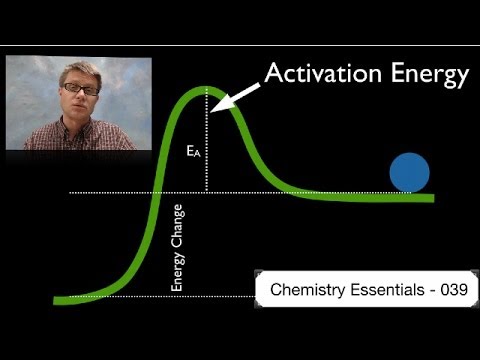
Q. What increases activation energy?
The minimum energy needed for a reaction to proceed, known as the activation energy, stays the same with increasing temperature. An increase in temperature causes a rise in the energy levels of the molecules involved in the reaction, so the rate of the reaction increases.
Q. What are 3 factors that will increase activation energy?
Lesson
Table of Contents
- Q. What increases activation energy?
- Q. What are 3 factors that will increase activation energy?
- Q. How is the activation energy achieved or created?
- Q. What decreases the activation energy of a reaction?
- Q. What are 4 ways Enzymes lower activation energy?
- Q. What happens as the activation energy increases the pressure of the system decreases?
- Q. Does the activation energy change with temperature?
- Q. What happens as the activation energy increases quizlet?
- Q. Why is the activation energy of reaction decreases with rise in temperature?
- Q. How is activation energy affected by rise in temperature class 12?
- Q. What is the relationship between activation energy and reaction rate?
- Q. Do catalysts lower activation energy?
- Q. Do catalysts increase activation energy?
- Q. Does Catalyst affect equilibrium constant?
- Q. Why do most reactions start fast and get slower and slower?
- Q. At what time rate of reaction is fastest?
- Q. What four factors would allow for the fastest reaction?
- Q. Which reaction is the quickest?
- Q. How do you know if a reaction is slow or fast?
- Q. Is rusting a slow or fast reaction?
- Q. What is an example of a slow reaction?
- Q. What is the minimum amount of energy required to start a reaction?
- Q. How can you tell from a graph where the reaction is fastest?
- Q. How do you know a reaction is complete?
- Q. Why do reactions slow down and eventually stop?
- Q. What are the drawbacks of very fast reactions?
- Q. What does 1 t represent?
- Q. Why do reactions eventually stop?
- Q. What are the 5 factors that affect reaction rate?
- surface area of a solid reactant.
- concentration or pressure of a reactant.
- temperature.
- nature of the reactants.
- presence/absence of a catalyst.
Q. How is the activation energy achieved or created?
In order for this transition state in the reaction to be achieved, some energy must enter into the reaction other than the chemical energy of the reactants. This energy is the activation energy. Once the intermediate product, or activated complex, is formed, the final products are formed from it.
Q. What decreases the activation energy of a reaction?
A catalyst is something that lowers the activation energy; in biology it is an enzyme. The catalyst speeds up the rate of reaction without being consumed; it does not change the initial reactants or the end products.
Q. What are 4 ways Enzymes lower activation energy?
Enzymes lower activation energy through various means, including positioning substrates together in the proper orientation, applying torque on the substrates, providing the proper charge or pH microenvironment, and adding or removing functional groups on the substrates.
Q. What happens as the activation energy increases the pressure of the system decreases?
The pressure of the system decreases. The kinetic energy of colliding molecules changes. The reactant surface area decreases. The reaction begins to slow down.
Q. Does the activation energy change with temperature?
Q. What happens as the activation energy increases quizlet?
The higher the activation energy, the more energy is required for a collision to be effective. The lower the activation energy, the less energy is required. Increasing the temperature will almost always increase the rate of reaction. This happens because decreasing the temperature causes the reactants to move slower.
Q. Why is the activation energy of reaction decreases with rise in temperature?
Q: Why does the rate of a reaction increase when the temperature increases? Solution: When the temperature increases, the fraction of molecules that have kinetic energies more than the activation energy of the reaction increases. Therefore, the total activation energy of the reaction decreases.
Q. How is activation energy affected by rise in temperature class 12?
Ans: As the temperature increases, the kinetic energy of molecules increases. So, on increasing the temperature, the collision between reacting molecules increases, and therefore, the activation energy increases.
