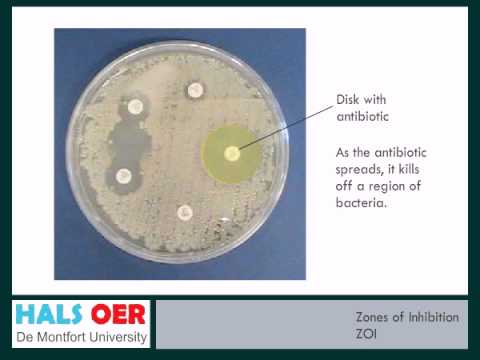
Q. What does a smaller zone of inhibition mean?
The plates are incubated overnight, and the zone of inhibition of bacterial growth is used as a measure of susceptibility (see below). Large zones of inhibition indicate that the organism is susceptible, while small or no zone of inhibition indicateresistance.
Q. What factors can affect the size of the zone of inhibition?
There are multiple factors that determine the size of a zone of inhibition in this assay, including drug solubility, rate of drug diffusion through agar, the thickness of the agar medium, and the drug concentration impregnated into the disk.
Table of Contents
- Q. What does a smaller zone of inhibition mean?
- Q. What factors can affect the size of the zone of inhibition?
- Q. Which organism is most sensitive to natural penicillin?
- Q. What is in Mueller Hinton agar?
- Q. What is the purpose of Mueller Hinton Agar?
- Q. Can salmonella grow on Mueller Hinton agar?
- Q. What is the pH of Mueller Hinton Agar?
- Q. Can Staphylococcus aureus grow on Mueller Hinton agar?
- Q. Which media is used for AST?
- Q. How do you prepare and sterilize nutrient agar?
- Q. What is the difference between broth and agar?
- Q. Can you eat Agar?
Q. Which organism is most sensitive to natural penicillin?
The natural penicillins have activity against non-beta-lactamase producing gram-positive cocci, including viridans streptococci, group A streptococci, Streptococcus pneumoniae, and anaerobic streptococcus (Peptostreptococcus, Peptococcus sp.). Enterococcus sp. is most susceptible to the natural penicillins.
Q. What is in Mueller Hinton agar?
Mueller Hinton Media contains Beef Extract, Acid Hydrolysate of Casein, Starch and Agar. Beef Extract and Acid Hydrolysate of Casein provide nitrogen, vitamins, carbon, amino acids, sulphur and other essential nutrients. Starch is added to absorb any toxic metabolites produced.
Q. What is the purpose of Mueller Hinton Agar?
Mueller Hinton Agar is a solid medium originally designed for the isolation of pathogenic Neisseria species, now widely used for antibiotic susceptibility testing (including sulfonamides) of aerobic and facultatively anaerobic bacteria isolated from clinical specimens.
Q. Can salmonella grow on Mueller Hinton agar?
Results: The prevalence of multiple drug resistance as determined on Mueller-Hinton agar was 83.3% for Salmonella typhi and 80% for Staphylococcus aureus. For Salmonella typhi, resistance ranged from 6.7% (gentamicin and amikacin) to 83.3% (cotrimoxazole, ampicillin and chloramphenicol).
Q. What is the pH of Mueller Hinton Agar?
7.3 ± 0.1
Q. Can Staphylococcus aureus grow on Mueller Hinton agar?
Mueller-Hinton agar is superior to PDM blood agar for detection of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Clin Microbiol Infect.
Q. Which media is used for AST?
Other media available for AST
- Brucella Blood agar.
- Mueller Hinton cloxa.
- Mueller Hinton Salt Etest®
- RPMI.
- BHI agar.
Q. How do you prepare and sterilize nutrient agar?
How to prepare nutrient agar?
- Suspend 28g of nutrient agar powder (CM0003B) in 1L of distilled water.
- Mix and dissolve them completely.
- Sterilize by autoclaving at 121°C for 15 minutes.
- Pour the liquid into the petri dish and wait for the medium to solidify.
Q. What is the difference between broth and agar?
The only difference between broth and agar media is that broths do not contain an agar component. We use broth tubes primarily for specific assays, or (rarely) for bacteria that will not form colonies on a solid surface. Unlike preparation of agar plates, tubes are prepared with media already in the incubation vessel.
Q. Can you eat Agar?
When taken by mouth: Agar is POSSIBLY SAFE for most adults when taken with at least one 8-ounce glass of water. If it is not taken with enough water, agar can swell and block the esophagus or bowel.