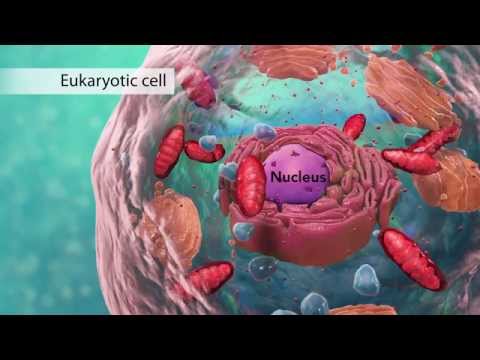
Q. What can a cytoplasm be compared to in real life?
The cytoplasm is like a jello salad because the cytoplasm surrounds and suspends the cell’s organelles like the jello surrounds and suspends the fruit in the jello salad.
Q. What is an example of cytoplasm?
An example of cytoplasm is the substance that fills every living cell in our bodies. The organelles of eukaryotic cells, such as mitochondria, the endoplasmic reticulum, and (in green plants) chloroplasts, are contained in the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm and the nucleus make up the cell’s protoplasm .
Table of Contents
- Q. What can a cytoplasm be compared to in real life?
- Q. What is an example of cytoplasm?
- Q. What is an example of cytoplasm in a house?
- Q. What is an example of cytoplasm in a school?
- Q. What part of the school is like cytoplasm?
- Q. What would the Golgi body be in a school?
- Q. How a cell is like a house?
- Q. What is a cell similar to?
- Q. Where is cytoplasm found?
- Q. What is cytoplasm one word?
- Q. What’s another word for cytoplasm?
- Q. What is the purpose of ribosomes?
- Q. What do Golgi bodies do?
- Q. What does Golgi body look like?
- Q. What is the Golgi body made of?
- Q. What is Golgi apparatus Class 9?
- Q. What is the main function of Golgi apparatus Class 9?
- Q. What is mitochondria class 9th?
- Q. What is cell made up of Class 9?
- Q. What cell is made up of?
- Q. What is a cell class 8?
- Q. What is cytoplasm Class 9?
- Q. What is cytoplasm with diagram?
- Q. What are the parts of cytoplasm?
- Q. What does endocytosis mean?
- Q. What causes endocytosis?
- Q. Why is endocytosis needed?
- Q. What is a real life example of a cell?
- Q. What is a real life example of a lysosome?
- Q. What is chromatin like in real life?
- Q. What is a real life example of a cytoskeleton?
- Q. What is a real life example of nucleus?
- Q. What is a real life example of a chromosome?
- Q. What is a real life example of ribosomes?
- Q. What is an example of a nucleus?
- Q. What is a nucleus easy definition?
- Q. What are 3 examples of nucleus?
- Q. What’s a nucleus made of?
- Q. Why is the nucleus so important?
- Q. What is inside the nucleolus?
- Q. Where is the nucleus found?
- Q. Which cells do not have a nucleus?
- Q. How do you say Golgi?
- Q. Is a cytoplasm?
- Q. What is called Nucleoplasm?
- Q. What is the meaning of Nucleoplasm?
- Q. What is the difference between Nucleoplasm and cytoplasm?
- Q. What do you mean by Cyclosis?
- Q. What is Nucleoplasm and its function?
Q. What is an example of cytoplasm in a house?
Endoplasmic Reticulum The cytoplasm is like the floor in a house because the floor contains all the parts of the house and holds them together, like the cytoplasm does for the cell.
Q. What is an example of cytoplasm in a school?
The cytoplasm of a cell can be compared to the hallways and classrooms of a school. The cytoplasm is everything but the nucleus of a cell and the hallways and classrooms is everything of the school.
Q. What part of the school is like cytoplasm?
hallways
Q. What would the Golgi body be in a school?
A cell is like a school because a school has many different parts to keep it running properly like a cell. The Golgi apparatus is like a school bus because a school bus transports kids to school like the Golgi apparatus ships proteins.
Q. How a cell is like a house?
The cytoplasm of a cell can be compared to the interior of a house. The interior of a house contains all the objects in the house in it, protecting them from any outside forces. Similarly, the cytoplasm protects the organelles within it by enclosing them and filling up any spaces between them.
Q. What is a cell similar to?
A cell is like a car. The nucleus of a cell would be like the driver of a car, they control the cell/car. Cell membrane is like the doors on a car. They regulate what goes in/out.
Q. Where is cytoplasm found?
Cytoplasm is contained within cells in the space between the cell membrane and the nuclear membrane.
Q. What is cytoplasm one word?
: the organized complex of inorganic and organic substances external to the nuclear membrane of a cell and including the cytosol and membrane-bound organelles (such as mitochondria or chloroplasts) — see cell illustration. Other Words from cytoplasm Example Sentences Learn More about cytoplasm.