Q. What is the relationship between activation energy and reaction rate?
The activation energy of a chemical reaction is closely related to its rate. Specifically, the higher the activation energy, the slower the chemical reaction will be. This is because molecules can only complete the reaction once they have reached the top of the activation energy barrier.
Q. Do catalysts lower activation energy?
Key points. A catalyst is a substance that can be added to a reaction to increase the reaction rate without getting consumed in the process. Catalysts typically speed up a reaction by reducing the activation energy or changing the reaction mechanism.
Q. Do catalysts increase activation energy?
A catalyst increases the energy of reactant molecules so that a chemical reaction can take place. A catalyst lowers the activation energy of a reaction, so that a chemical reaction can take place.
Q. Does Catalyst affect equilibrium constant?
Equilibrium constants are not changed if you add (or change) a catalyst. The only thing that changes an equilibrium constant is a change of temperature. The position of equilibrium is not changed if you add (or change) a catalyst. A catalyst speeds up both the forward and back reactions by exactly the same amount.
Q. Why do most reactions start fast and get slower and slower?
Concentration: If there is more of a substance in a system, there is a greater chance that molecules will collide and speed up the rate of the reaction. If there is less of something, there will be fewer collisions and the reaction will probably happen at a slower speed.
Q. At what time rate of reaction is fastest?
Temperature. Usually reactions speed up with increasing temperature. Physical state of reactants. Powders react faster than blocks – greater surface area and since the reaction occurs at the surface we get a faster rate.
Q. What four factors would allow for the fastest reaction?
Reactant concentration, the physical state of the reactants, and surface area, temperature, and the presence of a catalyst are the four main factors that affect reaction rate.
Q. Which reaction is the quickest?
Reactions in phases that easily mix, such as gases and liquids, occur much faster than reactions between solids. The extent of mixing of the reactants influences the frequency of molecular collisions – if reactants are more thoroughly mixed, the molecules will collide more often and thus react faster.
Q. How do you know if a reaction is slow or fast?
You can also determine which reaction is fast and which reaction is slow if you are given the rate law. Which ever reactants are present in the rate law are the reactants in the slow reaction.
Q. Is rusting a slow or fast reaction?
Rusting is a slow reaction.
Q. What is an example of a slow reaction?
Rusting of Iron Formation of crude oil by a geochemical reaction and disintegration of radium are other examples of slow reactions.
Q. What is the minimum amount of energy required to start a reaction?
the activation energy
Q. How can you tell from a graph where the reaction is fastest?
Rate graphs The magenta line has a steeper gradient and represents conditions favouring a faster reaction than the green line. When the reaction is finished (the end-point) the graph goes flat as no more products are being produced.
Q. How do you know a reaction is complete?
A reaction is “completed” when it has reached equilibrium — that is, when concentrations of the reactants and products are no longer changing. If the equilibrium constant is quite large, then the answer reduces to a simpler form: the reaction is completed when the concentration of a reactant falls to zero.
Q. Why do reactions slow down and eventually stop?
Reactions usually slow down as time goes on because of the depletion of the reactants. The rate constant, or the specific rate constant, is the proportionality constant in the equation that expresses the relationship between the rate of a chemical reaction and the concentrations of the reacting substances.
Q. What are the drawbacks of very fast reactions?
There are two difficulties with fast reactions. One is that the time that it takes to mix reactants or to change the temperature of the system may be significant in comparison with the half-life, so that the initial time cannot be measured accurately.
Q. What does 1 t represent?
1/t means that the order of reaction is a first order. Meaning that the rate of reaction is directly proportional to reactant concentration. Scientists work with the standard units, therefore 1/t is 1 divide by 1 second.
Q. Why do reactions eventually stop?
As the reaction products accumulate, the concentration of each reactant decreases and so does the reaction rate. Eventually, the rates of the forward and reverse reactions become equal, so that the concentrations of reactants and products stop changing.
Q. What are the 5 factors that affect reaction rate?
Five factors typically affecting the rates of chemical reactions will be explored in this section: the chemical nature of the reacting substances, the state of subdivision (one large lump versus many small particles) of the reactants, the temperature of the reactants, the concentration of the reactants, and the …