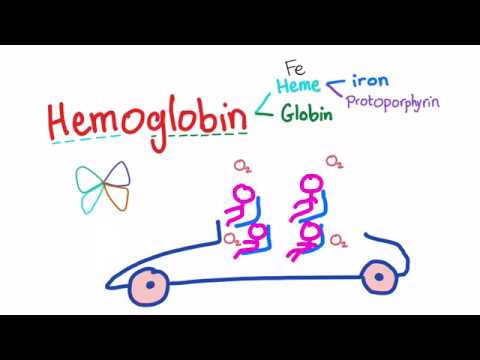
Q. What element is needed for hemoglobin?
The human body needs iron to make the oxygen-carrying proteins hemoglobin and myoglobin. Hemoglobin is found in red blood cells.
Q. What are the trace elements most important for making bones hard?
Calcium is the most important mineral for bone health.
Table of Contents
- Q. What element is needed for hemoglobin?
- Q. What are the trace elements most important for making bones hard?
- Q. What is the trace element for making bones hard?
- Q. Which essential elements make up the bulk of living matter?
- Q. What are the 25 elements essential to life?
- Q. What is the difference between essential elements and trace elements?
- Q. What are the 14 trace elements?
- Q. What are the essential elements to life?
- Q. What is the importance of trace elements?
- Q. What are the side effects of trace minerals?
- Q. What are the functions of trace elements in the body?
- Q. Are trace elements required for human life?
- Q. What is the most common element in your body?
- Q. What are the 6 major minerals?
- Q. What are the major elements?
- Q. What are the two essential elements that effect life?
- Q. What are three major elements?
- Q. What are the six elements of life?
- Q. What is the rarest natural element on earth?
- Q. What is the most abundant element in the universe?
- Q. What are the 10 most common elements on earth?
- Q. What is the rarest element in the universe?
- Q. What is the most common metal on earth?
- Q. What are the 5 most common elements on earth?
- Q. What element makes up 80 percent of the air?
- Q. Which is the most abundant metallic element in the human body?
- Q. Does the human body need gold?
- Q. Which is the least metal in human body?
- Q. Which metal is highly in human body?
Q. What is the trace element for making bones hard?
Phosphorus, along with calcium, is essential for calcification of bones (85% of body phosphorus is located in the skeleton).
Q. Which essential elements make up the bulk of living matter?
Living organisms contain relatively large amounts of oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and sulfur (these five elements are known as the bulk elements), along with sodium, magnesium, potassium, calcium, chlorine, and phosphorus (these six elements are known as macrominerals).
Q. What are the 25 elements essential to life?
25 Essential Elements for Life
- The Big 4.
- Carbon, oxygen, Hydrogen, and Nitrogen.
- 96%
- The Major elements.
- CAlcium, Phosphorous, Potassium, sulfur, Sodium, Chlorine and Magnesium.
- 3.5%
- Trace Elements.
- Boron, chromium, cobalt, copper, fluorine, iodine, iron, manganese, molybdenum, selenium, silicon, tin, & vanadium.
Q. What is the difference between essential elements and trace elements?
What is the difference between an essential element and a trace element? essential element: Essential elements are elements that an organism needs to live a healthy life and reproduce. trace element: Trace elements are required by an organism in only minute quantities.
Q. What are the 14 trace elements?
The concentrations of 14 serum trace elements, namely iron (Fe), copper (Cu), zinc (Zn), rubidium (Rb), selenium (Se), strontium (Sr), molybdenum (Mo), manganese (Mn), lead (Pb), arsenic (As), chromium (Cr), cobalt (Co), vanadium (V), and cadmium (Cd), were determined by high-resolution inductively coupled plasma mass …
Q. What are the essential elements to life?
The four basic elements of life are: Oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen and phosphorus. These four elements are found in abundance in both the human body and in animals.
Q. What is the importance of trace elements?
Trace elements are very important for cell functions at biological, chemical and molecular levels. These elements mediate vital biochemical reactions by acting as cofactors for many enzymes, as well as act as centers for stabilizing structures of enzymes and proteins.
