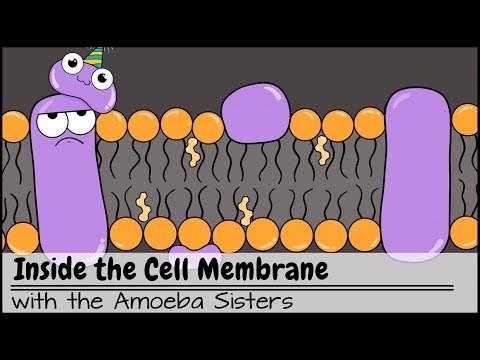
Q. What helps maintain flexibility of the cell membrane?
Cholesterol molecules also keep the phospholipid tails from coming into contact and solidifying. This ensures that the cell membrane stays fluid and flexible. Some plasma membrane proteins are located in the lipid bilayer and are called integral proteins.
Q. What increases the flexibility fluidity of the cell membrane?
One way to increase membrane fluidity is to heat up the membrane. Lipids acquire thermal energy when they are heated up; energetic lipids move around more, arranging and rearranging randomly, making the membrane more fluid.
Table of Contents
- Q. What helps maintain flexibility of the cell membrane?
- Q. What increases the flexibility fluidity of the cell membrane?
- Q. Why are cell membranes flexible?
- Q. What maintains cell membrane structure?
- Q. What is the basic structure of cell membrane?
- Q. What are the 4 parts of the cell membrane?
- Q. What are the 5 functions of cell membrane?
- Q. What controls DNA and cell activities?
- Q. What regulates cell activity?
- Q. Is the control center of cell activities?
- Q. What is the control center of all cell activities?
- Q. What is the control center of a cell called?
- Q. Who control the function of a cell?
- Q. What is the controlling unit of cell?
- Q. What is cell short answer?
Q. Why are cell membranes flexible?
A cell’s plasma membrane defines the boundary of the cell and determines the nature of its contact with the environment. The plasma membrane must be sufficiently flexible to allow certain cells, such as red blood cells and white blood cells, to change shape as they pass through narrow capillaries.
Q. What maintains cell membrane structure?
Cholesterol. Cholesterol is important in the membrane as it helps to maintain cell membrane stability and fluidity at varying temperatures. Cholesterol is bound to neighbouring phospholipid molecules via hydrogen bonds and therefore at low temperatures, reduces their packing.
Q. What is the basic structure of cell membrane?
The plasma membrane is composed of a bilayer of phospholipids, with their hydrophobic, fatty acid tails in contact with each other. The landscape of the membrane is studded with proteins, some of which span the membrane. Some of these proteins serve to transport materials into or out of the cell.
Q. What are the 4 parts of the cell membrane?
The four parts of the cell membrane are phospholipids, proteins, carbohydrates and cholesterol.
Q. What are the 5 functions of cell membrane?
Functions of the Plasma Membrane
- A Physical Barrier.
- Selective Permeability.
- Endocytosis and Exocytosis.
- Cell Signaling.
- Phospholipids.
- Proteins.
- Carbohydrates.
- Fluid Mosaic Model.
Q. What controls DNA and cell activities?
Known as the cell’s “command center,” the nucleus is a large organelle that stores the cell’s DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). The nucleus controls all of the cell’s activities, such as growth and metabolism, using the DNA’s genetic information.
Q. What regulates cell activity?
The major events of the cell cycle. The major events of the cell cycle are regulated by successive waves of kinase and ubiquitin ligase activity. G1-cyclin–CDK activity is required to initiate the cell cycle and activate B-type-cyclin–CDK activity.
Q. Is the control center of cell activities?
The nucleus is the membrane bound important structure of the cell. It controls all the cellular activities and thus, called as brain of the cell.
Q. What is the control center of all cell activities?
Nucleus controls the entire activities of the cell.
Q. What is the control center of a cell called?
The nucleus, formed by a nuclear membrane around a fluid nucleoplasm, is the control center of the cell. Threads of chromatin in the nucleus contain deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), the genetic material of the cell.
Q. Who control the function of a cell?
The nucleus is the control center of the cell that contains the chromosomes with their genetic material, DNA. The nucleus controls all cellular functions.
Q. What is the controlling unit of cell?
Nucleus
Q. What is cell short answer?
“A cell is defined as the smallest, basic unit of life that is responsible for all of life’s processes.” Cells are the structural, functional, and biological units of all living beings. A cell can replicate itself independently. Hence, they are known as the building blocks of life.