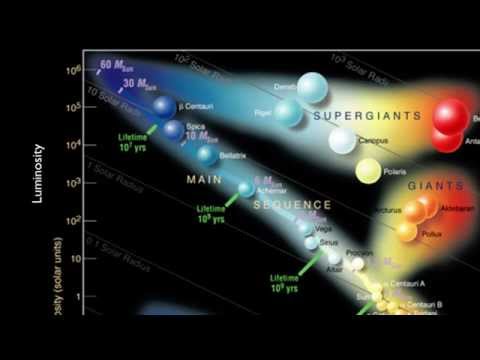
Q. What does the position of a star on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram suggest about a star?
An H-R diagram plots stars according to their surface temperatures (or spectral types) and luminosities. A stars position along the main sequence depends on its mass: High-mass stars are at the upper left and masses become progressively smaller as we move toward the lower right.
Q. What does it mean when a star moves on the HR diagram?
Stars on the main sequence have hydrogen-burning cores. A star’s position on the H-R diagram tells you a great deal of information about it. When stars have exhausted all their hydrogen fuel, they evolve to red giants. Their outer layers of gas expand and cool; therefore, the stars move to the right on the H-R diagram.
Table of Contents
- Q. What does the position of a star on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram suggest about a star?
- Q. What does it mean when a star moves on the HR diagram?
- Q. What two things can the HR diagram tell us about stars *?
- Q. What is known about stars that are placed toward the top of the HR diagram?
- Q. What are the four main classes of stars on an HR diagram?
- Q. What star color is the hottest what star color is the coolest?
- Q. Which color stars are the coldest?
- Q. Where is a red giant on the HR diagram?
- Q. Where is Rigel on the HR diagram?
- Q. How do you use an HR diagram?
- Q. What is the life cycle of Rigel?
- Q. Which star has the greatest luminosity?
- Q. Which star has the greatest size?
- Q. Which stars will die the quickest?
- Q. What is the hottest type of star in the universe?
- Q. What is the hottest star in the sky?
Q. What two things can the HR diagram tell us about stars *?
The position of each dot on the diagram tells us two things about each star: its luminosity (or absolute magnitude) and its temperature. The vertical axis represents the star’s luminosity or absolute magnitude.
Q. What is known about stars that are placed toward the top of the HR diagram?
Stars which lie along the top right of the diagram are luminous and cool and are known as supergiants. Knowing a star’s location on the HR diagram allows us to find its mass, its evolutionary state (and age), and its physical size.
Q. What are the four main classes of stars on an HR diagram?
The Supergiants are cool stars, which are very large and very bright. They are located towards the top right of the graph. The Giants are cool stars, which are a little smaller and dimmer than the Supergiants. The White Dwarfs are very hot stars, which are small in size and relatively dim.
Q. What star color is the hottest what star color is the coolest?
Red stars
Q. Which color stars are the coldest?
Stars have different colors, which are indicators of temperature. The hottest stars tend to appear blue or blue-white, whereas the coolest stars are red.
Q. Where is a red giant on the HR diagram?
Stars in the stable phase of hydrogen burning lie along the Main Sequence according to their mass. After a star uses up all the hydrogen in its core, it leaves the main sequence and moves towards the red giant branch. The most massive stars may also become red supergiants, in the upper right corner of the diagram.
Q. Where is Rigel on the HR diagram?
Two of the brightest stars in the evening sky lie at opposite corners of the rectangle: bright orange-red Betelgeuse at the northeastern corner (upper left in the photo) and even brighter Rigel at the southwest (lower right in the photo).
Q. How do you use an HR diagram?
In an H-R diagram the luminosity or energy output of a star is plotted on the vertical axis. This can be expressed as a ratio of the star’s luminosity to that of the Sun; L*/Lsun. Astronomers also use the historical concept of magnitude as a measure of a star’s luminosity.
Q. What is the life cycle of Rigel?
With an estimated age of seven to nine million years, Rigel has exhausted its core hydrogen fuel, expanded, and cooled to become a supergiant. It is expected to end its life as a type II supernova, leaving a neutron star or a black hole as a final remnant, depending on the initial mass of the star.
Q. Which star has the greatest luminosity?
Antares
Q. Which star has the greatest size?
The largest known star in the universe is UY Scuti, a hypergiant with a radius around 1,700 times larger than the sun. And it’s not alone in dwarfing Earth’s dominant star.
Q. Which stars will die the quickest?
Generally, the more massive the star, the faster it burns up its fuel supply, and the shorter its life. The most massive stars can burn out and explode in a supernova after only a few million years of fusion. A star with a mass like the Sun, on the other hand, can continue fusing hydrogen for about 10 billion years.
Q. What is the hottest type of star in the universe?
That’s even hotter. But the hottest known stars in the Universe are the blue hypergiant stars. These are stars with more than 100 times the mass of the Sun. One of the best known examples is Eta Carinae, located about 7,500 light-years from the Sun.
Q. What is the hottest star in the sky?
Sirius