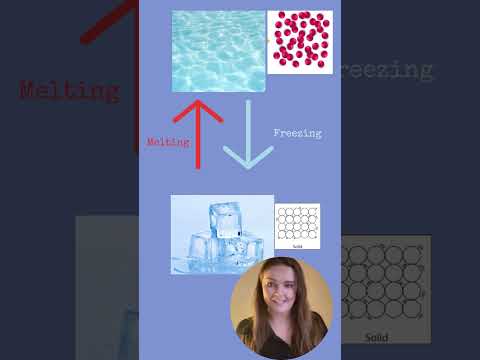
Q. What happens when a liquid freezes to become a solid?
Freezing occurs when a liquid is cooled and turns to a solid. Eventually the particles in a liquid stop moving about and settle into a stable arrangement, forming a solid.
Q. Can you solidify water?
Freezing is the process of a liquid turning solid, so by definition you can’t turn liquid water solid without freezing it. However, you can turn water solid at temperatures above 0 C by putting it under enough pressure.
Table of Contents
- Q. What happens when a liquid freezes to become a solid?
- Q. Can you solidify water?
- Q. What temperature does a liquid turn into a solid?
- Q. At what temperature will water change from a liquid to a solid freeze?
- Q. When a liquid turns into a solid what is it called?
- Q. What happens when a substance changes state?
- Q. What are the five changes of state?
- Q. What is an example of a change of state?
- Q. Which change of state turns a gas into a liquid?
- Q. What is the movement of particles in a gas?
- Q. What is the movement of particles in liquids?
- Q. Why the force of attraction between solid particles is stronger?
- Q. What are the strongest to weakest intermolecular forces?
- Q. Which state of matter has the weakest attractive force?
- Q. Has the strongest force of attraction between the particles?
- Q. Which matter has maximum force of attraction?
- Q. What is the force between particles called?
- Q. What causes the attractive forces between particles in matter?
- Q. What is required to cause changes in matter?
- Q. What are the forces of attraction?
- Q. Which attractive force is the weakest?
- Q. What are the 2 types of forces of attraction?
- Q. What is the force of attraction between matter?
- Q. What happens to the force of attraction?
Q. What temperature does a liquid turn into a solid?
Any substance can occur in any phase. Under standard atmospheric conditions, water exists as a liquid. But if we lower the temperature below 0 degrees Celsius, or 32 degrees Fahrenheit, water changes its phase into a solid called ice.
Q. At what temperature will water change from a liquid to a solid freeze?
32°F
Q. When a liquid turns into a solid what is it called?
FreezingFreezing or solidification is a phase transition in which a liquid turns into a solid when its temperature is lowered to its freezing point.
Q. What happens when a substance changes state?
The closeness, arrangement and motion of the particles in a substance change when it changes state. the movement of its particles increases. bonds between particles break when a substance melts or evaporates, or sublimes to form a gas from a solid.
Q. What are the five changes of state?
Evaporation, Condensation, Freezing, Melting, Sublimation and Deposition.
Q. What is an example of a change of state?
Changes of state are physical changes in matter. They are reversible changes that do not change matter’s chemical makeup or chemical properties. For example, when fog changes to water vapor, it is still water and can change back to liquid water again.
Q. Which change of state turns a gas into a liquid?
Condensation
Q. What is the movement of particles in a gas?
Gas – In a gas, particles are in continual straight-line motion. The kinetic energy of the molecule is greater than the attractive force between them, thus they are much farther apart and move freely of each other. In most cases, there are essentially no attractive forces between particles.
Q. What is the movement of particles in liquids?
In liquids, particles are quite close together and move with random motion throughout the container. Particles move rapidly in all directions but collide with each other more frequently than in gases due to shorter distances between particles.
Q. Why the force of attraction between solid particles is stronger?
Answer: Solid – In a solid, the attractive forces keep the particles together tightly enough so that the particles do not move past each other. The kinetic energy of the molecule is greater than the attractive force between them, thus they are much farther apart and move freely of each other.
Q. What are the strongest to weakest intermolecular forces?
In order from strongest to weakest, the intermolecular forces given in the answer choices are: ion-dipole, hydrogen bonding, dipole-dipole, and Van der Waals forces.
Q. Which state of matter has the weakest attractive force?
(2) The extent of random thermal motion of atoms and molecules of a substance (which depends upon temperature). The Intermolecular force is strongest in solids and weakest in gases.
Q. Has the strongest force of attraction between the particles?
The force of attraction between particles of a solid is maximum because they are closely packed. Where as between particles of a gas the force of attraction is minimum due to the random motion of the gaseous particles.
Q. Which matter has maximum force of attraction?
The force of attraction between the molecules of matter is called the intermolecular force of attraction. It is maximum in solids, less in liquid and least in gases.
Q. What is the force between particles called?
Intermolecular Forces. Intermolecular Forces. Two factors determine whether a substance is a solid, a liquid, or a gas: The kinetic energies of the particles (atoms, molecules, or ions) that make up a substance. Kinetic energy tends to keep the particles moving apart.
Q. What causes the attractive forces between particles in matter?
The particles that make up some matter are close together and vibrate back and forth. If the motion of particles slows the particles move closer together. This is because the attraction between them pulls them toward each other. Strong attractive forces hold particles close together.
Q. What is required to cause changes in matter?
Adding or removing energy from matter causes a physical change as matter moves from one state to another. For example, adding thermal energy (heat) to liquid water causes it to become steam or vapor (a gas). And removing energy from liquid water causes it to become ice (a solid). …
Q. What are the forces of attraction?
Force of attraction is a force that pulls the body near due to its attraction. There are numerous attractive forces prevailing in nature. Some of them are magnetic force, electric force, electrostatic force and gravitational force.
Q. Which attractive force is the weakest?
London dispersion force
Q. What are the 2 types of forces of attraction?
There are two kinds of forces, or attractions, that operate in a molecule—intramolecular and intermolecular.
Q. What is the force of attraction between matter?
Cohesion or cohesive attraction or cohesive force is the action or property of like molecules sticking together, being mutually attractive. It is an intrinsic property of a substance that is caused by the shape and structure of its molecules.
Q. What happens to the force of attraction?
Since the gravitational force is directly proportional to the mass of both interacting objects, more massive objects will attract each other with a greater gravitational force. So as the mass of either object increases, the force of gravitational attraction between them also increases.