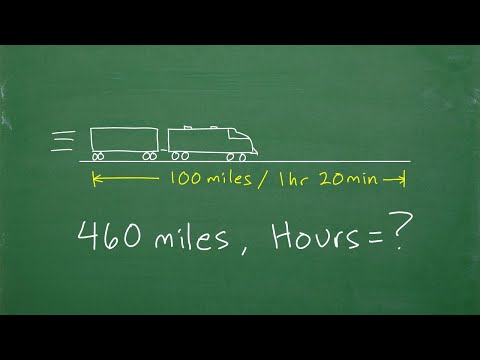
In other words, 100 miles per hour is 1.4570 times the speed of a Cheetah, and the speed of a Cheetah is 0.68630 times that amount. The cheetah can reach speeds of up to 68.660 miles per hour in short bursts. From a crouching position, the cheetah can attain these speeds in just 2.25 seconds.
Q. How far will a car travel in 20 min at a speed of 10 m s?
How much distance does he travel? speed = distance / time. With speed = 10 m/s and time = 20 x 60 s, the distance travelled = 10 x (20 x 60) m = 12 000 m or 12 km.
Table of Contents
- Q. How far will a car travel in 20 min at a speed of 10 m s?
- Q. How far can a car travel in 10 minutes?
- Q. How many miles can you travel in 2 hours?
- Q. How do you calculate travel time?
- Q. How do you calculate deceleration?
- Q. What’s the difference between acceleration and deceleration?
- Q. What is the symbol for deceleration?
- Q. What is another name for deceleration?
- Q. What does deceleration look like on a graph?
- Q. Is constant speed and uniform speed same?
- Q. Does uniform mean constant?
- Q. What is the example of uniform speed?
- Q. What is an example of a uniform motion?
- Q. What is the formula for non uniform motion?
- Q. What is the formula of uniform motion?
Q. How far can a car travel in 10 minutes?
The car is travelling for 10 minutes, so it will travel 12km. Here total time taken is 10 min. Vavg × total time taken= 20× 600=12000 m.
Q. How many miles can you travel in 2 hours?
140 miles
Q. How do you calculate travel time?
Estimate how fast you will go on your trip. Then, divide your total distance by your speed. This will give you an estimation of your travel time. For example, if your trip is 240 miles and you are going to be drive 40 miles an hour, your time will be 240/40 = 6 hours.
Q. How do you calculate deceleration?
Deceleration is the opposite of acceleration. The deceleration will be computed by dividing the final velocity minus the initial velocity, by the amount of time is taken for this drop in velocity. The formula for acceleration can be used here, with a negative sign, to identify the deceleration value.
Q. What’s the difference between acceleration and deceleration?
Acceleration can be caused by either a change in the magnitude or the direction of the velocity. Instantaneous acceleration a is the acceleration at a specific instant in time. Deceleration is an acceleration with a direction opposite to that of the velocity.
Q. What is the symbol for deceleration?
Deceleration is the opposite of acceleration. Deceleration also is known as negative acceleration. Hence it is denoted by – a. It is the final velocity minus the initial velocity, with a negative sign in the result because the velocity is decreasing.
Q. What is another name for deceleration?
What is another word for deceleration?
| slowdown | braking |
|---|---|
| slowing down | slowing up |
| stoppage | delay |
| freeze | slow-up |
| go-slow | wait |
Q. What does deceleration look like on a graph?
time graph, the slope of the line corresponds to the acceleration of the objects. Objects that are accelerating (speeding up) will have a positive slope on a speed vs. time graph, while objects that are decelerating (slowing down) will have a negative slope.
Q. Is constant speed and uniform speed same?
During uniform motion, velocity remains constant with time and change in velocity for any time interval is zero. Constant velocity is the velocity whose direction as well as magnitude remains constant. Uniform velocity is the velocity whose magnitude(only) increases with equal intervals of time.
Q. Does uniform mean constant?
Explanation: UNIFORM VELOCITY: when an object is moving in a straight line, without any acceleration. No change in speed or direction is experienced. CONSTANT VELOCITY: when the speed of an object has not changed even though the object may have experienced a change in direction (zero acceleration).
Q. What is the example of uniform speed?
Uniform speed:Motion of heavy vehicle like trucks on highway. Non-uniform speed:Motion of bike in city or busy roads. If a vehicle is moving on a circular path with uniform speed , then its velocity is said to be non – uniform , Was this answer helpful?
Q. What is an example of a uniform motion?
More examples of Uniform motion are: Movement of hands of a watch, Rotation and revolution of the earth, Movement of the blades of a ceiling fan etc. Do you know why Oil and Water does not mix together? A body is said to be in a non-uniform motion if it travels unequal distances in equal intervals of time.
Q. What is the formula for non uniform motion?
Diagram of non-uniform circular motion: In non-uniform circular motion, the magnitude of the angular velocity changes over time. The change in direction is accounted by radial acceleration ( centripetal acceleration ), which is given by following relation: ar=v2r a r = v 2 r .
Q. What is the formula of uniform motion?
The formula for uniform motion is d = rt, meaning distance is equal to rate times time.