Q. What are the side effects of trace minerals?
Minerals (especially taken in large doses) can cause side effects such as tooth staining, increased urination, stomach bleeding, uneven heart rate, confusion, and muscle weakness or limp feeling….Common side effects may include:
- upset stomach;
- headache; or.
- unusual or unpleasant taste in your mouth.
Q. What are the functions of trace elements in the body?
Trace elements function primarily as catalysts in enzyme systems; some metallic ions, such as iron and copper, participate in oxidation-reduction reactions in energy metabolism. Iron, as a constituent of hemoglobin and myoglobin, also plays a vital role in the transport of oxygen.
Q. Are trace elements required for human life?
Deficiencies or excess states of semi-major elements often result in water and electrolyte abnormalities. Essential trace elements of the human body include zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), selenium (Se), chromium (Cr), cobalt (Co), iodine (I), manga- nese (Mn), and molybdenum (Mo).
Q. What is the most common element in your body?
The function of the essential elements in the human body, by order of percentage of mass, are as follows:
- Oxygen. Oxygen is the most common element in the human body, comprising approximately 65.0% of body mass.
- Carbon.
- Hydrogen.
- Nitrogen.
- Calcium.
- Phosphorus.
- Potassium.
- Sulfur.
Q. What are the 6 major minerals?
The major minerals, which are used and stored in large quantities in the body, are calcium, chloride, magnesium, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, and sulfur. The trace minerals are just as vital to our health as the major minerals, but we don’t need large amounts.
Q. What are the major elements?
Geological major elements are defined as those elements that compose 95% of the earth’s crust. They are Si, Al, Ca, Mg, Na, K, Ti, Fe, Mn and P.
Q. What are the two essential elements that effect life?
The two essential elements that affect life are carbon and oxygen. Most of the carbon is found in the form of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Q. What are three major elements?
Three Elements
- We all know oxygen, silicon, and aluminum are common elements in the Earth’s crust.
- The combined occurrences for these three elements are very well known.
- For all three together, we find the mineral kyanite.
Q. What are the six elements of life?
The six most common elements of life on Earth (including more than 97% of the mass of a human body) are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, sulphur and phosphorus.
Q. What is the rarest natural element on earth?
element astatine
Q. What is the most abundant element in the universe?
Hydrogen
Q. What are the 10 most common elements on earth?
Glossary
| Element | Abundance percent by weight | Abundance parts per million by weight |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen | 46.1% | 461,000 |
| Silicon | 28.2% | 282,000 |
| Aluminum | 8.23% | 82,300 |
| Iron | 5.63% | 56,300 |
Q. What is the rarest element in the universe?
Astatine is the rarest naturally occurring element.
Q. What is the most common metal on earth?
steel
Q. What are the 5 most common elements on earth?
The mass-abundance of the nine most abundant elements in the Earth’s crust is approximately: oxygen 46%, silicon 28%, aluminum 8.3%, iron 5.6%, calcium 4.2%, sodium 2.5%, magnesium 2.4%, potassium 2.0%, and titanium 0.61%.
Q. What element makes up 80 percent of the air?
Nitrogen comprises the greatest part of the atmosphere, at almost 80 percent by volume. Nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless gas that reacts very little with other substances. The atmosphere also contains oxygen, at about 20 percent.
Q. Which is the most abundant metallic element in the human body?
calcium
Q. Does the human body need gold?
The actual point of human body containing Gold has recently been determined. It plays a vital role in health and maintenance of the joints. Also, being a good conductor of electricity, it actually helps in transmitting electrical signals throughout the body.
Q. Which is the least metal in human body?
All of the mass of the trace elements put together (less than 10 grams for a human body) do not add up to the body mass of magnesium, the least common of the 11 non-trace elements.
Q. Which metal is highly in human body?
Among the metals that are currently known to be essential for normal biological functions in humans are sodium (Na), potassium (K), magnesium (Mg), and calcium (Ca) that belong to main group of elements, and vanadium (V), chromium (Cr), manganese (Mn), iron (Fe), cobalt (Co), nickel (Ni), copper (Cu), zinc (Zn).