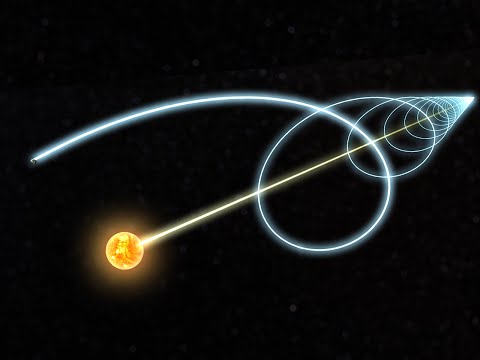
Q. What are the two ways Earth moves in space?
The earth moves two ways. It spins and it moves around the sun. The spinning of the earth is called rotation.
Q. What is the movement of Earth on its axis called?
revolution
Table of Contents
- Q. What are the two ways Earth moves in space?
- Q. What is the movement of Earth on its axis called?
- Q. How does the earth spin on its axis?
- Q. How is Earth moving through space?
- Q. What is the universe orbiting?
- Q. Why is everything in the universe spinning?
- Q. Does the whole universe rotate?
- Q. Why are there no directions in space?
- Q. What direction is the universe spinning?
- Q. Does the universe have an edge?
- Q. What does edge of universe look like?
- Q. What happens if you reach the edge of the universe?
- Q. Why can’t we see the edge of the universe?
- Q. What is beyond the end of the universe?
- Q. How Earth moves through space and how it affects life on Earth?
- Q. What are the 3 ways the earth moves?
- Q. When the earth moves through outer space How do these movements create the Four Seasons?
- Q. Is Earth closer to sun in summer?
- Q. What part of Earth is closest to the sun?
- Q. Why is Earth’s temperature just right for life?
- Q. What keeps Earth’s temperature at the proper level for life?
- Q. Why does the earth not freeze at night?
- Q. Do any solar systems have two suns?
- Q. Is there more than one sun in space?
- Q. How many suns can fit in the Milky Way galaxy?
- Q. How many Earths are in the DC multiverse?
Q. How does the earth spin on its axis?
Earth’s Rotation Imagine a line passing through the center of Earth that goes through both the North Pole and the South Pole. This imaginary line is called an axis. Earth spins around its axis, just as a top spins around its spindle. This spinning movement is called Earth’s rotation.
Q. How is Earth moving through space?
For one, the Earth rotates on its axis, hurtling us through space at nearly 1700 km/hr for someone on the equator. The Earth spinning on its axis gives us a speed of just 0.5 km/s, or less than 0.001% the speed of light. But there are other motions that matter more.
Q. What is the universe orbiting?
Bottom line: The planets in our solar system orbit (revolve) around the sun, and the sun orbits (revolves) around the center of the Milky Way galaxy. We take about 225-250 million years to revolve once around the galaxy’s center. This length of time is called a cosmic year.
Q. Why is everything in the universe spinning?
Regardless of whether it spins clockwise or counterclockwise, everything in the universe moves and spins: From small asteroids to entire galaxies. Gravity, momentum, inertia ensure that bodies big and small act upon each other, causing everything to move and spin.
Q. Does the whole universe rotate?
Almost everything in the universe spins. Planets rotate on their axis, stars spin around black holes, and galaxies spin in great spiral structures. Structures rotate because of a property known as angular momentum. Angular momentum is a measure of mass and rotation, and it is a conserved physical property.
Q. Why are there no directions in space?
There is an up and down in space. “Down” is simply the direction gravity is pulling you, and “up” is just the opposite direction. Since there is gravity everywhere in space, there is also an up and down everywhere in space.
Q. What direction is the universe spinning?
They found that galaxies have a preferred direction of rotation – there was an excess of left-handed, or counter-clockwise, rotating spiral galaxies in the part of the sky toward the north pole of the Milky Way. The effect extended beyond 600 million light-years away.
Q. Does the universe have an edge?
The Universe has many edges: the edge of transparency, the edge of stars and galaxies, the edge of neutral atoms, and the edge of our cosmic horizon from the Big Bang itself. We can look as far away as our telescopes can take us, but there will always be a fundamental limit.
