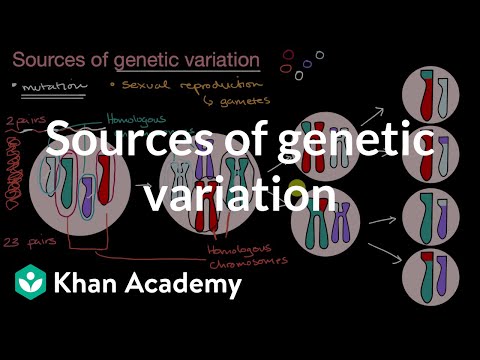
Natural selection acts upon two major sources of genetic variation: mutations and recombination of genes through sexual reproduction.
Q. What is the school of behaviorism?
The “School of Behaviorism” had developed as a reaction against “Structuralism” and “Functionalism” in the United States of America (USA). It is a systematic approach to understand behavior of both human being and animal. The law of effect is an exercise to strengthen behavior using reinforcement.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the school of behaviorism?
- Q. What is radical behaviorism in psychology?
- Q. What is Selectionism ABA?
- Q. What are the principles of behavior ABA?
- Q. What is used in phylogenetic studies to classify life?
- Q. What is the basis of phylogenetic classification?
- Q. What is cladistic classification?
- Q. What is a phylogenetic diagram?
- Q. What is a phylogenetic group?
Q. What is radical behaviorism in psychology?
Radical Behaviorism is the philosophy behind the science of behavior. Radical behaviorism argues that behavior, rather than mental states, should be the focus of study in psychology.
Q. What is Selectionism ABA?
Ontogenic: This refers to an how the environment changes an individual over his or her lifetime. Cultural: Passing behavior from one person to another by imitation and modeling.
Q. What are the principles of behavior ABA?
The principles of ABA applied behavior analysis target the four functions of behavior, which include: escape or avoidance, attention seeking, access to tangibles or reinforcements, and instant gratification (or “because it feels good”).
Q. What is used in phylogenetic studies to classify life?
Phylogenetics can use both molecular and morphological data in order to classify organisms. Molecular methods are based on studies of gene sequences. The relationships between species can be represented by a phylogenetic tree. This is a graphical representation that has nodes and branches.
Q. What is the basis of phylogenetic classification?
It is based on evolutionary ancestry and generates trees called cladograms. Cladistics also identifies clades, which are groups of organisms that include an ancestor species and its descendants. Classifying organisms on the basis of descent from a common ancestor is called phylogenetic classification.
Q. What is cladistic classification?
Cladistics refers to a biological classification system that involves the categorization of organisms based on shared traits. Organisms are typically grouped by how closely related they are and thus, cladistics can be used to trace ancestry back to shared common ancestors and the evolution of various characteristics.
Q. What is a phylogenetic diagram?
A phylogenetic tree, also known as a phylogeny, is a diagram that depicts the lines of evolutionary descent of different species, organisms, or genes from a common ancestor.
Q. What is a phylogenetic group?
A phylogenetic classification system attempts to arrange species into groups based on their evolutionary origins and relationships. It uses a hierarchy in which smaller groups are placed within larger groups, with no overlap between groups. Each group is called a taxon (plural taxa).