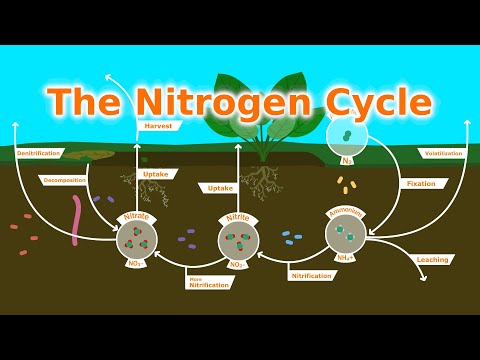
When organisms die, their bodies decompose bringing the nitrogen into soil on land or into the oceans. As dead plants and animals decompose, nitrogen is converted into inorganic forms such as ammonium salts (NH4+ ) by a process called mineralization.
Q. What are 2 ways nitrogen becomes usable to plants humans and animals?
Plant and animal wastes decompose, adding nitrogen to the soil. Bacteria in the soil convert those forms of nitrogen into forms plants can use. Plants use the nitrogen in the soil to grow. People and animals eat the plants; then animal and plant residues return nitrogen to the soil again, completing the cycle.
Table of Contents
- Q. What are 2 ways nitrogen becomes usable to plants humans and animals?
- Q. What are 2 ways nitrogen becomes useable to plants humans and animals quizlet?
- Q. What are two reservoirs for nitrogen?
- Q. What are the four ways of fixing nitrogen?
- Q. What are the two major ways nitrogen is fixed?
- Q. What are the different ways of fixing nitrogen?
- Q. What is nitrogen fixation with diagram?
- Q. How is nitrogen formed?
- Q. How can we increase nitrogen fixation naturally?
- Q. Do decomposers fix nitrogen?
- Q. What is the mechanism of nitrogen fixation?
- Q. Why nitrogen fixing bacteria are important?
- Q. What is nitrogen fixation and why is it important?
- Q. What is nitrogen fixation Class 9?
Q. What are 2 ways nitrogen becomes useable to plants humans and animals quizlet?
What are 2 ways nitrogen becomes useable to plants, humans and animals? When broken apart during lightning or fires. Bacteria or bacteria associated with bean plants. How do herbivores obtain the nitrogen they need?
Q. What are two reservoirs for nitrogen?
The atmosphere acts as vast storage reservoir for nitrogen because it is 78 percent nitrogen. Because of this, the atmosphere is the largest storage reservoir of nitrogen. Nitrogen is also stored in: watershed in soil, groundwater, ocean water, sediment and plant matter (dead and living).
Q. What are the four ways of fixing nitrogen?
Four processes participate in the cycling of nitrogen through the biosphere:
- nitrogen fixation.
- decay.
- nitrification.
- denitrification.
Q. What are the two major ways nitrogen is fixed?
Nitrogen fixation in nature Nitrogen is fixed, or combined, in nature as nitric oxide by lightning and ultraviolet rays, but more significant amounts of nitrogen are fixed as ammonia, nitrites, and nitrates by soil microorganisms. More than 90 percent of all nitrogen fixation is effected by them.
Q. What are the different ways of fixing nitrogen?
Plants acquire these forms of “combined” nitrogen by: 1) the addition of ammonia and/or nitrate fertilizer (from the Haber-Bosch process) or manure to soil, 2) the release of these compounds during organic matter decomposition, 3) the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen into the compounds by natural processes, such as …
Q. What is nitrogen fixation with diagram?
Biological nitrogen fixation (BNF) is the process whereby atmospheric nitrogen is reduced to ammonia in the presence of nitrogenize. Nitrogenize is a biological catalyst found naturally only in certain microorganisms such as the symbiotic Rhizobium and Frankia, or the free-living Azospirillum and Azotobacter and BGA.
Q. How is nitrogen formed?
Nitrogen can also be produced on a large scale by burning carbon or hydrocarbons in air and separating the resulting carbon dioxide and water from the residual nitrogen. On a small scale, pure nitrogen is made by heating barium azide, Ba(N3)2.
Q. How can we increase nitrogen fixation naturally?
Food and agriculture Among the common agricultural practices, fertilization with P and N have important effects in nitrogen fixation. In Kenya, fertilizing Phaseolus beans with 150 kg/ha of P increased seed yield by 62% and increased nitrogen fixation from an average of 8 kg/ha to 60 kg/ha.
Q. Do decomposers fix nitrogen?
Nitrogen is returned to the atmosphere by the activity of organisms known as decomposers. Some bacteria are decomposers and break down the complex nitrogen compounds in dead organisms and animal wastes. This returns simple nitrogen compounds to the soil where they can be used by plants to produce more nitrates.
Q. What is the mechanism of nitrogen fixation?
Biological nitrogen fixation (BNF) occurs when atmospheric nitrogen is converted to ammonia by an enzyme called nitrogenase. The reaction for BNF is: N2 + 8 H+ + 8 e− → 2 NH3 + H2. This type of reaction results in N2 gaining electrons (see above equation) and is thus termed a reduction reaction.
Q. Why nitrogen fixing bacteria are important?
Nitrogen-fixing bacteria, microorganisms capable of transforming atmospheric nitrogen into fixed nitrogen (inorganic compounds usable by plants). More than 90 percent of all nitrogen fixation is effected by these organisms, which thus play an important role in the nitrogen cycle.
Q. What is nitrogen fixation and why is it important?
Nitrogen fixation refers to the conversion of atmospheric nitrogen gas (N 2 ) into a form usable by plants and other organisms. Because it is the principal source of the nitrogen in the soil, nitrogen that plants need to grow, nitrogen fixation is one of the most important biochemical processes on Earth.
Q. What is nitrogen fixation Class 9?
Nitrogen Fixation. It is a process by which atmospheric nitrogen is converted into the form which can be easily absorbed the organisms on earth.