Q. What’s another word for cytoplasm?
Cytoplasm is also called protoplasm.
Q. What is the purpose of ribosomes?
Ribosomes have two main functions — decoding the message and the formation of peptide bonds. These two activities reside in two large ribonucleoprotein particles (RNPs) of unequal size, the ribosomal subunits. Each subunit is made of one or more ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs) and many ribosomal proteins (r-proteins).
Q. What do Golgi bodies do?
A Golgi body, also known as a Golgi apparatus, is a cell organelle that helps process and package proteins and lipid molecules, especially proteins destined to be exported from the cell. Named after its discoverer, Camillo Golgi, the Golgi body appears as a series of stacked membranes.
Q. What does Golgi body look like?
The Golgi apparatus (GA), also called Golgi body or Golgi complex and found universally in both plant and animal cells, is typically comprised of a series of five to eight cup-shaped, membrane-covered sacs called cisternae that look something like a stack of deflated balloons.
Q. What is the Golgi body made of?
The Golgi apparatus, also called Golgi complex or Golgi body, is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells (cells with clearly defined nuclei) that is made up of a series of flattened stacked pouches called cisternae. It is located in the cytoplasm next to the endoplasmic reticulum and near the cell nucleus.
Q. What is Golgi apparatus Class 9?
Golgi apparatus. Golgi apparatus. The stacks of flattened membranous vesicles are called Golgi apparatus. It basically stores, packs and modifies the products in vesicles. It temporarily stores protein that moves out of the cell through the vesicles of the Golgi apparatus.
Q. What is the main function of Golgi apparatus Class 9?
The main function of Golgi apparatus is secretory. It produces vacuoles or secretory vesicles which contain cellular secretions like enzymes, proteins, cellulose etc. Golgi apparatus is also involved in the synthesis of cell wall, plasma membrane and lysosomes.
Q. What is mitochondria class 9th?
Mitochondria are round “tube-like” organelles that provide energy to a cell in the form of ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) for performing different chemical activities for the sustainance of life. Fig. Structure of mitochondria. The mitochondria is also called powerhouse of the cell. It is surrounded by two membranes.
Q. What is cell made up of Class 9?
Cells are made up of components called cell organelles. A cell is capable to live and perform all their respective functions due to the presence of cell organelles.
Q. What cell is made up of?
All cells are made from the same major classes of organic molecules: nucleic acids, proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids.
Q. What is a cell class 8?
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life. All living organisms are made up of cells. Cells make tissues, tissues make organs, organs make organ systems and organ systems make a living organism. Thus, the cell is the building block, or the structural unit of the living body.
Q. What is cytoplasm Class 9?
The part of the cell which occurs between plasma membrane and nuclear membrane is called cytoplasm. The inner granular mass of cytoplasm is called endoplasm. Cytoplasm consist of an aqueous ground substance called Cytosol which contain variety of cell organelles.,insoluble waste,storage products.
Q. What is cytoplasm with diagram?
The cytoplasm is the semi-viscous ground substance of the cell. All the volume of such substance outside the nucleus and inside the plasma membrane is cytoplasm. It is sometimes described as the non-nuclear content of the protoplasm. All the cellular contents in prokaryotes are contained within the cell’s cytoplasm.
Q. What are the parts of cytoplasm?
The main components of the cytoplasm are cytosol (a gel-like substance), the organelles (the cell’s internal sub-structures), and various cytoplasmic inclusions. The cytoplasm is about 80% water and usually colorless.
Q. What does endocytosis mean?
Endocytosis definition and purposes. Endocytosis is the process by which cells take in substances from outside of the cell by engulfing them in a vesicle.
Q. What causes endocytosis?
Endocytosis is a cellular process in which substances are brought into the cell. The material to be internalized is surrounded by an area of cell membrane, which then buds off inside the cell to form a vesicle containing the ingested material.
Q. Why is endocytosis needed?
Endocytosis enables uptake of nutrients and helps to control the composition of the plasma membrane. The process is important for the regulation of major cellular functions such as antigen presentation or intracellular signaling cascades. Due to this functional diversity, endocytosis is a very active research area.
Q. What is a real life example of a cell?
The real life example is like the brain to a human. It makes protiens for the cell in which amino acids are hooked together to make the proteins. It works as a packaging system. A real life example is the company Fed-Ex that ships and transports things everywhere in the world.
Q. What is a real life example of a lysosome?
Lysosomes are nicknamed “Cleanup Crews”. Their function within a cell is break down food that the cell can use to destroy older cells. A real-life example of lysosomes in a restaurant is the cleaning staff or busboys.
