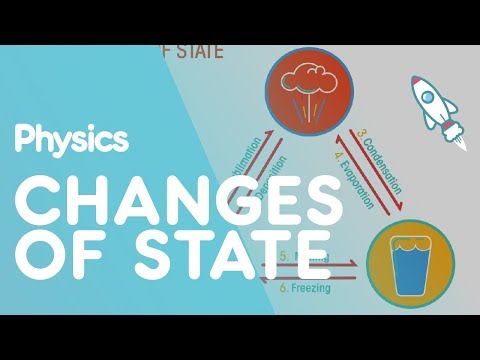
Changes of state are physical changes. They occur when matter absorbs or loses energy. Processes in which matter changes between liquid and solid states are freezing and melting. Processes in which matter changes between liquid and gaseous states are vaporization, evaporation, and condensation.
Q. Does potential energy decrease in a cooling curve?
All of the diagonal line segments on a heating or cooling curve show a temperature change and therefore a change in kinetic energy. However, all the energy that is absorbed or released is related to changes in potential energy. Remember the 3 Ps: Plateau, Phase change and Potential Energy Change.
Table of Contents
- Q. Does potential energy decrease in a cooling curve?
- Q. Why does temperature remain constant during change of state?
- Q. Which one following is the state function?
- Q. Which properties are state functions?
- Q. Which one is not state function?
- Q. Which of the following is a state function of thermodynamics process?
- Q. What is the difference between state and path function?
- Q. Is temperature is a state function?
- Q. Why temperature is not a state function?
- Q. Why internal energy is a state function but work is not?
- Q. Why is internal energy is a state function?
- Q. What is meant by internal energy is a function of state?
- Q. What is the relationship between temperature and phase changes?
- Q. Why does temperature not change during change of state?
- Q. Why doesn’t the temperature change when a state changes?
- Q. Which of the following is not a change of state?
- Q. What affects the change of state the most?
- Q. What is the effect of temperature on change of state of matter?
- Q. Can matter changes its state?
- Q. What makes matter change from one state to another?
- Q. Can Matter change its state without heating or cooling?
- Q. How does matter change when heated or cooled?
- Q. When you add heat to a solid it will?
- Q. What is meant by change of state of matter?
- Q. Is a change of state a chemical or physical change?
- Q. What happens if atoms lose energy during a change of state?
- Q. What is meant by change of state how can you change the physical state of a substance?
- Q. What are two changes of state that release energy?
- Q. Which changes of state require an increase in energy?
- Q. At which two temperatures does water experience a change of state?
- Q. What happens to energy and mass in a change of state?
- Q. Does a change of state conserve mass?
Q. Why does temperature remain constant during change of state?
The temperature remains constant during the change of state because the heat energy which is supplied to change the state of matter is used in breaking the intermolecular forces and other attractive forces. Hence the temperature remains constant as all the heat is used up and no external heat is released or absorbed.
Q. Which one following is the state function?
Answer: (1) List of state functions is pressure, temperature, volume, mass, internal energy, Gibb’s free energy, entropy.
Q. Which properties are state functions?
A state function is a property whose value does not depend on the path taken to reach a specific value. For the sake of this class, pressure, density, temperature, volume, enthalpy, internal energy, Gibb’s free energy, and entropy are state functions.
Q. Which one is not state function?
Heat and work are not state functions. Work can’t be a state function because it is proportional to the distance an object is moved, which depends on the path used to go from the initial to the final state.
Q. Which of the following is a state function of thermodynamics process?
This means internal energy is a state function (as it is independent of the path). Enthalpy is the sum of internal energy and product of pressure and volume of the thermodynamic system. This means enthalpy is a state function. Entropy is defined as thermal energy per unit temperature that is available for doing work.
Q. What is the difference between state and path function?
A state function is a property describes a particular state, without depending on the path taken to reach this state. In contrast, functions whose value depends on the path taken to get between two states are called path functions.
Q. Is temperature is a state function?
Temperature is a state function as it is one of the values used to define the state of an object. Furthermore, temperature is dependent on the final and initial values, not on the path taken to establish the values. As a result, volume is a state function because it is not dependent on the object’s path or history.
Q. Why temperature is not a state function?
Temperature is a state function. Heat and work are not state functions. Work can’t be a state function because it is proportional to the distance an object is moved, which depends on the path used to go from the initial to the final state. If work isn’t a state function, then heat can’t be a state function either.
Q. Why internal energy is a state function but work is not?
The change in internal energy during a process depends only upon the initial state and final state while work depends on upon the path followed. Thus, internal energy is a state function and work is not.
Q. Why is internal energy is a state function?
The Internal Energy, U, of a system is an extensive thermodynamic property that measures the energy stored in a system as a result of its microscopic structure. Both of these energy transfer processes are path dependent, however, the internal energy is a function only of the state of the system.
