Q. What does multiplex PCR test for?
The multiplex RT-PCR assay detects 15 common enteropathogens including 5 viruses (Adenovirus, Astrovirus, Norovirus GII, Rotavirus, and Sapovirus), 7 bacteria (Campylobacter jejuni /C. coli, Salmonella spp, Vibrio cholerae, enteroaggregative E.
Q. What are the steps involved in multiplex PCR?
Therefore, one of the main factors that are crucial for successful amplification-based target enrichment is primer design for multiplex PCR. PCR amplification includes repetitive cycles of DNA denaturation, primer annealing, and sequence extension.
Table of Contents
- Q. What does multiplex PCR test for?
- Q. What are the steps involved in multiplex PCR?
- Q. What is the principle of multiplex PCR?
- Q. How is multiplex PCR different from standard PCR?
- Q. What is multiplex PCR assay?
- Q. How do you make a multiplex PCR primer?
- Q. How does a multiplex work?
- Q. Why is it called digital PCR?
Q. What is the principle of multiplex PCR?
The basic principle of multiplex PCR is the same as that of the conventional PCR, except that more than one pair of primers are required in the same reaction. The primers can specifically combine with their corresponding DNA template, and more than one DNA fragment will be amplified in one reaction simultaneously.
Q. How is multiplex PCR different from standard PCR?
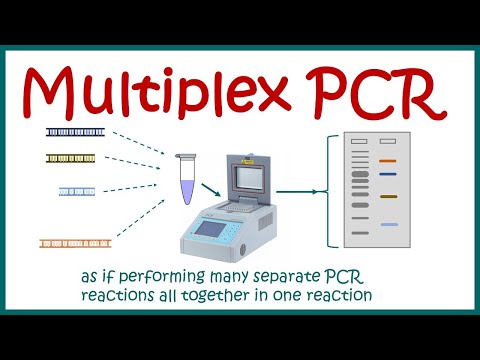
In conventional singleplex PCR, a single target is amplified in a single reaction tube. In contrast, multiplex PCR allows for simultaneous amplification of multiple target sequences in a single tube using specific primer sets in combination with probes labeled with spectrally distinct fluorophores.
Q. What is multiplex PCR assay?
Multiplex PCR is a widespread molecular biology technique for amplification of multiple targets in a single PCR experiment. In a multiplexing assay, more than one target sequence can be amplified by using multiple primer pairs in a reaction mixture.
Q. How do you make a multiplex PCR primer?
Key primer features
- PCR primers are generally designed to be 18 – 30 bp in length.
- The melting temperature (Tm) of the primers should be between 58°C – 60°C, and all primers in the reaction should have a Tm within 0.5 – 1°C of each other.
- The GC content of the primers should be between 40% and 60%.
Q. How does a multiplex work?
How Does a Multiplexer Work? The multiplexer works like a multiple-input and single-output switch. The output gets connected to only one of the n data inputs at a given instant of time. Therefore, the multiplexer is ‘many into one’ and it works as the digital equivalent of an analog selector switch.
Q. Why is it called digital PCR?
In 1999, Bert Vogelstein and Kenneth Kinzler coined the term “digital PCR” and showed that the technique could be used to find rare cancer mutations. However, dPCR was difficult to perform; it was labor intensive, required a lot of training to do properly, and was difficult to do in large quantities.