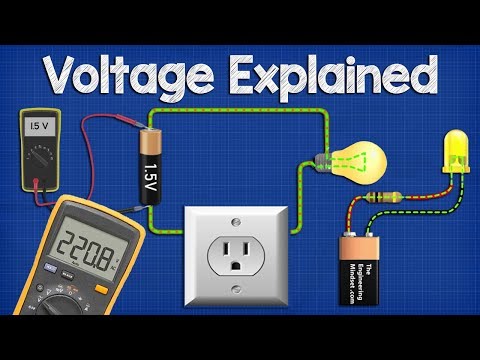
Voltage, ( V ) is the potential energy of an electrical supply stored in the form of an electrical charge. Voltage can be thought of as the force that pushes electrons through a conductor and the greater the voltage the greater is its ability to “push” the electrons through a given circuit.
Q. Do electrons actually travel from positive to negative?
The direction of an electric current is by convention the direction in which a positive charge would move. Thus, the current in the external circuit is directed away from the positive terminal and toward the negative terminal of the battery. Electrons would actually move through the wires in the opposite direction.
Table of Contents
- Q. Do electrons actually travel from positive to negative?
- Q. What actually causes the electrons to move?
- Q. Do electrons move the speed of light?
- Q. How do electrons carry energy?
- Q. Do electrons hold energy?
- Q. Why do electrons provide energy?
- Q. Is an electron a form of energy?
- Q. What occurs when an electron moves from high energy to a low one?
- Q. What happens when electrons return to their ground state?
- Q. Why do electrons go back to ground state?
- Q. Why can there only be two electrons in an orbital?
- Q. Which electron configuration principle rule matches the hog Hilton rule that hogs are lazy?
- Q. How many orbitals are in the p sublevel how many electrons will fill the p sublevel?
Q. What actually causes the electrons to move?
The “electrical pressure” due to the difference in voltage between the positive and negative terminals of a battery causes the charge (electrons) to move from the positive terminal to the negative terminal. Any path through which charges can move is called an electric circuit.
Q. Do electrons move the speed of light?
No, electrons have mass and nothing with mass can travel at the speed of light. If a particle starts out massless then yes, it would slow down if it gained mass from the Higgs field, but electrons are never massless and so never travel at the speed of light.
Q. How do electrons carry energy?
Electrical energy is caused by moving particles that have a negative or positive charge. These particles are called electrons. Current electricity is electrical energy that flows from one place to another, usually through a wire. Electricity is a type of energy that comes from electrical energy.
Q. Do electrons hold energy?
If a load is connected between negative and positive terminal, electrons will start to flow through it and heat it in the process – do work. Energy is stored in the system, not water or electrons themselves.
Q. Why do electrons provide energy?
Electrons in atoms can act as our charge carrier, because every electron carries a negative charge. If we can free an electron from an atom and force it to move, we can create electricity.
Q. Is an electron a form of energy?
Energy created through the movement of electrons among the atoms of matter. Although electricity is seldom used directly, it is one of the most useful and versatile forms of energy.
Q. What occurs when an electron moves from high energy to a low one?
Answer: The electrons in an atom exist in various energy levels. When an electron moves from a lower energy level to a higher energy level, energy is absorbed by the atom. When an electron moves from a higher to a lower energy level, energy is released (often as light).
Q. What happens when electrons return to their ground state?
An electron in an excited state can release energy and ‘fall’ to a lower state. When it does, the electron releases a photon of electromagnetic energy. When the electron returns to the ground state, it can no longer release energy but can absorb quanta of energy and move up to excitation states (higher orbitals).
Q. Why do electrons go back to ground state?
When an atom is in an excited state, the electron can drop all the way to the ground state in one go, or stop on the way in an intermediate level. Electrons do not stay in excited states for very long – they soon return to their ground states, emitting a photon with the same energy as the one that was absorbed.
Q. Why can there only be two electrons in an orbital?
The Pauli Exclusion Principle states that, in an atom or molecule, no two electrons can have the same four electronic quantum numbers. As an orbital can contain a maximum of only two electrons, the two electrons must have opposing spins. This is due to Pauli’s exclusion principle.
Q. Which electron configuration principle rule matches the hog Hilton rule that hogs are lazy?
Aufbau principle
Q. How many orbitals are in the p sublevel how many electrons will fill the p sublevel?
3 orbitals