Q. What does RNA translation produce?
In translation, messenger RNA (mRNA) is decoded in a ribosome, outside the nucleus, to produce a specific amino acid chain, or polypeptide. The polypeptide later folds into an active protein and performs its functions in the cell.
Q. What is translated from mRNA?
Translation is the process by which a protein is synthesized from the information contained in a molecule of messenger RNA (mRNA). Then a transfer RNA (tRNA) molecule carrying the amino acid methionine binds to what is called the start codon of the mRNA sequence.
Q. Is translation RNA to protein?
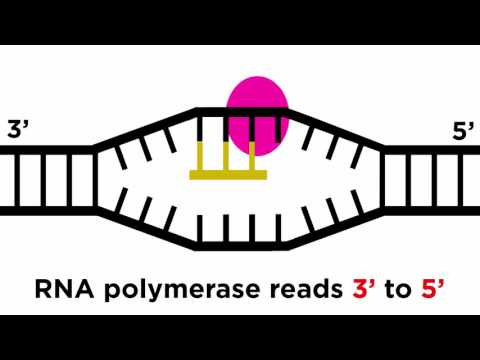
Translation is the RNA → Protein part of the central dogma. Translation occurs at a ribosome. During translation, a protein is synthesized using the codons in mRNA as a guide. All three types of RNA play a role in translation.
Q. What is the product of translation?
The products of translation are proteins. During translation mRNA created during transcription is localized to the ribosome.
Q. What are the start products of translation?
In initiation, the ribosome assembles around the mRNA to be read and the first tRNA (carrying the amino acid methionine, which matches the start codon, AUG). This setup, called the initiation complex, is needed in order for translation to get started.
Q. Which is the end product of translation?
Polypeptides
Q. What is produced from transcription?
Transcription is the process by which the information in a strand of DNA is copied into a new molecule of messenger RNA (mRNA). The newly formed mRNA copies of the gene then serve as blueprints for protein synthesis during the process of translation.
Q. What does the T in tRNA stand for?
transfer
Q. How many tRNA molecules are there?
31 different tRNAs
Q. Are there 64 types of tRNA?
Types of tRNA. A tRNA can be classified based on the amino acid it carries, giving rise to 20 different tRNAs. Alternatively, they can also be grouped based on their anticodon. There are 64 possible codons arising from a combination of four nucleotides.
Q. Why is 45 tRNA?
Although there are 61 different codons that code for the 20 amino acids, there are only 45 different tRNAs because the third base in the tRNA anticodon can recognize two or more different codons on a mRNA. This ability to recognize different codons is called wobble.
Q. Is carbon a DNA?
A single basic unit or “building block” of DNA consists of a sugar , a phosphate group and a base. Sugars are rings of carbon and oxygen atoms. The sugar in DNA has 5 carbon atoms (labelled 1′ – 5′), and is called deoxy-ribose (hence the “Deoxy-ribo” in DNA).
Q. Does RNA have base pairs?
RNA consists of four nitrogenous bases: adenine, cytosine, uracil, and guanine. Like thymine, uracil can base-pair with adenine (Figure 2). Figure 3. Although RNA is a single-stranded molecule, researchers soon discovered that it can form double-stranded structures, which are important to its function.