Q. What do many tissues working together make?
Answer and Explanation: When a group of tissues work together to perform a particular role in the human body, they make up an organ.
Q. What tissues make up organs?
As we saw above, every organ is made up of two or more tissues, groups of similar cells that work together to perform a specific task. Humans—and other large multicellular animals—are made up of four basic tissue types: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue.
Table of Contents
- Q. What do many tissues working together make?
- Q. What tissues make up organs?
- Q. What is a group of tissues working together called?
- Q. When organs and tissues work together they form?
- Q. What are 4 types of tissues and their functions?
- Q. How do the four types of tissues work together?
- Q. What is the most important type of tissue your body needs?
- Q. Where is nervous tissue found?
- Q. What is the most important tissue?
- Q. What is tissue Short answer?
- Q. What are the 5 types of tissue?
- Q. Where is muscle tissue located in the body?
- Q. What are the 4 types of muscle tissue?
- Q. What are the 4 types of muscles?
- Q. What are the three main types of muscle tissue How do they differ?
- Q. What do all muscle tissues have in common?
- Q. What are the 4 functions of muscle tissue?
- Q. What are the 5 characteristics of muscle tissue?
- Q. What are 6 major types of muscles?
- Q. What are 5 types of muscle movements?
- Q. What are the three main purposes of muscles?
- Q. What is another name for smooth muscles?
- Q. What are two major types of smooth muscle?
- Q. What are 2 different places in the body where you can find smooth muscles?
- Q. What are examples of smooth muscles?
Q. What is a group of tissues working together called?
An organ is a structure that is composed of at least two or more tissue types and performs a specific set of functions for the body. Many organs working together to accomplish a common purpose is called an organ system.
Q. When organs and tissues work together they form?
Just as cells join together to form tissues, different tissues join together to form organs. An organ is a structure made up of two or more tissues that work together to carry out a specific job….
| System | Main Organs | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Digestive | Stomach, Small Intestine | Break down food for absorption into the blood |
Q. What are 4 types of tissues and their functions?
There are 4 basic types of tissue: connective tissue, epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. Connective tissue supports other tissues and binds them together (bone, blood, and lymph tissues). Epithelial tissue provides a covering (skin, the linings of the various passages inside the body).
Q. How do the four types of tissues work together?
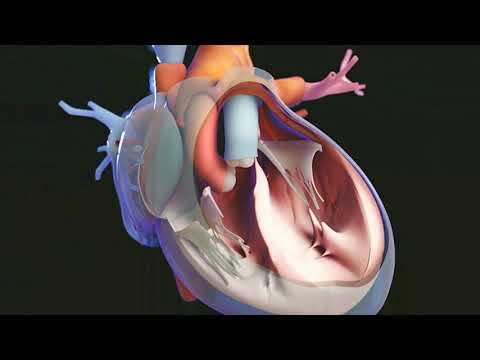
Groups of Tissues Form Organs An organ is a structure made of two or more tissues that work together. The heart (Figure below) is made up of the four types of tissues. The four different tissue types work together in the heart as they do in the other organs.
Q. What is the most important type of tissue your body needs?
Connective tissue is the most abundant tissue type in our body. This shows that connective tissue is very important in providing support and protection in our body. In bones and cartilage, it provides support whereas the collagen in our skin is meant to be elastic and provide protection due to its interlocking matrix.
Q. Where is nervous tissue found?
Nervous tissue is found in the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. It is responsible for coordinating and controlling many body activities.
Q. What is the most important tissue?
Connective tissue
Q. What is tissue Short answer?
A group of similar or dissimilar cells which performs essentially the same function and has a common origin is called a tissue.
Q. What are the 5 types of tissue?
These categories are epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous. The primary tissue types work together to contribute to the overall health and maintenance of the human body.
Q. Where is muscle tissue located in the body?
Smooth muscle fibers are located in walls of hollow visceral organs, except the heart, appear spindle-shaped, and are also under involuntary control. Skeletal muscle fibers occur in muscles which are attached to the skeleton. They are striated in appearance and are under voluntary control.
Q. What are the 4 types of muscle tissue?
Muscle is one of the four primary tissue types of the body, and the body contains three types of muscle tissue: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle (Figure 7.2).
Q. What are the 4 types of muscles?
Different types of muscle
- Skeletal muscle – the specialised tissue that is attached to bones and allows movement.
- Smooth muscle – located in various internal structures including the digestive tract, uterus and blood vessels such as arteries.
- Cardiac muscle – the muscle specific to the heart.
Q. What are the three main types of muscle tissue How do they differ?
Each type of muscle tissue in the human body has a unique structure and a specific role. Skeletal muscle moves bones and other structures. Cardiac muscle contracts the heart to pump blood. The smooth muscle tissue that forms organs like the stomach and bladder changes shape to facilitate bodily functions.
Q. What do all muscle tissues have in common?
All muscle tissues have 4 characteristics in common: excitability. contractility. extensibility – they can be stretched.
Q. What are the 4 functions of muscle tissue?
Terms in this set (7)
- four main functions. movement, maintenance of posture, heat production, joint stability.
- movement. locomotion, blood circulation, food digestion.
- uses all three types. blood circulation.
- smooth muscle. food digestion.
- posture maintenance.
- heat production.
- joint stability.
Q. What are the 5 characteristics of muscle tissue?
Terms in this set (5)
- Excitability- can be stimulated by chemical signals, nerves and stretch.
- Conductivity- the signal for a muscle to contract is spread from the point of stimulation throughout the entire muscle.
- Contractility- ability of the muscle to shorten.
- Extensibility-
- Elasticity-
Q. What are 6 major types of muscles?
Structure
- Comparison of types.
- Skeletal muscle.
- Smooth muscle.
- Cardiac muscle.
- Smooth muscle.
- Cardiac muscle.
Q. What are 5 types of muscle movements?
- Flexion and Extension. Flexion and extension are movements that take place within the sagittal plane and involve anterior or posterior movements of the body or limbs.
- Abduction and Adduction.
- Circumduction.
- Rotation.
- Supination and Pronation.
- Dorsiflexion and Plantar Flexion.
- Inversion and Eversion.
- Protraction and Retraction.
Q. What are the three main purposes of muscles?
The main functions of the muscular system are as follows:
- Mobility. The muscular system’s main function is to allow movement.
- Stability. Muscle tendons stretch over joints and contribute to joint stability.
- Posture.
- Circulation.
- Respiration.
- Digestion.
- Urination.
- Childbirth.
Q. What is another name for smooth muscles?
Smooth muscle, also called involuntary muscle, muscle that shows no cross stripes under microscopic magnification. It consists of narrow spindle-shaped cells with a single, centrally located nucleus. Smooth muscle tissue, unlike striated muscle, contracts slowly and automatically.
Q. What are two major types of smooth muscle?
Smooth muscle is organized in two ways: as single-unit smooth muscle, which is much more common; and as multiunit smooth muscle. The two types have different locations in the body and have different characteristics.
Q. What are 2 different places in the body where you can find smooth muscles?
You can find smooth muscle in the following places:
- Walls of blood vessels.
- Walls of stomach.
- Ureters.
- Intestines.
- In the aorta (tunica media layer)
- Iris of the eye.
- Prostate.
- Gastrointestinal Tract.
Q. What are examples of smooth muscles?
Smooth muscle (so-named because the cells do not have striations) is present in the walls of hollow organs like the urinary bladder, uterus, stomach, intestines, and in the walls of passageways, such as the arteries and veins of the circulatory system, and the tracts of the respiratory, urinary, and reproductive …