Q. What catalyst is used in hydrogenation?
Nickel catalyst
Nickel catalyst is used in commercial hydrogenation of edible oils. Other catalysts, such as platinum, palladium, copper, etc., have also been applied in hydrogenation applications.
Q. What is the catalyst in the hydrogenation reaction?
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to reduce or saturate organic compounds.
Table of Contents
- Q. What catalyst is used in hydrogenation?
- Q. What is the catalyst in the hydrogenation reaction?
- Q. Why is a catalyst needed for hydrogenation?
- Q. What is catalytic hydrogenation and explain the process?
- Q. Why nickel is used as a catalyst?
- Q. What is catalytic hydrogenation of alkene?
- Q. Is Palladium a catalyst?
- Q. What does ethene and hydrogen make?
- Q. How is hydrogenation of Buta 1, 3-diene investigated?
- Q. What kind of catalyst is used for butadiene hydrogenation?
- Q. How is calcination of catalysts carried out in air?
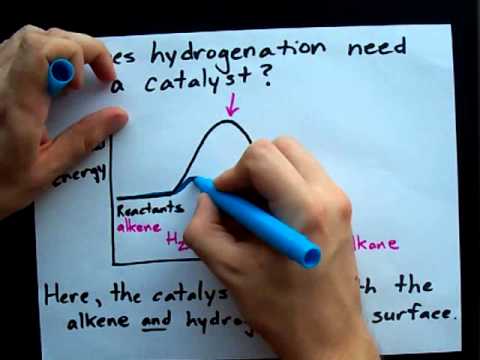
Q. Why is a catalyst needed for hydrogenation?
Hydrogenation requires a catalyst to make the reaction go at a reasonable rate. The reaction will go without a catalyst , but it needs extremely high temperatures. A metal catalyst provides an alternate pathway with a lower activation energy. This allows the reaction to take place at lower temperatures.
Q. What is catalytic hydrogenation and explain the process?
Catalytic hydrogenation is treatment with hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. Catalysts are required for the reaction to be usable; non-catalytic hydrogenation takes place only at very high temperatures. Hydrogenation reduces double and triple bonds in hydrocarbons.
Q. Why nickel is used as a catalyst?
Nickel-based catalysts are the most frequently used in reforming reactions due to C–C bond rupture capability. Nickel has been generally supported onto alumina because of its ability to withstand reaction conditions. On the contrary to noble metals, ESR over nickel catalysts takes place at moderate temperatures.
Q. What is catalytic hydrogenation of alkene?
Alkene hydrogenation is the syn-addition of hydrogen to an alkene, saturating the bond. The alkene reacts with hydrogen gas in the presence of a metal catalyst which allows the reaction to occur quickly.
Q. Is Palladium a catalyst?
Finely divided palladium is a good catalyst and is used for hydrogenation and dehydrogenation reactions.
Q. What does ethene and hydrogen make?
Ethene reacts with hydrogen in the presence of a finely divided nickel catalyst at a temperature of about 150°C. Ethane is produced. This is a fairly pointless reaction because ethene is a far more useful compound than ethane!
Q. How is hydrogenation of Buta 1, 3-diene investigated?
The gas-phase hydrogenation of buta-1,3-diene to, but-1-ene, trans and cis -but-2-ene and butane over several monometallic Pd and bimetallic PdPb catalysts was studied. The reaction was investigated at atmospheric pressure and 0–20°C over a wide range of conversions.
Q. What kind of catalyst is used for butadiene hydrogenation?
Recently we proposed a kinetic model for butadiene hydrogenation over a palladium (0.3 % Pd/ c~-A1203) catalyst (Goetz et.al., 1995b). But-l-ene was thought to be produced either from syn or from anti-adsorbed buta- 1,3-diene; trans- and cis-butene from anti- and syn-forms of butadiene respectively.
Q. How is calcination of catalysts carried out in air?
Calcination of catalysts in air was carried out at 573 K for 2 h, followed by reduction in a flow of hydrogen at the same temperature and for the same period of time.