Q. What are the two resulting cells in mitosis?
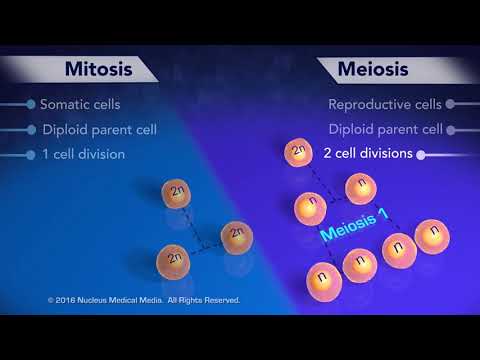
Mitosis results in two identical daughter cells, whereas meiosis results in four sex cells.
Q. What happens when a cell divides by mitosis?
Mitosis is a process of nuclear division in eukaryotic cells that occurs when a parent cell divides to produce two identical daughter cells. During cell division, mitosis refers specifically to the separation of the duplicated genetic material carried in the nucleus.
Table of Contents
- Q. What are the two resulting cells in mitosis?
- Q. What happens when a cell divides by mitosis?
- Q. How does mitosis cause two daughter cells?
- Q. What happens to chromosomes during mitosis?
- Q. How many chromosomes are there before mitosis?
- Q. How many chromosomes are at the end of meiosis?
- Q. What type of cells does mitosis produce?
- Q. What type of cells do not undergo mitosis?
- Q. What type of cells are made during meiosis?
- Q. Where does mitosis occur in the human body?
- Q. Does mitosis occur in our body?
- Q. Does mitosis happen in humans?
- Q. What is the main goal of mitosis?
- Q. What is needed for mitosis?
- Q. What would happen if mitosis stopped?
- Q. Does mitosis ever stop?
- Q. Does mitosis slow down with age?
- Q. Why does mitosis slow with age?
- Q. Where does mitosis happen the fastest?
- Q. How fast can a cell divide?
- Q. Why do some cells divide slowly?
- Q. Can cells divide too much?
- Q. How many times a cell can divide?
- Q. What will happen if cell division is not controlled?
- Q. How do you calculate cell division in percentages?
Q. How does mitosis cause two daughter cells?
Mitosis leads to two daughter cells when the DNA is duplicated and the cell splits. THe cells goes through interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. When the chromosomes line up in the center they have reached metaphase. The chromosomes then split apart during telophase.
Q. What happens to chromosomes during mitosis?
Mitosis is the process of nuclear division, which occurs just prior to cell division, or cytokinesis. During this multistep process, cell chromosomes condense and the spindle assembles. Each set of chromosomes is then surrounded by a nuclear membrane, and the parent cell splits into two complete daughter cells.
Q. How many chromosomes are there before mitosis?
46 chromosomes
Q. How many chromosomes are at the end of meiosis?
23
Q. What type of cells does mitosis produce?
Mitosis is used to produce daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cells. The cell copies – or ‘replicates’ – its chromosomes, and then splits the copied chromosomes equally to make sure that each daughter cell has a full set.
Q. What type of cells do not undergo mitosis?
What types of cells do not undergo mitosis? Sperm cells and egg cells don’t go through mitosis. Describe how mitosis is important for your body. Mitosis is just one small part of the cell cycle!
Q. What type of cells are made during meiosis?
Meiosis is a type of cell division that reduces the number of chromosomes in the parent cell by half and produces four gamete cells. This process is required to produce egg and sperm cells for sexual reproduction.
Q. Where does mitosis occur in the human body?
The cells of the skin and bone marrow are sites of active mitosis replacing skin cells and red blood cells that only have a limited life. Repair. When an area of tissue is damaged internally or externally, mitosis is used to repair the damage.
Q. Does mitosis occur in our body?
Mitosis occurs all over the body. It is not specific to one area. Any cell that divides and creates a new cell is said to undergo mitosis and cells…
Q. Does mitosis happen in humans?
There are two ways cell division can happen in humans and most other animals, called mitosis and meiosis. When a cell divides by way of mitosis, it produces two clones of itself, each with the same number of chromosomes. When a cell divides by way of meiosis, it produces four cells, called gametes.
Q. What is the main goal of mitosis?
Mitosis is a process where a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells (cell division). During mitosis one cell? divides once to form two identical cells. The major purpose of mitosis is for growth and to replace worn out cells.
Q. What is needed for mitosis?
Before mitosis begins, the chromosomes in the nucleus of the cell undergo replication. This is because mitosis produces two daughter cells identical to the parent cell; so the number of chromosomes in the parent and daughter cells must be the same. Thus, chromosome numbers must double before mitosis occurs.
Q. What would happen if mitosis stopped?
If there is no mitosis, there would be no cell growth and cell reproduction. Most importantly, genetic information cannot be passed on. All cell functions would be hugely affected.
Q. Does mitosis ever stop?
Mitosis ends with telophase, or the stage at which the chromosomes reach the poles. Telophase is followed by cytokinesis, or the division of the cytoplasm into two daughter cells. The daughter cells that result from this process have identical genetic compositions.
Q. Does mitosis slow down with age?
In a novel study comparing healthy cells from people in their 20s with cells from people in their 80s, researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center say they have documented that cell division rates appear to consistently and markedly slow down in humans at older ages.
Q. Why does mitosis slow with age?
However, when researchers reanalyzed old data in dozens of published papers, they found that mutations accumulate more slowly in old age. That analysis led researchers to suspect that cell division rates slow down markedly in old age, giving cells fewer chances to accumulate DNA mistakes.
Q. Where does mitosis happen the fastest?
epidermis
Q. How fast can a cell divide?
In ideal growth conditions, the bacterial cell cycle is repeated every 30 minutes. Only a few types of eukaryotic cells can grow and divide as quickly as bacteria. Most growing plant and animal cells take 10 – 20 hours to double in number, and some duplicate at a much slower rate.
Q. Why do some cells divide slowly?
Every time a cell divides, the DNA has to be copied and divided so that the new cells each get a full set of DNA. When the DNA divides, a part of it at the end called the telomere gets shorter. When a cell’s telomere gets too short, it will no longer divide. This puts a limit on cell division.
Q. Can cells divide too much?
Errors in cell division can lead to the birth of new cells with abnormal sets of chromosomes, a phenomenon called aneuploidy. Normal cells have 46 chromosomes, but most cancer cells are aneuploid, containing one or several chromosomes too few or too many.
Q. How many times a cell can divide?
The Hayflick Limit is a concept that helps to explain the mechanisms behind cellular aging. The concept states that a normal human cell can only replicate and divide forty to sixty times before it cannot divide anymore, and will break down by programmed cell death or apoptosis.
Q. What will happen if cell division is not controlled?
After the cytoplasm divides, cell division is complete. If the cell cycle is not carefully controlled, it can cause a disease called cancer, which causes cell division to happen too fast. A tumor can result from this kind of growth.
Q. How do you calculate cell division in percentages?
(total # cells dividing/total # cells from both samples) X 100 = average % cellsdividingFor example, if sample 1 has 2 cells in prophase, 2 cells in metaphase, 1 cell inanaphase, and 5 cells in telophase out of 20 total), and sample 2 has 3 cells inprophase, 1 cells in metaphase, 0 cells in anaphase, and 2 cells in …