What are two characteristics of protraction? An anterior movement of the bone. Movement along the transverse plane….
Q. What is abduction and adduction movement?
Abduction is a movement away from the midline – just as abducting someone is to take them away. For example, abduction of the shoulder raises the arms out to the sides of the body. Adduction is a movement towards the midline. Adduction of the hip squeezes the legs together.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is abduction and adduction movement?
- Q. What is abduction muscle movement?
- Q. What are the two types of movements of muscles within the body?
- Q. Which types of movements of joints are described in anatomical terms explain?
- Q. What characteristics do all joints have in common?
- Q. What are the 7 types of joints?
- Q. What are the two main types of joints?
- Q. What are the two basic types of joints?
- Q. What are the two types of immovable joints?
- Q. What are the different types of movement in joints?
- Q. What are examples of movable joints?
- Q. What are the 6 types of freely movable joints?
- Q. What is mean by movable joint?
- Q. What are the 4 types of joints and examples?
- Q. What type of synovial joint is the wrist?
- Q. What type of joint is the head and neck?
- Q. How many types of joints are there and explain major movements?
- Q. What are the 5 types of synovial joints?
- Q. Which joint do not allow any moment?
- Q. What are the 6 major joints?
- Q. What is a Diarthrosis joint?
- Q. What are the 8 major joints of the body?
- Q. What type of synovial joint is the shoulder?
- Q. Which joint is the most complex Diarthrosis in the body?
- Q. What type of movement does the shoulder joint allow?
- Q. What are the 3 shoulder joints?
Q. What is abduction muscle movement?
Abduction is any motion of the limbs or other body parts that pulls away from the midline of the body. Abduction of the wrist, moving the hand away from the body at the wrist when that arm is at the person’s side, is called radial deviation. Any muscle that creates this type of motion is termed an abductor.
Q. What are the two types of movements of muscles within the body?
Flexion and extension are usually movements forward and backward from the body, such as nodding the head.
- Flexion: decreasing the angle between two bones (bending).
- Extension: increasing the angle between two bones (straightening a bend).
- Abduction: moving away from the body’s midline.
Q. Which types of movements of joints are described in anatomical terms explain?
When a joint can move forward and backward, such as the neck and trunk, flexion is movement in the anterior direction. Flexion of the shoulder or hip is movement of the arm or leg forward. Extension is the opposite of flexion, describing a straightening movement that increases the angle between body parts.
- Extension of the arm at the elbow.
- Depressing the jaw at the temporomandibular joint.
- Elevating the jaw at the temporomandibular joint.
Q. What characteristics do all joints have in common?
What characteristics do all joints have in common. All consist of bony regions held together by fibrous or cartilaginous connective tissue’s or by a joint capsule.
Q. What are the 7 types of joints?
Types of freely movable joints
- Ball and socket joint. Permitting movement in all directions, the ball and socket joint features the rounded head of one bone sitting in the cup of another bone.
- Hinge joint.
- Condyloid joint.
- Pivot joint.
- Gliding joint.
- Saddle joint.
Q. What are the two main types of joints?
A joint is a point where two or more bones meet. There are three main types of joints; Fibrous (immovable), Cartilaginous (partially moveable) and the Synovial (freely moveable) joint.
Q. What are the two basic types of joints?
There are two basic structural types of joint: diarthrosis, in which fluid is present, and synarthrosis, in which there is no fluid. All the diarthroses (commonly called synovial joints) are permanent. Some of the synarthroses are transient; others are permanent.
Q. What are the two types of immovable joints?
Description. An immovable joint can be either one of two types of joints, fibrous or cartilaginous.
Q. What are the different types of movement in joints?
Types of joint movement
| Joint | Type | Movement |
|---|---|---|
| Elbow | Hinge | Flexion, extension |
| Knee | Hinge | Flexion, extension |
| Hip | Ball and socket | Flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, rotation, circumduction |
| Shoulder | Ball and socket | Flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, rotation, circumduction |
Q. What are examples of movable joints?
Movable joints are also the most common type of joint in your body. Your fingers, toes, hips, elbows, and knees all provide examples of movable joints. The surfaces of bones at movable joints are covered with a smooth layer of cartilage.
