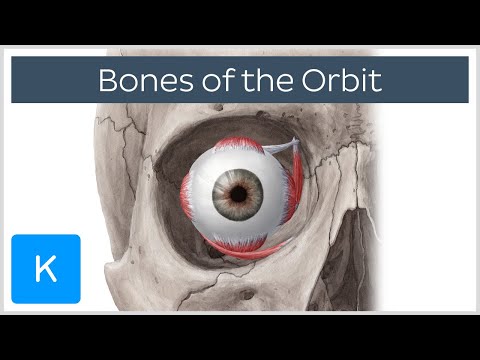
Q. What does the orbital cavity contain?
The orbital cavity contains the globe, nerves, vessels, lacrimal gland, extraocular muscles, tendons, and the trochlea as well as fat and other connective tissue.
Q. Where is ocular cavity?
Ontology: Ocular orbit (C0029180) The bony cavity of the skull which contains the eye, anterior portion of the optic nerve, ocular muscles and ocular adnexa.
Table of Contents
- Q. What does the orbital cavity contain?
- Q. Where is ocular cavity?
- Q. How do I relieve pain behind my left eye?
- Q. When should I worry about eye pain?
- Q. Can lack of sleep cause eye pain?
- Q. Can dental problems cause eye pain?
- Q. What does high eye pressure feel like?
- Q. What is the safest eye drop for glaucoma?
- Q. What happens if you have too much pressure in your eye?
- Q. Can anxiety cause high eye pressure?
- Q. Can eye pressure go down on its own?
Q. How do I relieve pain behind my left eye?
How is eye pain treated?
- Home care. The best way to treat many of the conditions that cause eye pain is to allow your eyes to rest.
- Glasses. If you frequently wear contact lenses, give your corneas time to heal by wearing your glasses.
- Warm compress.
- Flushing.
- Antibiotics.
- Antihistamines.
- Eye drops.
- Corticosteroids.
Q. When should I worry about eye pain?
Call 911 or your local emergency number for eye pain if: It is unusually severe or accompanied by headache, fever or unusual sensitivity to light. Your vision changes suddenly. You also experience nausea or vomiting.
Q. Can lack of sleep cause eye pain?
Why do my eyes hurt when I don’t get enough sleep? When you don’t get enough sleep, your eyes can feel strained, dry and itchy the next day. Lack of sleep can cause eye strain, burst blood vessels and dry eye.
Q. Can dental problems cause eye pain?
Common Dental Issues that can Result to Headache or Eye Pain Missing, loose or misaligned teeth are what is referred to bad bite. This problem can cause the jaw muscles to work more than normal to bring the teeth together and keep the mouth closed. This can result in some headache or even eye pain.
Q. What does high eye pressure feel like?
Pain generally feels like a stabbing, burning, or stinging sensation. Pressure behind the eyes feels like fullness or a stretching sensation inside the eye.
Q. What is the safest eye drop for glaucoma?
I did much of the clinical work on apraclonidine, a relatively selective alpha-2 agonist. It is probably the safest drug we have seen so far in the therapy of glaucoma. The only disadvantage to apraclonidine is that 15%-25% of patients develop a localized allergy involving the eyes, the eyelids and surrounding skin.
Q. What happens if you have too much pressure in your eye?
Media file 2: Elevated eye pressure is caused by a build-up of fluid inside the eye because the drainage channels (trabecular meshwork) cannot drain it properly. Elevated eye pressure can cause optic nerve damage and vision loss.
Q. Can anxiety cause high eye pressure?
Results suggest that high levels of both anxiety-state and anxiety-trait significantly predicted a clinically relevant increase of intraocular pressure.
Q. Can eye pressure go down on its own?
However, recent studies show that just measuring eye pressure is not a reliable way to detect glaucoma. Eye pressure can go up and down during the day or in a month. Also, some people’s optic nerves are not damaged by high pressure while others’ optic nerves are damaged by relatively low pressure.