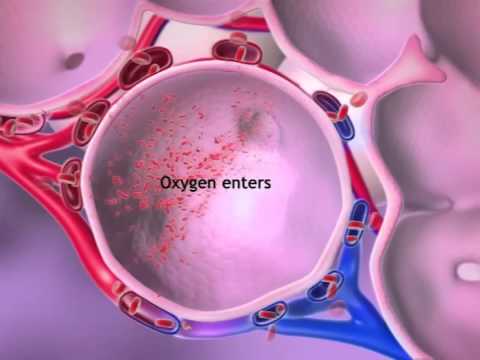
Q. What does the blood exchange when it travels around the body?
Observe how a red blood cell travels from the heart to the lungs and other body tissues to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide. In a circuit through the cardiovascular system, red blood cells transport oxygen…
Q. What is gas exchange and why is it important?
Gas exchange is the process by which oxygen and carbon dioxide move between the bloodstream and the lungs. This is the primary function of the respiratory system and is essential for ensuring a constant supply of oxygen to tissues, as well as removing carbon dioxide to prevent its accumulation.
Table of Contents
- Q. What does the blood exchange when it travels around the body?
- Q. What is gas exchange and why is it important?
- Q. What are the characteristics of gas exchange?
- Q. What two organ systems are involved in gas exchange?
- Q. Which name best describes the process of gas exchange?
- Q. Does gas exchange occur in the arteries?
- Q. Which blood contains more oxygen?
Q. What are the characteristics of gas exchange?
Gas exchange in the lungs
- they give the lungs a really big surface area.
- they have moist, thin walls (just one cell thick)
- they have a lot of tiny blood vessels called capillaries.
Q. What two organ systems are involved in gas exchange?
Gas exchange between tissues and the blood is an essential function of the circulatory system. In humans, other mammals, and birds, blood absorbs oxygen and releases carbon dioxide in the lungs. Thus the circulatory and respiratory system, whose function is to obtain oxygen and discharge carbon dioxide, work in tandem.
Q. Which name best describes the process of gas exchange?
External Respiration. External respiration is the formal term for gas exchange. It describes both the bulk flow of air into and out of the lungs and the transfer of oxygen and carbon dioxide into the bloodstream through diffusion.
Q. Does gas exchange occur in the arteries?
Arteries- these carry “oxygen rich” blood away from the heart, except in the case of the artery to the lungs. Capillaries- these are the sites of gas exchange between the tissues. Veins- these return “oxygen poor” blood to the heart, except for the vein that carries blood from the lungs.
Q. Which blood contains more oxygen?
The left atrium receives blood from the lungs. This blood is rich in oxygen. The left ventricle pumps the blood from the left atrium out to the body, supplying all organs with oxygen-rich blood.