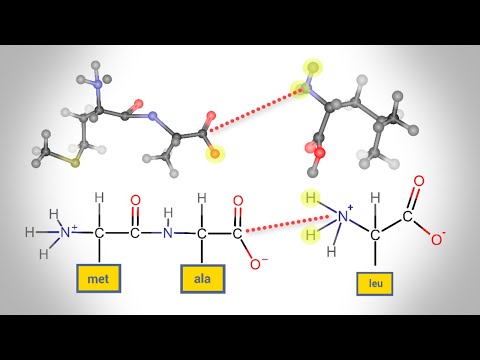
Q. What does it mean for a bond to be planar?
Planar: Said of a molecule when all of its atoms lie in the same plane. Can also be said for a portion of a molecule, such as a ring. Atoms, groups, bonds, or other objects lying within the same plane are periplanar or coplanar.
Q. Can you rotate around a peptide bond?
When two atoms share two electrons, the atoms are said to share a double bond. The partial double bond nature of the peptide bond has profound consequences for protein structure since only the alpha carbons in a protein backbone can potentially rotate freely around their bond axes (bonds 2 and 3, above).
Table of Contents
- Q. What does it mean for a bond to be planar?
- Q. Can you rotate around a peptide bond?
- Q. What is a peptide formula?
- Q. What is the no of peptide bond?
- Q. When two amino acids are joined together to form a peptide bond there is a net?
- Q. Is formed when two amino acids bond together?
- Q. When two amino acids are joined together they form a?
- Q. How would a second amino acid bond to cysteine?
- Q. What is special about the amino acid cysteine?
- Q. What can break peptide bonds?
- Q. What is the role of peptide bonds?
- Q. What are the characteristics of peptide bond?
- Q. Why do peptide bonds have a positive charge?
- Q. What are the 4 levels of protein?
- Q. Do free amino acids have peptide bonds?
Q. What is a peptide formula?
Peptide-based formulas, also known as semi-elemental formulas, contain partially broken down (hydrolyzed) proteins, resulting in shorter chains of amino acids. These shorter chains mimic the process that occurs during digestion of proteins in the intestines.
Q. What is the no of peptide bond?
The CO-NH bond is called a peptide bond. In the given peptide chain the number of peptide bonds is 2 (shown in the above image by red mark).
Q. When two amino acids are joined together to form a peptide bond there is a net?
Peptide-Bond Formation. The linking of two amino acids is accompanied by the loss of a molecule of water. A series of amino acids joined by peptide bonds form a polypeptide chain, and each amino acid unit in a polypeptide is called a residue.
Q. Is formed when two amino acids bond together?
A peptides is a molecule composed of two or more amino acids. The bond that holds together the two amino acids is a peptide bond, or a covalent chemical bond between two compounds (in this case, two amino acids).
Q. When two amino acids are joined together they form a?
dipeptide
Q. How would a second amino acid bond to cysteine?
The most common reaction of this group is a reversible oxidation that forms a disulfide. Oxidation of two molecules of cysteine forms cystine, a molecule that contains a disulfide bond. When two cysteine residues in a protein form such a bond, it is referred to as a disulfide bridge.
Q. What is special about the amino acid cysteine?
Cysteine is a unique amino acid because its side chain contains a free thiol group that can react with another thiol (usually from another cysteine residue) to form a disulfide bond. If properly formed, disulfide bonds can stabilize proteins and promote stability.
Q. What can break peptide bonds?
A peptide bond can be broken by hydrolysis (the addition of water). In the presence of water they will break down and release 8–16 kilojoule/mol (2–4 kcal/mol) of Gibbs energy.
Q. What is the role of peptide bonds?
A peptide bond is a covalent bond formed between two amino acids. Living organisms use peptide bonds to form long chains of amino acids, known as proteins. Proteins are used in many roles including structural support, catalyzing important reactions, and recognizing molecules in the environment.
Q. What are the characteristics of peptide bond?
A peptide bond is a planar, trans and rigid configuration. It also shows a partial double bond character. The coplanarity of the peptide bond denotes the resonance or partial sharing of two pairs of electrons between the amide nitrogen and carboxyl oxygen.
Q. Why do peptide bonds have a positive charge?
carboxyl group has a slight negative charge (due to the high electronegativity of the oxygen atom), whereas the hydrogen atom in the amine group (=N-H) of a peptide bond has a tiny positive charge. These lengths of chain are held to one another by hydrogen bonds forming between peptide bonds on opposing lengths.
Q. What are the 4 levels of protein?
To understand how a protein gets its final shape or conformation, we need to understand the four levels of protein structure: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary.
Q. Do free amino acids have peptide bonds?
Peptide bond formation between two amino acids. In a peptide bond, the carbonyl C of one amino acid is connected to the amino N of another. At one end, the polypeptide has a free amino group, and this end is called the amino terminus (or N-terminus).