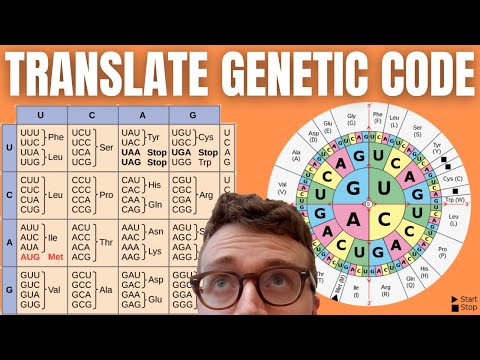
If the first triplet codon after the start codon is CAA then the amino acid which is formed is the glutamine.
Q. What is the difference between DNA and proteins?
DNA contains the genetic information of all living organisms. Proteins are large molecules made up by 20 small molecules called amino acids. All living organisms have the same 20 amino acids, but they are arranged in different ways and this determines the different function for each protein.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the difference between DNA and proteins?
- Q. What is the relationship between DNA and amino acids?
- Q. What amino acid has only one codon?
- Q. What is the relationship between DNA and a protein?
- Q. What comes first protein or DNA?
- Q. Does DNA control the production of protein?
- Q. Why is it important for DNA to control the production of proteins?
- Q. What is the first step of protein synthesis called?
- Q. What is the function of DNA in protein synthesis?
- Q. How does DNA do protein synthesis?
- Q. Is RNA important for protein synthesis?
- Q. What is the importance of protein synthesis?
- Q. What are the six steps of protein synthesis?
- Q. How does RNA contribute to protein synthesis?
- Q. What is the main function of tRNA in relation to protein synthesis?
- Q. How is the two stage process of protein synthesis advantageous?
- Q. What are the two functions of tRNA?
- Q. In what two places in the cell can translation occur?
- Q. What occurs during translation?
Q. What is the relationship between DNA and amino acids?
The genetic code is the relation between the sequence of bases in DNA (or its RNA transcripts) and the sequence of amino acids in proteins. Experiments by Francis Crick, Sydney Brenner, and others established the following features of the genetic code by 1961: 1. Three nucleotides encode an amino acid.
Q. What amino acid has only one codon?
Tryptophan
Q. What is the relationship between DNA and a protein?
DNA carries the genetic information for making proteins. The four bases A, T, C and G make up the genetic code. The base sequence determines amino acid sequence in protein.
Q. What comes first protein or DNA?
RNA First. One possible solution is the so-called RNA World approach, in which RNA came before either proteins or DNA. This solution is attractive because RNA combines some of the features of proteins and DNA. RNA can catalyze chemical reactions just like proteins, and it can store genetic information just like DNA.
Q. Does DNA control the production of protein?
The information to make proteins is stored in an organism’s DNA. Each protein is coded for by a specific section of DNA called a gene. A gene is the section of DNA required to produce one protein.
Q. Why is it important for DNA to control the production of proteins?
The flow of information from DNA to RNA to proteins is one of the fundamental principles of molecular biology. It is so important that it is sometimes called the “central dogma.” Through the processes of transcription and translation, information from genes is used to make proteins.
Q. What is the first step of protein synthesis called?
Transcription
Q. What is the function of DNA in protein synthesis?
DNA is the primary genetic material contained within your cells and in nearly all organisms. It’s used to create proteins during protein synthesis, which is a multi-step process that takes the coded message of DNA and converts it into a usable protein molecule.
Q. How does DNA do protein synthesis?
The Art of Protein Synthesis During transcription, DNA is used as a template to make a molecule of messenger RNA (mRNA). The molecule of mRNA then leaves the nucleus and goes to a ribosome in the cytoplasm, where translation occurs. During translation, the genetic code in mRNA is read and used to make a protein.
Q. Is RNA important for protein synthesis?
Messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules carry the coding sequences for protein synthesis and are called transcripts; ribosomal RNA (rRNA) molecules form the core of a cell’s ribosomes (the structures in which protein synthesis takes place); and transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules carry amino acids to the ribosomes during protein …
Q. What is the importance of protein synthesis?
Although the outcome of protein synthesis can be involved and quite complex, its purpose is rather straightforward. The purpose of protein synthesis is simply to create a polypeptide — a protein made out of a chain of amino acids. In a hair follicle cell, a protein called keratin is made.
Q. What are the six steps of protein synthesis?
Put the following steps of protein synthesis in correct order of occurrence:
- mRNA is produced in nucleus.
- ribosome moves along mRNA.
- DNA uncoils for transcription.
- polypeptide is produced.
- tRNA brings amino acids to ribosome.
- mRNA moves to ribosome.
Q. How does RNA contribute to protein synthesis?
Q. What is the main function of tRNA in relation to protein synthesis?
Role of the t RNA in protein synthesis to decode a codon of mRNA, using its anticodon so as to transfer a specific amino acid to the end of a chain in the ribosome. Thus, forming a protein.
Q. How is the two stage process of protein synthesis advantageous?
The protein synthesis is a two stage process, this reduces the complexity of the process involved in protein synthesis. Explanation: The transcription is the process in which RNA molecules are produced by using the double stranded DNA molecule.
Q. What are the two functions of tRNA?
All tRNAs have two functions: to be chemically linked to a particular amino acid and to base-pair with a codon in mRNA so that the amino acid can be added to a growing peptide chain. Each tRNA molecule is recognized by one and only one of the 20 aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases.
Q. In what two places in the cell can translation occur?
In eukaryotes, transcription and translation take place in different cellular compartments: transcription takes place in the membrane-bounded nucleus, whereas translation takes place outside the nucleus in the cytoplasm. In prokaryotes, the two processes are closely coupled (Figure 28.15).
Q. What occurs during translation?
In translation, messenger RNA (mRNA) is decoded in a ribosome, outside the nucleus, to produce a specific amino acid chain, or polypeptide. The polypeptide later folds into an active protein and performs its functions in the cell.