Q. What does edge of universe look like?
It is just spacetime, expanding. “All the measurements indicate that all of the universe we can see, including the edge of the observable universe, looks approximately like our local universe does today: with stars, galaxies, and clusters of galaxies and lots of empty space.”
Q. What happens if you reach the edge of the universe?
You would see the same as you would in ordinary space. The universe expands at the speed of light, so light would not be able to bounce off the “edge of the universe” in order for it to be reflected back into your eyes.
Q. Why can’t we see the edge of the universe?
There is no evidence that the universe has an edge. The part of the universe we can observe from Earth is filled more or less uniformly with galaxies extending in every direction as far as we can see – more than 10 billion light-years, or about 6 billion trillion miles.
Q. What is beyond the end of the universe?
But “infinity” means that, beyond the observable universe, you won’t just find more planets and stars and other forms of material…you will eventually find every possible thing.
Q. How Earth moves through space and how it affects life on Earth?
The Earth’s movement through space affects life on Earth. We experience day and night because of this movement on the Earth’s axis known as rotation. It takes the Earth 24 hours to rotate one time in which we experience day and night. The Earth moves along a path around the Sun.
Q. What are the 3 ways the earth moves?
4 The Earth’s Three Motions. The Earth turns (rotation around the polar axis), goes along on its orbit (revolution around the Sun), swings smoothly as un unbalanced spinning top (equinoctial precession).
Q. When the earth moves through outer space How do these movements create the Four Seasons?
The Earth’s Orbit Moreover, as the Earth spins on its axis, it orbits the sun, taking 365 days to complete a whole orbit. Because of the tilt of the Earth’s axis, different areas receive different amounts of sunlight during the Earth’s orbit, creating the four seasons.
Q. Is Earth closer to sun in summer?
Many people believe that the temperature changes because the Earth is closer to the sun in summer and farther from the sun in winter. In fact, the Earth is farthest from the sun in July and is closest to the sun in January! During the summer, the sun’s rays hit the Earth at a steep angle.
Q. What part of Earth is closest to the sun?
The Earth is closest to the Sun, or at the perihelion, about two weeks after the December solstice, when it is winter in the Northern Hemisphere. Conversely, the Earth is farthest away from the Sun, at the aphelion point, two weeks after the June solstice, when the Northern Hemisphere is enjoying warm summer months.
Q. Why is Earth’s temperature just right for life?
Earth’s atmosphere contains more oxygen than carbon dioxide. D.) Earth’s atmosphere contains carbon dioxide, which all life forms breathe in. Earth is the smallest of the outer planets, making its temperature just right for life forms.
Q. What keeps Earth’s temperature at the proper level for life?
The greenhouse effect has kept the Earth’s average temperature a good deal higher for billions of years, making it possible for life as we know it to evolve.
Q. Why does the earth not freeze at night?
Since things like lakes, rivers, the atmosphere and the ground are much larger than a pot of water, it takes them a long time to cool down – longer than one night without sun. But they do lose some heat at night, and cool down a little bit, and so they have to make it up with the next day’s sunlight.
Q. Do any solar systems have two suns?
A circumbinary planet is a planet that orbits two stars instead of one. Planets in stable orbits around one of the two stars in a binary are known. New studies showed that there is a strong hint that the planet and stars originate from a single disk.
Q. Is there more than one sun in space?
Suns with friends But solar systems can have more than one sun. In fact, that’s often the case. More than half of all stars are in multiple star systems. That means the solar system has two or more suns in it.
Q. How many suns can fit in the Milky Way galaxy?
It’s mind-boggling. The Milky Way has a mass of 1.5 trillion suns.
Q. How many Earths are in the DC multiverse?
“Dan DiDio explained that there are 52 earths, and then alternate dimensions within each universe, as well as alternate timelines and microverses within each.” Many of these worlds resembled Pre-Crisis and Elseworlds universes such as Kingdom Come, Red Son and The Dark Knight Returns.