Besides the lachrymatory sensation, and clearing of the sinuses, there are no known side-effects attributed to wasabi consumption although some individuals may experience an allergic reaction.
Q. Are there any health benefits to wasabi?
The compounds in wasabi have been analyzed for their antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer properties in test-tube and animal studies. They have also been researched for their ability to promote fat loss, as well as bone and brain health.
Table of Contents
- Q. Are there any health benefits to wasabi?
- Q. What does wasabi do to your brain?
- Q. Is wasabi good for the heart?
- Q. Does wasabi burn when you poop?
- Q. Has anyone died from eating wasabi?
- Q. Who eats wasabi?
- Q. Why does wasabi hurt?
- Q. What is wasabi made of?
- Q. Is real wasabi rare?
- Q. What color is real wasabi?
- Q. Do Japanese restaurants use real wasabi?
- Q. Is wasabi hotter than horseradish?
- Q. Why wasabi is so expensive?
- Q. Why is wasabi so rare?
- Q. What is wasabi worth?
- Q. Can you get real wasabi in the US?
- Q. Why is wasabi fake in America?
- Q. What is wasabi normally?
Q. What does wasabi do to your brain?
When an irritating substance—such as wasabi, onion, mustard oil, tear gas, cigarette smoke, or automobile exhaust—comes into contact with the receptor, it prods the cell into sending a distress signal to the brain, which responds by causing the body to variously sting, burn, itch, cough, choke, or drip tears.
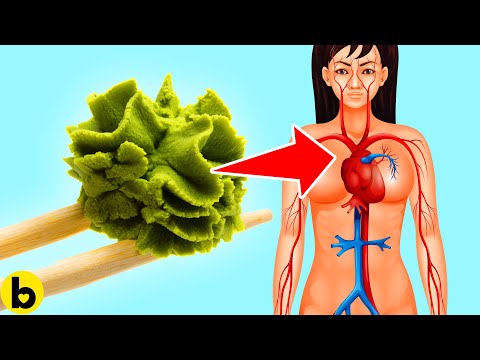
Q. Is wasabi good for the heart?
Potential Health Benefits of Wasabi Wasabi contains a small amount of iron. Getting enough iron in your diet lowers your risk of developing anemia, a condition that causes symptoms like fatigue, heart palpitations, and other issues related to blood iron levels.
Q. Does wasabi burn when you poop?
“There is a spiciness followed by sweetness.” While the tastes aren’t exactly identical, both wasabi and this horseradish imposter will burn the shit out of your nasal passage if you put too big of a glob on your sushi.
Q. Has anyone died from eating wasabi?
The shock led to ‘broken heart syndrome. ‘ A 60-year-old Israeli woman went to an emergency room complaining of chest pain. Doctors found she was suffering from a wasabi-induced “broken heart syndrome” — a condition sometimes seen in people who have recently lost a loved one.
Q. Who eats wasabi?
According to historical records, Japanese people have been adding wasabi to a variety of dishes for over a thousand years, and today it can be found in most restaurants.
Q. Why does wasabi hurt?
The reason wasabi burns is because it contains large quantities of allyl isothiocyanate. Allyl isothiocyanate is a volatile, colorless to pale yellow oil that causes the burning sensation one experiences after consuming wasabi, horseradish, and mustard.
Q. What is wasabi made of?
True wasabi is made from the rhizome (like a plant stem that grows underground where you would expect to see a root) of the Wasabia japonica plant. Its signature clean spiciness comes from allyl isothiocyanate instead of pepper’s capsaicin.
Q. Is real wasabi rare?
True wasabi (Wasabia japonica), a semiaquatic herb native to Japanese mountain streams, is rare and pricey, and doesn’t keep nearly as well as horseradish, which explains why it has been abandoned by all but the most ferociously authentic sushi chefs.
Q. What color is real wasabi?
green
Q. Do Japanese restaurants use real wasabi?
Yes, it’s true. Over 95% of wasabi served in sushi restaurants does not contain any real wasabi. Most fake wasabi is made from a blend of horseradish, mustard flour, cornstarch and green food colorant. This means that most people who think they know wasabi have actually never tasted the stuff!
Q. Is wasabi hotter than horseradish?
Differences between horseradish and wasabi Firstly, real wasabi isn’t as hot as horseradish. Its flavour is fresher, sweeter and more fragrant. Its colour is generally a more natural green, which makes sense as it’s not added artificially. Moreover, the shade of green varies greatly depending on the specific cultivar.
Q. Why wasabi is so expensive?
Because of its price, the “wasabi” you’re used to is probably just a mixture of horseradish, coloring, and sweetener. These products often only have 1-5% of the real thing in. Fresh wasabi is rare to come across and costs around $250 per kilo.
Q. Why is wasabi so rare?
Wasabi plants require very specific conditions to grow and thrive: constant running spring water, shade, rocky soil, and temperatures between 46 to 68 degrees Fahrenheit year-round. Wasabi is hard to grow, which makes it rare, which makes it expensive, which means you eat green horseradish and don’t know until now.
Q. What is wasabi worth?
The price. Fetching nearly $160 (£98) per kilogram at wholesale, in addition to being hard to nurture, wasabi is also one of the most lucrative plants on the planet. “It is much like gold – we expect to pay a lot for gold.
Q. Can you get real wasabi in the US?
Outside of Japan, real wasabi is difficult to find. The green paste that is usually served along with sushi in the U.S. is actually a mix of horseradish, mustard powder and food coloring. However, Frog Eyes Wasabi in Oregon is one of the only North American wasabi operations, and the only one in the state of Oregon.
Q. Why is wasabi fake in America?
In fact, about 99% of all wasabi sold in the US is fake, The Washington Post reports. Even in Japan where most wasabi is grown, you won’t have much better luck. Horseradish has a similar chemical makeup to wasabi, allowing it to mimic its spicy zing.
Q. What is wasabi normally?
It’s usually horseradish, tinted green. Horseradish and wasabi, a.k.a Japanese horseradish, are in the same Brassica family of plants that also includes mustard, cabbage, broccoli, and Brussels sprouts.