Q. What are the 6 types of freely movable joints?
The six types of freely movable joint include ball and socket, saddle, hinge, condyloid, pivot and gliding.
Q. What is mean by movable joint?
Definition. noun. The most common and movable type of joint which is characterized by the presence of a layer of fibrocartilage or hyaline cartilage that lines the opposing bony surfaces, as well as a lubricating synovial fluid within the synovial cavity.
Q. What are the 4 types of joints and examples?
What are the different types of joints?
- Ball-and-socket joints. Ball-and-socket joints, such as the shoulder and hip joints, allow backward, forward, sideways, and rotating movements.
- Hinge joints.
- Pivot joints.
- Ellipsoidal joints.
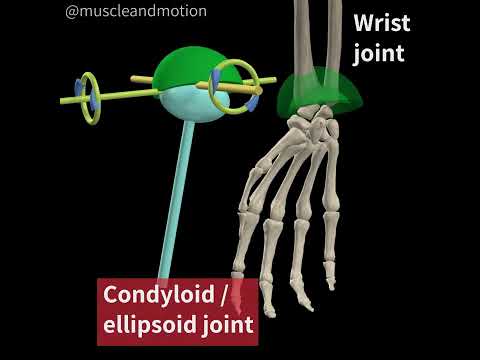
Q. What type of synovial joint is the wrist?
condyloid synovial joint
Q. What type of joint is the head and neck?
The atlas and the occipital bone form the atlanto-occipital joint, which allows neck flexion. When you nod your head as if to say “yes,” that is neck flexion. The atlas and axis form the atlanto-axial joint, which allows head rotation. If you shake your head as if to say “no,” that is head rotation.
Q. How many types of joints are there and explain major movements?
Types of Movable Joints. Movable joints can be classified further according to the type of movement they allow. There are six classes of movable joints: pivot, hinge, saddle, plane, condyloid, and ball-and-socket joints.
Q. What are the 5 types of synovial joints?
Planar, hinge, pivot, condyloid, saddle, and ball-and-socket are all types of synovial joints.
Q. Which joint do not allow any moment?
Fibrous or immovable joints are the joints in which no movement occurs between the bones concerned.
Q. What are the 6 major joints?
The six types of synovial joints are pivot, hinge, condyloid, saddle, plane, and ball-and socket-joints (Figure 9.4. 3). Figure 9.4. 3 – Types of Synovial Joints: The six types of synovial joints allow the body to move in a variety of ways.
Q. What is a Diarthrosis joint?
Diarthrosis. A freely mobile joint is classified as a diarthrosis. These types of joints include all synovial joints of the body, which provide the majority of body movements. Most diarthrotic joints are found in the appendicular skeleton and thus give the limbs a wide range of motion.
Q. What are the 8 major joints of the body?
Anatomy Explorer
- Ball & Socket Joint.
- Elbow Joint.
- Gliding Joint.
- Hand.
- Hinge Joint.
- Hip Joint.
- Saddle Joint.
- Spine.
Q. What type of synovial joint is the shoulder?
ball-and-socket joint
Q. Which joint is the most complex Diarthrosis in the body?
knee
Q. What type of movement does the shoulder joint allow?
The human shoulder is the most mobile joint in the body. This mobility provides the upper extremity with tremendous range of motion such as adduction, abduction, flexion, extension, internal rotation, external rotation, and 360° circumduction in the sagittal plane.
Q. What are the 3 shoulder joints?
The shoulder is made up of three bones: the scapula (shoulder blade), clavicle (collarbone) and humerus (upper arm bone). Two joints in the shoulder allow it to move: the acromioclavicular joint, where the highest point of the scapula (acromion) meets the clavicle, and the glenohumeral joint.