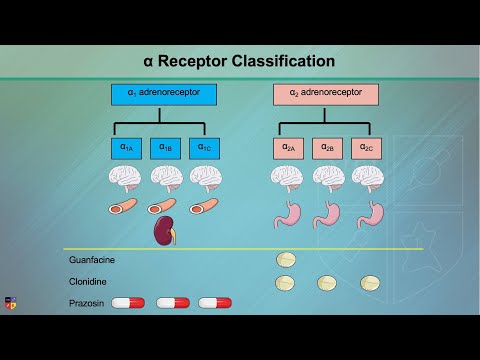
Q. What does alpha 1 adrenergic stimulation cause?
Alpha-1 adrenergic receptors are present on vascular smooth muscle and myocardial tissue; therefore, stimulation causes vasoconstriction and positive inotropic effects, respectively. Higher acuity indications for alpha-1 receptor agonists include cases of vasodilatory shock, hypotension, and hypoperfusion.
Q. What do a1 adrenergic receptors do?
α1-adrenergic receptors are G-Protein Coupled Receptors that are involved in neurotransmission and regulate the sympathetic nervous system through binding and activating the neurotransmitter, norepinephrine, and the neurohormone, epinephrine.
Table of Contents
- Q. What does alpha 1 adrenergic stimulation cause?
- Q. What do a1 adrenergic receptors do?
- Q. What happens when a1 receptors are stimulated?
- Q. How do Alpha1 blockers work?
- Q. How are Alpha1 receptors activated?
- Q. How are alpha1 receptors activated?
- Q. What receptors does Levophed work?
- Q. Do alpha 1 agonists decrease heart rate?
- Q. What happens when the α 1 adrenergic receptor is activated?
- Q. How does adrenergic stimulation affect the human body?
- Q. Is the α1 adrenergic receptor a Gq coupled receptor?
- Q. Is the alpha 1 adrenergic receptor homologous or heterotrimeric?
Q. What happens when a1 receptors are stimulated?
When the alpha receptor is stimulated by epinephrine or norepinephrine, the arteries constrict. This increases the blood pressure and the blood flow returning to the heart.
Q. How do Alpha1 blockers work?
Alpha blockers are a type of blood pressure medication. They lower blood pressure by preventing a hormone called norepinephrine from tightening the muscles in the walls of smaller arteries and veins. As a result, the blood vessels remain open and relaxed. This improves blood flow and lowers blood pressure.
Q. How are Alpha1 receptors activated?
Alpha-1 adrenoceptors are activated by the catecholamines norepinephrine and epinephrine, and are members of the adrenoceptor family of the 7-transmembrane superfamily of receptors. There are three alpha-1 adrenoceptor subtypes: alpha-1A, alpha-1B, and alpha-1D.
Q. How are alpha1 receptors activated?
Q. What receptors does Levophed work?
Norepinephrine acts on beta-1 adrenergic receptors, causing increase in heart rate and cardiac output. However, the elevation in heart rate is only transient, as baroreceptor response to the rise in blood pressure as well as enhanced vagal tone ultimately result in a sustained decrease in heart rate.
Q. Do alpha 1 agonists decrease heart rate?
alpha 1-adrenoceptor activation can increase heart rate directly or decrease it indirectly through parasympathetic activation.
Q. What happens when the α 1 adrenergic receptor is activated?
α 1 -Adrenergic receptors are members of the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily. Upon activation, a heterotrimeric G protein, G q, activates phospholipase C (PLC), which causes phosphatidylinositol to be transformed into inositol triphosphate (IP 3) and diacylglycerol (DAG).
Q. How does adrenergic stimulation affect the human body?
Adrenergic stimulation —by epinephrine in the blood and by norepinephrine released from sympathetic nerve endings—has both excitatory and inhibitory effects. The heart, dilatory muscles of the iris, and the smooth muscles of many blood vessels are stimulated to contract.
Q. Is the α1 adrenergic receptor a Gq coupled receptor?
The alpha-1 (α1) adrenergic receptor is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) associated with the Gq heterotrimeric G-protein.
Q. Is the alpha 1 adrenergic receptor homologous or heterotrimeric?
The alpha-1 (α1) adrenergic receptor is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) associated with the Gq heterotrimeric G-protein. It consists of three highly homologous subtypes, including α1A-, α1B-, and α1D-adrenergic.