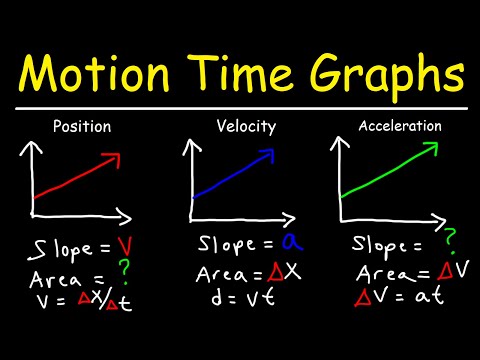
The slope of an acceleration graph represents a quantity called the jerk. The jerk is the rate of change of the acceleration.
Q. What is AVT graph?
The principle is that the slope of the line on a velocity-time graph reveals useful information about the acceleration of the object. If the acceleration is zero, then the slope is zero (i.e., a horizontal line). If the acceleration is positive, then the slope is positive (i.e., an upward sloping line).
Table of Contents
- Q. What is AVT graph?
- Q. How many types of graphs are there in motion?
- Q. What does acceleration look like on a distance time graph?
- Q. Can a particle with zero acceleration speed up?
- Q. Can a body have 0 speed but non zero velocity?
- Q. Is it possible that the speed of a particle is zero but acceleration is non zero?
- Q. Can you have 0 velocity?
Q. How many types of graphs are there in motion?
three
Q. What does acceleration look like on a distance time graph?
If the speed of an object changes, it will be accelerating or decelerating . This can be shown as a curved line on a distance-time graph. If an object is accelerating or decelerating, its speed can be calculated at any particular time by: drawing a tangent to the curve at that time.
Q. Can a particle with zero acceleration speed up?
Yes particles with zero acceleration can speed up by the chande of direction in particles.
Q. Can a body have 0 speed but non zero velocity?
Answer: (a) True. When a body begins to fall freely under gravity, its speed is zero but it has non-zero acceleration of . Speed is the magnitude of velocity and the magnitude of non-zero velocity cannot be zero.
Q. Is it possible that the speed of a particle is zero but acceleration is non zero?
A body may have zero velocity but non-zero acceleration. For example, when a body is thrown vertically upwards at the maximum height the body momentarily comes to rest.
Q. Can you have 0 velocity?
While this might result in a frenzy of activity, it would result in a zero velocity. Because the person always returns to the original position, the motion would never result in a change in position. Since velocity is defined as the rate at which the position changes, this motion results in zero velocity.