like quartz, micas, clays, and rock fragments. Rock types include Siltstone, Shale, and Quartz Arenite.