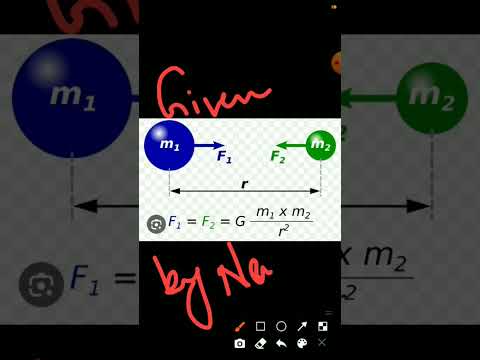
Q. What effect would increasing the mass of two objects have on the gravitational attraction?
Since the gravitational force is directly proportional to the mass of both interacting objects, more massive objects will attract each other with a greater gravitational force. So as the mass of either object increases, the force of gravitational attraction between them also increases.
Q. How does an increase in mass affect gravity?
The strength of the gravitational force between two objects depends on two factors, mass and distance. If one of the masses is doubled, the force of gravity between the objects is doubled. The Distance Between the Objects As distance between the objects. increases, the force of gravity decreases.
Table of Contents
- Q. What effect would increasing the mass of two objects have on the gravitational attraction?
- Q. How does an increase in mass affect gravity?
- Q. How does mass affect the strength of gravitational force?
- Q. How is gravity affected by mass and distance?
- Q. Does gravitational force increase with distance?
- Q. Does weight affect gravity?
- Q. Does gravitational force increase weight?
- Q. Is gravity dependent on mass?
- Q. Why is mass not dependent on gravity?
- Q. Why does mass not affect gravity?
- Q. Why does mass not affect speed?
- Q. Why does mass not affect range?
- Q. Does mass increase with speed?
- Q. How does mass depend on speed?
- Q. What is the difference between rest mass and relativistic mass?
- Q. Can anything travel faster than the speed of light?
- Q. Can neutrinos travel faster than light?
- Q. Is Higgs boson faster than light?
Q. How does mass affect the strength of gravitational force?
The strength of the gravitational force between two objects depends on two factors, mass and distance. the force of gravity the masses exert on each other. If one of the masses is doubled, the force of gravity between the objects is doubled. increases, the force of gravity decreases.
Q. How is gravity affected by mass and distance?
Objects with more mass have more gravity. Gravity also gets weaker with distance. So, the closer objects are to each other, the stronger their gravitational pull is. Earth’s gravity comes from all its mass.
Q. Does gravitational force increase with distance?
The force of gravity depends directly upon the masses of the two objects, and inversely on the square of the distance between them. This means that the force of gravity increases with mass, but decreases with increasing distance between objects.
Q. Does weight affect gravity?
Heavier things have a greater gravitational force AND heavier things have a lower acceleration. It turns out that these two effects exactly cancel to make falling objects have the same acceleration regardless of mass.
Q. Does gravitational force increase weight?
In a stronger gravitational field a given mass will have a larger weight. If an object is nearer a centre of mass then r will be smaller so g will be larger. In that case the weight of the object will be larger.
Q. Is gravity dependent on mass?
Basically, gravity is dependent on mass, where all things – from stars, planets, and galaxies to light and sub-atomic particles – are attracted to one another. Depending on the size, mass and density of the object, the gravitational force it exerts varies.
Q. Why is mass not dependent on gravity?
Mass is the amount of matter in an object. It can also be defined as the property of a body that causes it to have weight in a gravitational field. It is important to understand that the mass of an object is not dependent on gravity. Bodies with greater mass are accelerated less by the same force.
Q. Why does mass not affect gravity?
“What are the factors that affect the acceleration due to gravity?” Mass does not affect the acceleration due to gravity in any measurable way. The two quantities are independent of one another. Light objects accelerate more slowly than heavy objects only when forces other than gravity are also at work.
Q. Why does mass not affect speed?
Mass doesn’t affect speed directly. It determines how quickly an object can change speed (accelerate) under the action of a given force. Lighter objects need less time to change speed by a given amount under a given force.
Q. Why does mass not affect range?
When writing equations of motion for a dropped object, mass is in the equations in 2 places and they cancel out. That is basically the reason that mass does not affect the results of analysis of a projectile. (In answering your question, you are obviously meant to ignore air resistance.
Q. Does mass increase with speed?
The mass of an object does not change with speed; it changes only if we cut off or add a piece to the object. Since mass doesn’t change, when the kinetic energy of an object changes, its speed must be changing. Special Relativity (one of Einstein’s 1905 theories) deals with faster-moving objects.
Q. How does mass depend on speed?
As an object increases in speed, so does the amount of energy that it has, this energy is what we refer to as ‘the increase in mass’ (just remember, this is inertial mass). Since an object has infinite kinetic energy when it approaches the speed of light, it therefore has infinite mass as well.
Q. What is the difference between rest mass and relativistic mass?
Rest Mass: The mass of the body when not in motion with respect to inertial frame(non accelerating). Relativistic Mass: The mass of the body when in motion with respect to inertial frame. The concept of relativistic mass is used when the speed of the body is very high or comparable to speed of light.
Q. Can anything travel faster than the speed of light?
Albert Einstein’s special theory of relativity famously dictates that no known object can travel faster than the speed of light in vacuum, which is 299,792 km/s. Unlike objects within space–time, space–time itself can bend, expand or warp at any speed.
Q. Can neutrinos travel faster than light?
Scientists working at the facility have discovered that subatomic neutrino particles may have traveled through the 17-mile (27 kilometers) long particle collider at faster than the speed of light. nothing can travel faster than the speed of light.
Q. Is Higgs boson faster than light?
This little equation predicts that nothing with mass can move as fast as light, or faster. These colossal machines accelerate subatomic particles to more than 99.99% the speed of light, but as Physics Nobel laureate David Gross explains, these particles will never reach the cosmic speed limit.