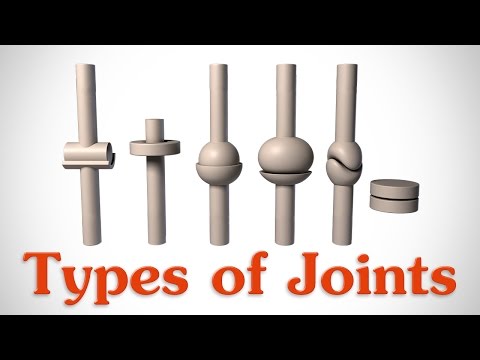
What are the different types of joints?
Q. How is movement used in design?
Movement is the path the viewer’s eye takes through the work of art, often to focal areas. Such movement can be directed along lines, edges, shape, and color within the work of art. The repetition of elements of design creates unity within the work of art.
Table of Contents
- Q. How is movement used in design?
- Q. What are joint types?
- Q. What are the 3 classifications of joints?
- Q. Which type of joint is the most movable?
- Q. What is the strongest joint in the body?
- Q. What characteristics do all joints have in common?
- Q. What are the 6 major features of synovial joints?
- Q. What are the four distinguishing features of synovial joints?
- Q. What type of joint is between the jaw and skull?
- Q. What are the 5 types of synovial joints?
- Q. What are the 5 main joints in the body?
- Q. What is Diarthroses?
- Q. What are the six types of Diarthroses?
- Q. What are two types of Amphiarthrosis joints?
- Q. What is an example of Amphiarthrosis?
Q. What are joint types?
There are three types of joints in the structural classification: fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial joints.
- Fibrous joints are joints in which bones are joined by dense connective tissue that is rich in collagen fibers.
- Cartilaginous joints are joints in which bones are joined by cartilage.
- Ball-and-socket joints. Ball-and-socket joints, such as the shoulder and hip joints, allow backward, forward, sideways, and rotating movements.
- Hinge joints.
- Pivot joints.
- Ellipsoidal joints.
Q. What are the 3 classifications of joints?
Joints can be classified by the type of the tissue present (fibrous, cartilaginous or synovial), or by the degree of movement permitted (synarthrosis, amphiarthrosis or diarthrosis).
Q. Which type of joint is the most movable?
Synovial joints
Q. What is the strongest joint in the body?
The muscles and ligaments that surround the joint are also some of the largest and strongest in the body. So why does the biggest, strongest joint in the body become a problem?
Q. What characteristics do all joints have in common?
What characteristics do all joints have in common. All consist of bony regions held together by fibrous or cartilaginous connective tissue’s or by a joint capsule. The large head of the humerus moves easily against the shallow glenoid cavity of the scapula.
Q. What are the 6 major features of synovial joints?
Terms in this set (7)
- synovial joints. articulating bones are separated by a fluid-filled joint cavity.
- All bone ends (epiphyseas) have articular cartilage. absorbs compression, keeps bone ends from crushing each other.
- Joint cavity.
- Articular cartilage.
- Synovial fluid.
- Reinforcing ligaments.
- Lots of nerves and blood vessels.
Q. What are the four distinguishing features of synovial joints?
Terms in this set (6)
- articular cartilage. hyaline cartilage.
- Joint cavity (synovial) small potential space.
- Articular capsule. – outer fibrous capsule of dense irregular connective tissue.
- Synovial fluid. – viscous slippery filtrate of plasma.
- Reinforcing ligaments. …
- Rich nerve and blood vessel supply.
Q. What type of joint is between the jaw and skull?
temporomandibular joints
Q. What are the 5 types of synovial joints?
Planar, hinge, pivot, condyloid, saddle, and ball-and-socket are all types of synovial joints.
Q. What are the 5 main joints in the body?
There are six types of freely movable diarthrosis (synovial) joints:
- Ball and socket joint. Permitting movement in all directions, the ball and socket joint features the rounded head of one bone sitting in the cup of another bone.
- Hinge joint.
- Condyloid joint.
- Pivot joint.
- Gliding joint.
- Saddle joint.
Q. What is Diarthroses?
Medical Definition of diarthrosis 1 : articulation that permits free movement. 2 : a freely movable joint. — called also synovial joint.
Q. What are the six types of Diarthroses?
The six types of synovial joints are the pivot, hinge, saddle, plane, condyloid, and ball-and-socket joints.
Q. What are two types of Amphiarthrosis joints?
There are two types of slightly movable joints (amphiarthrosis): syndesmosis and symphysis. A syndesmosis is similar to a suture, complete with the fibrous connective tissue, but it is more flexible. Such a joint is useful if the body needs to link two bones, but allow a little flexibility.
Q. What is an example of Amphiarthrosis?
Amphiarthrosis. An amphiarthrosis is a joint that has limited mobility. An example of this type of joint is the cartilaginous joint that unites the bodies of adjacent vertebrae. Another example of an amphiarthrosis is the pubic symphysis of the pelvis.