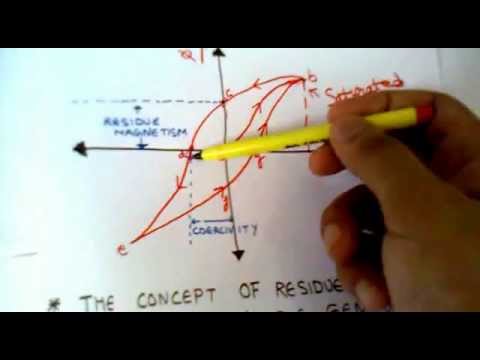
Q. What causes residual magnetism?
Remanence or remanent magnetization or residual magnetism is the magnetization left behind in a ferromagnetic material (such as iron) after an external magnetic field is removed. Colloquially, when a magnet is “magnetized” it has remanence.
Q. Can magnetism be controlled?
Researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology say they have discovered a new way to electrically control magnetism using a gate voltage that could be applied to a wide variety of magnetic materials, including oxides and metals.
Table of Contents
- Q. What causes residual magnetism?
- Q. Can magnetism be controlled?
- Q. What is residual magnetism where is it important?
- Q. How does a generator lose residual magnetism?
- Q. Which generator Cannot start if there is no residual magnetism?
- Q. Does the residual magnetism of a generator decrease with time?
- Q. What is the basic source of magnetism?
- Q. How would you get a self excited generator to work after it has lost all of its residual magnetism?
- Q. What is residual flux?
- Q. What is residual flux density?
- Q. What is residual voltage?
- Q. What causes residual voltage?
- Q. What residual means?
- Q. What is residual voltage in motor?
- Q. What is residual voltage in LVDT?
- Q. What is residual voltage of surge arrester?
- Q. What is induced voltage?
- Q. What increases induced voltage?
- Q. How can we reduce voltage induced?
- Q. How you can make the electromagnet stronger?
- Q. What is the best material for an electromagnet?
- Q. Which metal is used for electromagnet?
- Q. What is the biggest magnet on Earth?
- Q. Is Earth a magnet?
- Q. Is Earth losing its magnetic field?
Q. What is residual magnetism where is it important?
Residual magnetism is very important to start a generator,if its absent generator will not be started so , to build up its emf we need to excite the field winding by low voltage dc supply or in practical by a battery.
Q. How does a generator lose residual magnetism?
Residual magnetism in the generator exciter field allows the generator to build up voltage during start-up. This magnetism is sometimes lost due to shelf time or improper operation, among other reasons. Restoring this residual magnetism is possible and is sometimes referred to as “flashing the exciter field”.
Q. Which generator Cannot start if there is no residual magnetism?
Which generator cannot start if there is no residual magnetism ? Both shunt and series generator cannot start without residual flux . But a separately exited generator can because it has a source for field excitation. Best Answer Residual magnetism is one of importan properties of ferromagnetic materials.
Q. Does the residual magnetism of a generator decrease with time?
Not really. Nearly all generators only have a small magnet to start things off. Once started, the small field generates a small current – which then fed back into generator to reinforce the magnetic field. Thus within a few seconds the generator is capable of producing usable power.
Q. What is the basic source of magnetism?
The source of magnetism is the electric charges. The movement of the electric charge causes magnetism. Substances are made from tiny atoms. These atoms have protons, electrons and neutrons.
Q. How would you get a self excited generator to work after it has lost all of its residual magnetism?
If all the residual magnetism is lost, the generator won’t start producing current and can’t build a magnetic field. Momentarily supplying the field coils with an electric current—a process called flashing—will supply a magnetic field to start the alternator and build the required magnetic field.
Q. What is residual flux?
[rə′zij·ə·wəl ′fləks ‚den·səd·ē] (electromagnetism) The magnetic flux density at which the magnetizing force is zero when the material is in a symmetrically and cyclically magnetized condition. Also known as residual induction; residual magnetic induction; residual magnetism.
Q. What is residual flux density?
Residual magnetic flux density (remanence) In the magnetic hysteresis loops showing the magnetic characteristics of a material, the remanence is the value of the flux density remaining when the external field returns from the high value of saturation magnetization to 0.
Q. What is residual voltage?
The residual voltage is the voltage that remains in an output transistor while it is ON. For example, consider an NPN output with a power supply voltage of 24 V and a residual voltage of 2 V. While the output transistor is ON, there will be 2 V between the output line (the black wire) and the 0-V line (the blue wire).
Q. What causes residual voltage?
The residual voltage is due to the Faradaic impedance [6] as well as mismatch errors in the transistors used to make the stimulator. The presence of a residual voltage may lead to irreversible chemical reactions at the electrode-tissue interface and cause tissue damage [8].
Q. What residual means?
(Entry 1 of 2) 1 : remainder, residuum: such as. a : the difference between results obtained by observation and by computation from a formula or between the mean of several observations and any one of them. b : a residual product or substance.
Q. What is residual voltage in motor?
Residual voltage is the voltage that is remaining in form. of induced emf i.e., magnetic field in the windings of. generator or motor which will help in producing voltage in. generators and back emf in motors.
Q. What is residual voltage in LVDT?
What is residual voltage in lvdt? Ideally, the output voltage at the null position should be equal to zero. However, in actual practice, there exists a small voltage known as Residual Voltage, at the null position. This residual voltage is generally less than 1% of the maximum output voltage in the linear range.
Q. What is residual voltage of surge arrester?
The residual voltages as mentioned above of the selected surge arresters should be well below the equipment withstand level. E.g., for a 33kV system the BIL of transformer is 170kV and LIPL of surge arrester is 90kV then 80 kV is the protective margin.
Q. What is induced voltage?
The induced voltage is produced as a product of electromagnetic induction. The induced voltage of a closed-circuit is described as the rate of change of magnetic flux through that closed circuit. …
Q. What increases induced voltage?
Coils of wire are used to increase the induced voltage and current since the EMF so generated is proportional to the time rate of change of magnetic flux per Faraday’s Law. The more turns of wire, the more flux is generated since the number of surfaces/loops traversed by the flux is increased.
Q. How can we reduce voltage induced?
Methods to reduce the effect of Inductive Coupling Between Cables
- Limit the cables length running in parallel.
- Increase the distance between the disturbing cable and the victim cable.
- Ground one shield end of both cables.
Q. How you can make the electromagnet stronger?
You can make an electromagnet stronger by doing these things:
- wrapping the coil around a piece of iron (such as an iron nail)
- adding more turns to the coil.
- increasing the current flowing through the coil.
Q. What is the best material for an electromagnet?
Iron
Q. Which metal is used for electromagnet?
Electromagnets consist of coils, usually copper, wrapped tightly around a laminated core of ferromagnetic material (soft iron, steel, cobalt).
Q. What is the biggest magnet on Earth?
Answer 2: The strongest magnet ever build is 22-foot tall and weights 34 tons. It was built in a research lab in Tallahassee and it produces a magnetic field of at least 45 Tesla. To understand how powerful this is you have to know that the strength of a magnetic field is measured in Gauss (G) or Tesla (T).
Q. Is Earth a magnet?
In a sense, yes. The crust of the Earth has some permanent magnetization, and the Earth’s core generates its own magnetic field, sustaining the main part of the field we measure at the surface. So we could say that the Earth is, therefore, a “magnet.”
Q. Is Earth losing its magnetic field?
Over the last 200 years, the magnetic field has lost around 9% of its strength on a global average. A large region of reduced magnetic intensity has developed between Africa and South America and is known as the South Atlantic Anomaly.