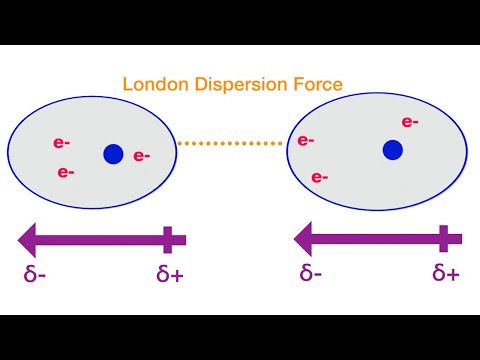
The attraction between neighboring molecules causes dispersion forces. The electron cloud of one molecule becomes attracted to the nucleus of another molecule, so the distribution of electrons changes and creates a temporary dipole.
Q. Which has the strongest dispersion force?
iodine molecules
Table of Contents
- Q. Which has the strongest dispersion force?
- Q. Do London forces exist in all substances?
- Q. What increases intermolecular?
- Q. What factors affect the strength of forces?
- Q. What two factors affect the strength of frictional force?
- Q. What determines the strength of van der Waals forces?
- Q. Is Van der Waals force electrostatic?
- Q. Is Van der Waals the same as electrostatic?
- Q. Are van der Waals interactions electrostatic interactions?
- Q. What causes a dipole dipole force?
Q. Do London forces exist in all substances?
London forces exist in ALL substances. London forces will be strongest in large molecules (or ions, or atoms) and weakest in small molecules. In larger molecules, London forces tend to be stronger than dipole-dipole forces (even stronger than hydrogen bonds).
Q. What increases intermolecular?
Bottom Line. Boiling points are a measure of intermolecular forces. The intermolecular forces increase with increasing polarization of bonds. Boiling point increases with molecular weight, and with surface area.
Q. What factors affect the strength of forces?
Newton’s law also states that the strength of gravity between any two objects depends on two factors: the masses of the objects and the distance between them.
Q. What two factors affect the strength of frictional force?
The strength of the force of friction depends on two factors; the type of surfaces involves and how hard the surfaces push together, What is one way you could reduce the friction between two surfaces? Ball bearing are one way of reducing friction between two surfaces.
Q. What determines the strength of van der Waals forces?
Van der Waals attraction is greater if the molecules are closer. Van der Waals forces are independent of temperature except for dipole – dipole interactions.
Q. Is Van der Waals force electrostatic?
Van der Waals forces are weak electrostatic forces that attract neutral molecules to one another. Particles in liquid or air vibrate and move constantly. Thus, they collide with other particles, including the media’s particles such as water molecules—the process known as Brownian motion (Figure 50).
Q. Is Van der Waals the same as electrostatic?
Van der Waals force is the sum of the attractive and the repulsive non-bond forces between atoms or molecules other than the electrostatic forces. Although the van der Waals force between two carbon atoms is very weak, there are a lot of van der Waals forces between two particles, leading to a very strong interaction.
Q. Are van der Waals interactions electrostatic interactions?
Electrostatic interaction (van der Waals interaction): The attractive or repulsive interaction between objects having electric charges. Electrostatic attraction (shown in red) between the δ+ and δ- ends of a polar covalent N-H bond allow for hydrogen bonding and base pairing within the DNA double helix.
Q. What causes a dipole dipole force?
Dipole -dipole interactions occur when the partial charges formed within one molecule are attracted to an opposite partial charge in a nearby molecule. Polar molecules align so that the positive end of one molecule interacts with the negative end of another molecule.