Q. What does a Rhizoid do for nonvascular plants?
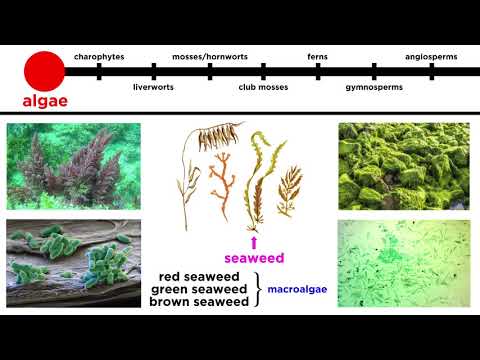
Lesson Summary Bryophytes are a group of nonvascular plants that includes mosses, liverworts, and hornworts. Rhizoids are the tiny structures that stick out from the roots of bryophytes. Rhizoids absorb water and nutrients from the soil through the process of capillary action.
Q. How do nonvascular plants get water?
Nonvascular plants are plants that do not have any special internal pipelines or channels to carry water and nutrients. Instead, nonvascular plants absorb water and minerals directly through their leaflike scales. Nonvascular plants are usually found growing close to the ground in damp, moist places.
Table of Contents
- Q. What does a Rhizoid do for nonvascular plants?
- Q. How do nonvascular plants get water?
- Q. Which of the following plants is non vascular?
- Q. Is Mint a vascular plant?
- Q. Is lettuce vascular or nonvascular?
- Q. Is Cactus a vascular plant?
- Q. Are daisies vascular or nonvascular?
- Q. Are onions vascular?
- Q. Are vascular plants bigger?
Q. Which of the following plants is non vascular?
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| bryophyte | Type of plant that lacks vascular tissues, such as a liverwort, hornwort, or moss. |
| hornworts | Minute nonvascular plants that have very fine rhizoids and long and pointed sporophytes, like tiny horns; a division of bryophyte plants. |
Q. Is Mint a vascular plant?
Mentha x piperita is in the subkingdom Tracheobionta; this means it is a vascular plant.
Q. Is lettuce vascular or nonvascular?
*Tomatoes, wheat, and lettuce and many more are vascular plants.
Q. Is Cactus a vascular plant?
More on Vascular Plants Some examples of vascular plants are duckweed,cacti,giant redwood trees,ferns,conifers,flowering plants, etc.
Q. Are daisies vascular or nonvascular?
Vascular plants, like the daisy, are covered with a waxy layer, or cuticle, that holds in water, and they have pores called stomata that help them take in and let out gasses like carbon dioxide and oxygen.
Q. Are onions vascular?
Monocots are one of the two major types of flowering plants, and are characterized by having a single cotyledon, or seed leaf. Grains, grasses, bamboo and onions are all examples of monocots. Xylem is vascular tissue that carries water and nutrients from roots to the other parts of a plant.
Q. Are vascular plants bigger?
These special tubes, the xylem and phloem, are part of what enable vascular plants to grow larger than nonvascular plants. Vascular plants have stems, roots, leaves, and can have flowers and grow tall. They don’t have leaves and can’t get super big like vascular plants.