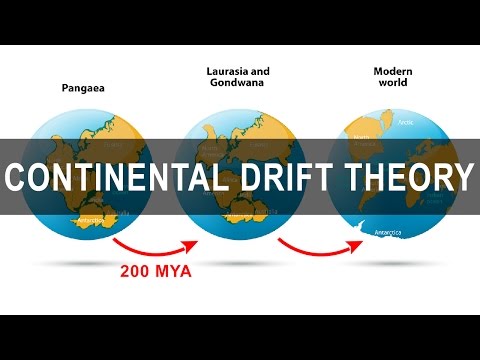
According to the theory, all the continents formed a single continental mass- Pangea and mega ocean- Panthalassa surrounded it. Around 200 million years ago Pangaea started splitting and broke down into two large continental masses as Laurasia and Gondwanaland forming the northern and southern components respectively.
Q. What is continental drift theory and what are the evidences that support it?
Continental drift was a theory that explained how continents shift position on Earth’s surface. Set forth in 1912 by Alfred Wegener, a geophysicist and meteorologist, continental drift also explained why look-alike animal and plant fossils, and similar rock formations, are found on different continents.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is continental drift theory and what are the evidences that support it?
- Q. What is are pieces of evidence that support the theory of continental drift?
- Q. What is the importance of convection current to the plate tectonics?
- Q. In which year was the convection current theory introduced?
- Q. Where does the convection cycles occur?
- Q. What causes the convection cell to turn to the left?
- Q. What are the three main sources of convection?
- Q. What causes convection within Earth?
- Q. What is happening with convection?
Q. What is are pieces of evidence that support the theory of continental drift?
In the early part of the 20th century, scientists began to put together evidence that the continents could move around on Earth’s surface. The evidence for continental drift included the fit of the continents; the distribution of ancient fossils, rocks, and mountain ranges; and the locations of ancient climatic zones.
Q. What is the importance of convection current to the plate tectonics?
Convection currents drive the movement of Earth’s rigid tectonic plates in the planet’s fluid molten mantle. In places where convection currents rise up towards the crust’s surface, tectonic plates move away from each other in a process known as seafloor spreading (Fig. 7.21).
Q. In which year was the convection current theory introduced?
1928-29
Q. Where does the convection cycles occur?
Convection currents in the Earth occur in the mantle. The core of the Earth is extremely hot, and material in the mantle close to the core is heated…
Q. What causes the convection cell to turn to the left?
Point B is in between two convections, and is just below a ridge. This causes the cell to turn left because the flow of fluid hits the bottom of the crust/lithosphere, and is forced to turn left. As the fluid flows between these points, it adjusts to the lower temperature at the top of the mantle and cools down.
Q. What are the three main sources of convection?
I Heat Production and Heat Transfer in the Mantle The primary sources of thermal energy for mantle convection are three: (1) internal heating due to the decay of the radioactive isotopes of uranium, thorium, and potassium; (2) the long-term secular cooling of the earth; and (3) heat from the core.
Q. What causes convection within Earth?
Convection Currents and Geography Radiant heating from the Sun warms the surface of the Earth. That warmth transfers to the adjacent air mass via conduction. The warmed air rises and is replaced by cooler air, creating convection currents in the atmosphere.
Q. What is happening with convection?
rock cools, the density increases, causing the material to sink. What causes the convection cell to turn to the left at point B? lithosphere forcing the convection current to turn left. Temperature increases (closer to the core) and density decreases as a result.