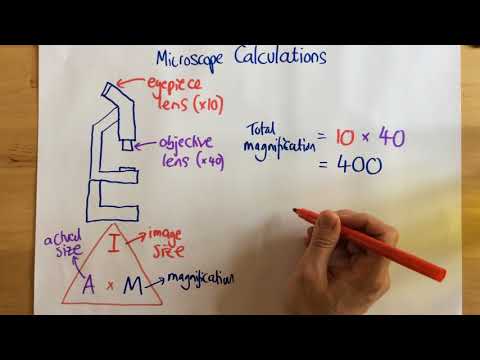
Magnification: the process of enlarging the size of an object, as an optical image. Total magnification: In a compound microscope the total magnification is the product of the objective and ocular lenses (see figure below). The magnification of the ocular lenses on your scope is 10X.
Q. How do you calculate magnification on a light microscope?
To calculate the total magnification of the compound light microscope multiply the magnification power of the ocular lens by the power of the objective lens. For instance, a 10x ocular and a 40x objective would have a 400x total magnification. The highest total magnification for a compound light microscope is 1000x.
Table of Contents
- Q. How do you calculate magnification on a light microscope?
- Q. What is the magnification of the eyepiece?
- Q. What is the total magnification at 40x?
- Q. What is the total magnification of 10X and 10X?
- Q. What is the 40X objective lens called?
- Q. What are four objective lenses?
- Q. What are objective lenses used for?
- Q. What are the different types of objectives?
- Q. What are the three objectives called?
- Q. What structure should never be used with high power?
- Q. Which lens should never be used with the coarse focus?
Q. What is the magnification of the eyepiece?
The standard eyepiece magnifies 10x. Check the objective lens of the microscope to determine the magnification, which is usually printed on the casing of the objective.
Q. What is the total magnification at 40x?
4x is a common magnification for scanning objectives and, when combined with the magnification power of a 10x eyepiece lens, a 4x scanning objective lens gives a total magnification of 40x.
Q. What is the total magnification of 10X and 10X?
100X
Q. What is the 40X objective lens called?
The 40X lens is known as the high power objective.
Q. What are four objective lenses?
Your microscope has 4 objective lenses: Scanning (4x), Low (10x), High (40x), and Oil Immersion (100x).
Q. What are objective lenses used for?
In microscopy, the objective lenses are the optical elements closest to the specimen. The objective lens gathers light from the specimen, which is focused to produce the real image that is seen on the ocular lens. Objective lenses are the most complex part of the microscope due to their multi-element design.
Q. What are the different types of objectives?
Objectives are the specific measurable results of the initiative….There are three basic types of objectives.
- Process objectives. These are the objectives that provide the groundwork or implementation necessary to achieve your other objectives.
- Behavioral objectives.
- Community-level outcome objectives.
Q. What are the three objectives called?
The shortest of the three objectives is the scanning-power objective lens (N), and has a power of 4X. Leave the 4X objective white. The second objective is the low-power objective (F), which is almost always made to produce a magnification of 10 times (10X).
Q. What structure should never be used with high power?
Microscope Short Answer Review
| A | B |
|---|---|
| Which two structures on the microscope will you use to focus on your specimen? | Coarse Adjustment Knob & Fine Adjustment Knob |
| Why should you never use the coarse adjustment knob on high power? | It will crack the slide. |
Q. Which lens should never be used with the coarse focus?
Coarse and fine adjustment The coarse adjustment knob should only be used with the lowest power objective lens. Once it is in focus, you will only need to use the fine focus. Using the coarse focus with higher lenses may result in crashing the lens into the slide. 6.