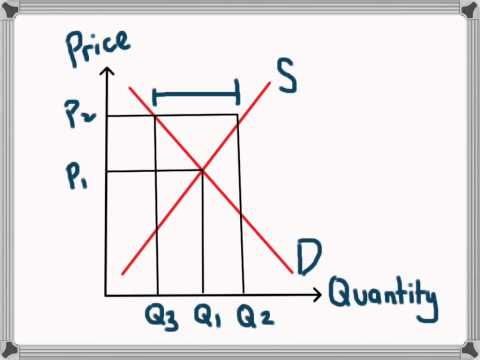
Q. What happens to price when there is excess supply?
Excess supply causes the price to fall and quantity demanded to increase. b. An dcrease in supply will cause an increase in the equilibrium price and a decrease in the equilibrium quantity of a good. 1.
Q. What happens if a price floor is set below equilibrium?
A price ceiling (which is below the equilibrium price) will cause the quantity demanded to rise and the quantity supplied to fall. This is why a price ceiling creates a shortage. In other words, a price floor below equilibrium will not be binding and will have no effect.
Table of Contents
- Q. What happens to price when there is excess supply?
- Q. What happens if a price floor is set below equilibrium?
- Q. What happens to total surplus with a price floor?
- Q. What is the result of a price floor?
- Q. What is meant by excess supply?
- Q. What causes excess supply?
- Q. Does price floor change equilibrium?
- Q. What happens to equilibrium supply and demand if a price floor is set below the equilibrium price?
- Q. Why do price floors reduce total surplus?
- Q. Why are price floors implemented by governments?
- Q. Why are there price floors?
- Q. Does a price floor increase producer surplus?
- Q. What happens when there is excess supply in the market?
- Q. How does a price floor affect supply and demand?
- Q. When is a price floor above the equilibrium price?
- Q. What happens when a price floor is set at PF?
Q. What happens to total surplus with a price floor?
Consumer surplus always decreases when a binding price floor is instituted in a market above the equilibrium price. The total economic surplus equals the sum of the consumer and producer surpluses. Price helps define consumer surplus, but overall surplus is maximized when the price is pareto optimal, or at equilibrium.
Q. What is the result of a price floor?
The result of the price floor is that the quantity supplied Qs exceeds the quantity demanded Qd. There is excess supply, also called a surplus.
Q. What is meant by excess supply?
In economics, an excess supply, economic surplus market surplus or briefly surply is a situation in which the quantity of a good or service supplied is more than the quantity demanded, and the price is above the equilibrium level determined by supply and demand.
Q. What causes excess supply?
Excess supply occurs when the quantity supplied is higher than the quantity demanded. In this situation, price is above the equilibrium price, and, therefore, there is downward pressure on the price. This term also refers to production surplus, overproduction, or oversupply.
Q. Does price floor change equilibrium?
Neither price ceilings nor price floors cause demand or supply to change. Remember, changes in price do not cause demand or supply to change. In other words, they do not change the equilibrium.
Q. What happens to equilibrium supply and demand if a price floor is set below the equilibrium price?
What happens to equilibrium supply and demand if a price floor is set below the equilibrium price? Nothing happens. Since the floor is below equilibrium, the market is still able to determine the quantity and price the same way it always does. 2.
Q. Why do price floors reduce total surplus?
If a price floor benefits producers, why does a price floor reduce social surplus? Because the losses to consumers are greater than the benefits to producers, so the net effect is negative. Since the lost consumer surplus is greater than the additional producer surplus, social surplus falls.
Q. Why are price floors implemented by governments?
Governments use price floors to keep certain prices from going too low. A related government- or group-imposed intervention, which is also a price control, is the price ceiling; it sets the maximum price that can legally be charged for a good or service, with a common government-imposed example being rent control.
Q. Why are there price floors?
Governments use price floors to keep certain prices from going too low. Two common price floors are minimum wage laws and supply management in Canadian agriculture. Other price floors include regulated US airfares prior to 1978 and minimum price per-drink laws for alcohol.
Q. Does a price floor increase producer surplus?
In effect, the price floor causes the area H to be transferred from consumer to producer surplus, but also causes a deadweight loss of J + K. Removing such barriers, so that prices and quantities can adjust to their equilibrium level, will increase the economy’s social surplus.
Q. What happens when there is excess supply in the market?
As a definition, excess supply occurs when the price is higher than the equilibrium price. Say, the price of the product is 6. The quantity demanded will be equal to 17 (20 – 0.5*6), while the quantity supplied is 22 (10 + 2*6). So, at that price, the market faces a surplus of 5 units. What happens when there is excess supply?
Q. How does a price floor affect supply and demand?
Likewise, since supply is proportional to price, a price floor creates excess supply if the legal price is above the market price. Suppliers are willing to supply more at the price floor than the market wants at that price.
Q. When is a price floor above the equilibrium price?
The result is a quantity supplied in excess of the quantity demanded (Qd). When quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded, a surplus exists. When a price floor is set above the equilibrium price, as in this example, it is considered a binding price floor. Figure 2. European Wheat Prices: A Price Floor Example.
Q. What happens when a price floor is set at PF?
The intersection of demand (D) and supply (S) would be at the equilibrium point E 0. However, a price floor set at Pf holds the price above E 0 and prevents it from falling. The result of the price floor is that the quantity supplied Qs exceeds the quantity demanded Qd. There is excess supply, also called a surplus.