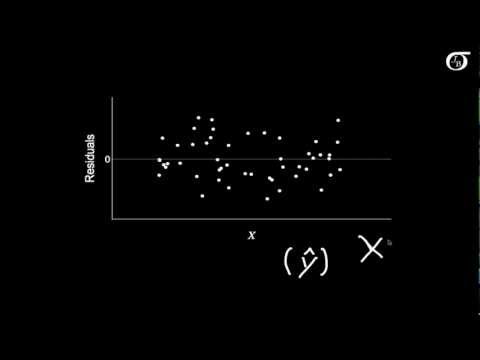
Q. What does a residuals vs fitted plot tell you?
When conducting a residual analysis, a “residuals versus fits plot” is the most frequently created plot. It is a scatter plot of residuals on the y axis and fitted values (estimated responses) on the x axis. The plot is used to detect non-linearity, unequal error variances, and outliers.
Q. What do residuals tell us?
Residuals help to determine if a curve (shape) is appropriate for the data. A residual is the difference between what is plotted in your scatter plot at a specific point, and what the regression equation predicts “should be plotted” at this specific point.
Table of Contents
- Q. What does a residuals vs fitted plot tell you?
- Q. What do residuals tell us?
- Q. What are residuals and why are they so important?
- Q. What is the correlation between residuals and predicted values?
- Q. How do you interpret residual value?
- Q. What are fitted values and residuals?
- Q. Why is residual analysis important?
- Q. What is the purpose of residuals?
- Q. Why residual analysis is important?
- Q. What does correlation between residuals mean?
- Q. What do you understand by residuals in regression?
- Q. Why are the residuals and fitted values uncorrelated?
- Q. What can we learn from a fitted vs residual plot?
- Q. How to see residuals vs fits in Excel?
- Q. How are fitted and residuals used in linear regression?
Q. What are residuals and why are they so important?
Residuals are important when determining the quality of a model. You can examine residuals in terms of their magnitude and/or whether they form a pattern. Where the residuals are all 0, the model predicts perfectly. The further residuals are from 0, the less accurate the model.
Q. What is the correlation between residuals and predicted values?
If adjacent residuals are correlated, one residual can predict the next residual. In statistics, this is known as autocorrelation. This correlation represents explanatory information that the independent variables do not describe. Models that use time-series data are susceptible to this problem.
Q. How do you interpret residual value?
A residual is a measure of how well a line fits an individual data point. This vertical distance is known as a residual. For data points above the line, the residual is positive, and for data points below the line, the residual is negative. The closer a data point’s residual is to 0, the better the fit.
Q. What are fitted values and residuals?
The “residuals” in a time series model are what is left over after fitting a model. The residuals are equal to the difference between the observations and the corresponding fitted values: et=yt−^yt.
Q. Why is residual analysis important?
Residual analysis is a useful class of techniques for the evaluation of the goodness of a fitted model. Checking the underlying assumptions is important since most linear regression estimators require a correctly specified regression function and independent and identically distributed errors to be consistent.
Q. What is the purpose of residuals?
Q. Why residual analysis is important?
Q. What does correlation between residuals mean?
If your residuals are correlated with your independent variables, then your model is heteroskedastic”–I would say that if the variance of your residuals depends on the level of an independent variable, then you have heteroscedasticity.
Q. What do you understand by residuals in regression?
In regression analysis, the difference between the observed value of the dependent variable (y) and the predicted value (ŷ) is called the residual (e). Each data point has one residual. Residual = Observed value – Predicted value. e = y – ŷ
Q. Why are the residuals and fitted values uncorrelated?
The first plot seems to indicate that the residuals and the fitted values are uncorrelated, as they should be in a homoscedastic linear model with normally distributed errors. Therefore, the second and third plots, which seem to indicate dependency between the residuals and the fitted values, suggest a different model.
Q. What can we learn from a fitted vs residual plot?
In this post we’ll describe what we can learn from a residuals vs fitted plot, and then make the plot for several R datasets and analyze them. The fitted vs residuals plot is mainly useful for investigating: Whether linearity holds. This is indicated by the mean residual value for every fitted value region being close to .
Q. How to see residuals vs fits in Excel?
You should be able to look back at the scatter plot of the data and see how the data points there correspond to the data points in the residual versus fits plot here. In case you’re having trouble with doing that, look at the five data points in the original scatter plot that appear in red.
Q. How are fitted and residuals used in linear regression?
Linear Regression Plots: Fitted vs Residuals. The fitted vs residuals plot allows us to detect several types of violations in the linear regression assumptions. Here, one plots on the x-axis, and on the y-axis.