Q. What is meant by internal energy is a function of state?
Internal energy, in thermodynamics, the property or state function that defines the energy of a substance in the absence of effects due to capillarity and external electric, magnetic, and other fields.
Q. What is the relationship between temperature and phase changes?
Substances can change phase—often because of a temperature change. At low temperatures, most substances are solid; as the temperature increases, they become liquid; at higher temperatures still, they become gaseous. The process of a solid becoming a liquid is called melting.
Q. Why does temperature not change during change of state?
During a phase change, the temperature of the system does not change, because the added heat is melting the solid at its melting point or evaporating the liquid at its boiling point.
Q. Why doesn’t the temperature change when a state changes?
Evaporation is increased by higher temperatures, a greater surface area or a draft over this surface area. A substance must absorb heat energy so that it can melt or boil. The temperature of the substance does not change during melting, boiling or freezing – even though energy is still being transferred.
Q. Which of the following is not a change of state?
Changes of state are physical changes in matter. They are reversible changes that do not involve changes in matter’s chemical makeup or chemical properties. Common changes of state include melting, freezing, sublimation, deposition, condensation, and vaporization. These changes are shown in Figure below.
Q. What affects the change of state the most?
Physical conditions like temperature and pressure affect state of matter. When thermal energy is added to a substance, its temperature increases, which can change its state from solid to liquid (melting), liquid to gas (vaporization), or solid to gas (sublimation).
Q. What is the effect of temperature on change of state of matter?
As temperatures increase, additional heat energy is applied to the constituent parts of a solid, which causes additional molecular motion. Molecules begin to push against one another and the overall volume of a substance increases. At this point, the matter has entered the liquid state.
Q. Can matter changes its state?
Matter changes state when energy is added or taken away. Most matter changes because of heat energy. When matter is heated enough, the molecules move faster and with greater energy. If enough heat is added, a solid can become liquid and a liquid can become gas.
Q. What makes matter change from one state to another?
Adding or removing energy from matter causes a physical change as matter moves from one state to another. For example, adding thermal energy (heat) to liquid water causes it to become steam or vapor (a gas). Physical changes can also be caused by motion and pressure.
Q. Can Matter change its state without heating or cooling?
All matter exists as solids, liquids, or gases. Matter can change from one state to another if heated or cooled. If ice (a solid) is heated it changes to water (a liquid). This change is called MELTING.
Q. How does matter change when heated or cooled?
When a substance is heated, it gains thermal energy. Therefore, its particles move faster and its temperature rises. When a substance is cooled, it loses thermal energy, which causes its particles to move more slowly and its temperature to drop.
Q. When you add heat to a solid it will?
When a solid is heated, the particles gain sufficient energy to break away from one another and move past each other. The change from solid to liquid is called melting or fusion.
Q. What is meant by change of state of matter?
A change of state is a physical change in a matter. They are reversible changes and do not involve any changes in the chemical makeup of the matter. Common changes of the state include melting, freezing, sublimation, deposition, condensation, and vaporization.
Q. Is a change of state a chemical or physical change?
Change in state of matter is a physical change because of the physical condition and appearance changes but not the chemical composition.
Q. What happens if atoms lose energy during a change of state?
Explanation: Atoms lose energy as a gas changes to a solid. Atoms gain energy as a solid changes to a liquid. If atoms energy during a change of state, they are pulled together by attractive forces and become more organized.
Q. What is meant by change of state how can you change the physical state of a substance?
change of state is defined as the physical process where matter moves from one state to another. Evaporation changes the form of water from liquid state to gaseous state. Usually in order to change the state of liquids into a solid state, one reduces the temperature.
Q. What are two changes of state that release energy?
The changes of state include melting, sublimation, evaporation, freezing, condensation, and deposition. All changes of state involve the transfer of energy. The water particles in each state behave as energy is absorbed or released. .
Q. Which changes of state require an increase in energy?
Thus any transition from a more ordered to a less ordered state (solid to liquid, liquid to gas, or solid to gas) requires an input of energy; it is endothermic. Conversely, any transition from a less ordered to a more ordered state (liquid to solid, gas to liquid, or gas to solid) releases energy; it is exothermic.
Q. At which two temperatures does water experience a change of state?
When a solid reaches the temperature of its melting point, it can become a liquid. For water, the temperature needs to be a little over zero degrees Celsius (0oC) for you to melt. If you were salt, sugar, or rock, your melting point is higher than that of water.
Q. What happens to energy and mass in a change of state?
State the law of conservation of mass and the law of conservation of energy and explain how they apply to changes of state. Mass cannot be created or destroyed. Energy cannot be created or destroyed. During a change of state, The total mass and the total energy of the system remain constant.
Q. Does a change of state conserve mass?
Conservation of mass The number of particles does not change during a change of state, only their spacing and arrangement. As a result, the total mass has not changed. It does not matter if a substance melts, freezes, boils, evaporates, condenses or sublimates – the mass does not change.