Q. What is chromatin like in real life?
Chromatin. Chromatin is like a book beacuse it holds the instructions for mitosis and meiosis.
Q. What is a real life example of a cytoskeleton?
The cytoskeleton acts as a “track” on which cells can move organelles, chromosomes and other things. Some examples are: Vesicle movement between organelles and the cell surface, frequently studied in the squid axon.
Q. What is a real life example of nucleus?
a real life example of the nucleus is like a boss of a company. a real life example of the dna is like the instructions on how to cook cookies.
Q. What is a real life example of a chromosome?
Frequency: The definition of a chromosome is a thread-like structure of DNA (nucleic acids and proteins) that carries genes. The “X” or “Y” gene that determines whether you will be a boy or a girl is an example of a chromosome.
Q. What is a real life example of ribosomes?
A carpenters work bench. Any workbench because the ribosome is the ” workbench “upon which proteins are assembled.
Q. What is an example of a nucleus?
An example of a nucleus is the center core of an atom. An example of a nucleus is the fiction department of a book publisher where most of the money is made and which is considered the heart of the publisher’s organization. A central or essential part around which other parts are gathered or grouped; a core.
Q. What is a nucleus easy definition?
1 : a usually round part of most cells that is enclosed in a double membrane, controls the activities of the cell, and contains the chromosomes. 2 : the central part of an atom that comprises nearly all of the atomic mass and that consists of protons and neutrons.
Q. What are 3 examples of nucleus?
Nucleus
- Chromatin/chromosomes.
- Nuclear DNA.
- Nuclear bodies.
- Nuclear matrix.
- Nucleoplasm.
- Nuclear envelope.
Q. What’s a nucleus made of?
The nucleus is a collection of particles called protons, which are positively charged, and neutrons, which are electrically neutral. Protons and neutrons are in turn made up of particles called quarks. The chemical element of an atom is determined by the number of protons, or the atomic number, Z, of the nucleus.
Q. Why is the nucleus so important?
The nucleus is considered to be one of the most important structures of eukaryotic cells as it serves the function of information storage, retrieval and duplication of genetic information. It is a double membrane-bound organelle that harbours the genetic material in the form of chromatin.
Q. What is inside the nucleolus?
What does the nucleolus contain? The nucleolus contains DNA, RNA and proteins. It is a ribosome factory. Cells from other species often have multiple nucleoli.
Q. Where is the nucleus found?
The nucleus is an organelle that contains the genetic information for that organism. In an animal cell, the nucleus is located in the central region of the cell. In a plant cell, the nucleus is located more on the periphery due to the large water-filled vacuole in the center of the cell.
Q. Which cells do not have a nucleus?
Prokaryotes are organisms whose cells lack a nucleus and other organelles. Prokaryotes are divided into two distinct groups: the bacteria and the archaea, which scientists believe have unique evolutionary lineages.
Q. How do you say Golgi?
2 syllables: “GOL” + “jee”…Here are 4 tips that should help you perfect your pronunciation of ‘Golgi’:
- Break ‘Golgi’ down into sounds: [GOL] + [JEE] – say it out loud and exaggerate the sounds until you can consistently produce them.
- Record yourself saying ‘Golgi’ in full sentences, then watch yourself and listen.
Q. Is a cytoplasm?
Cytoplasm is the gelatinous liquid that fills the inside of a cell. It is composed of water, salts, and various organic molecules. Some intracellular organelles, such the nucleus and mitochondria, are enclosed by membranes that separate them from the cytoplasm.
Q. What is called Nucleoplasm?
Similar to the cytoplasm of a cell, the nucleus contains nucleoplasm, also known as karyoplasm, or karyolymph or nucleus sap. The nucleoplasm is a type of protoplasm, and is enveloped by the nuclear envelope (also known as the nuclear membrane). The nucleoplasm includes the chromosomes and nucleolus.
Q. What is the meaning of Nucleoplasm?
: the protoplasm of a nucleus especially : nuclear sap. Other Words from nucleoplasm.
Q. What is the difference between Nucleoplasm and cytoplasm?
What is the difference between cytoplasm and nucleoplasm? The cytoplasm is found in all the cells while nucleoplasm is found only in eukaryotic cells. The cytoplasm is the fluid mass of the cell consisting of organelles whereas nucleoplasm is the sap of the nucleus that contains nucleoplasm.
Q. What do you mean by Cyclosis?
the streaming of protoplasm
Q. What is Nucleoplasm and its function?
Inside the nuclear membrane is the nucleoplasm, which main function is to store DNA and facilitate an isolated environment where controlled transcription and gene regulation is enabled. The nucleoplasm contains several non-membrane bound substructures,such as nuclear bodies and nuclear speckles.