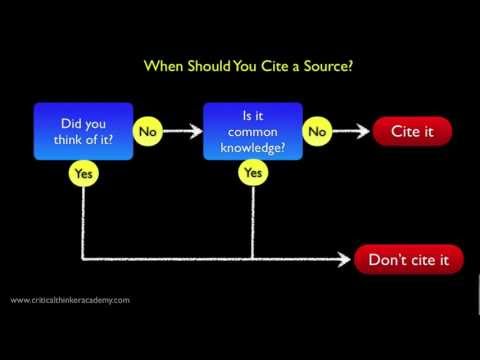
Common knowledge does not need to be cited. Common knowledge includes facts that are known by a lot of people and can be found in many sources. For example, you do not need to cite the following: Abraham Lincoln was the 16th President of the United States.
Q. Do original ideas need to be cited?
If you are putting thoughts and words into your paper that are both original to you and are not things you’ve written before, then there is generally no need to cite them in your work. As such, anything that is not cited in your work is presumed to be yours.
Table of Contents
- Q. Do original ideas need to be cited?
- Q. Do you have to cite an idea?
- Q. What are the four things that need to be cited?
- Q. What are 5 things that don’t need to be cited?
- Q. What are five things that must be cited or documented?
- Q. What are 3 ways to keep track of your sources?
- Q. What are 3 ways you can cite a source in your work?
- Q. Do you have to cite if you summarize?
- Q. Do you need to cite the source even if you paraphrase or summarize?
- Q. Do you have to cite your source if you rewrite the sentence in your own words?
- Q. When you summarize a source you do not need to cite it?
- Q. Are summarizing and paraphrasing the same?
- Q. When would you want to directly quote a source over paraphrasing it?
- Q. Should I cite every sentence?
- Q. How many times do you need to cite the same source in a paragraph?
- Q. How many in-text citations is too many?
- Q. Can I end a paragraph with a citation APA?
Q. Do you have to cite an idea?
You must cite the source every time you incorporate research, words, ideas, data, or information that is not your own (2). While you are synthesizing and often summarizing many pieces of information, you must cite any concept that is not your own.
Q. What are the four things that need to be cited?
What Information Should Be Cited and Why?
- Discuss, summarize, or paraphrase the ideas of an author.
- Provide a direct quotation.
- Use statistical or other data.
- Use images, graphics, videos, and other media.
Q. What are 5 things that don’t need to be cited?
There are certain things that do not need documentation or credit, including:
- Writing your own lived experiences, your own observations and insights, your own thoughts, and your own conclusions about a subject.
- When you are writing up your own results obtained through lab or field experiments.
Q. What are five things that must be cited or documented?
Information that always must be cited—whether web-based or print-based—includes:
- Quotations, opinions, and predictions, whether directly quoted or paraphrased.
- Statistics derived by the original author.
- Visuals in the original.
- Another author’s theories.
- Case studies.
Q. What are 3 ways to keep track of your sources?
Track Useful Sources as You Find Them
- Send an article’s citation information to your account with a citation management tool like EndNote.
- Download and save or print articles as you find them.
- Most databases have ways to send a list of articles to your email.
- Write down information about your sources as you find them.
Q. What are 3 ways you can cite a source in your work?
These methods are direct quotation from another source, paraphasing or summarising material, and citing the whole of a source document.
Q. Do you have to cite if you summarize?
Always use in-text citations when you paraphrase or summarize, to let the reader know that the information comes from another source.
Q. Do you need to cite the source even if you paraphrase or summarize?
ALWAYS CITE, in the following cases: When you quote two or more words verbatim, or even one word if it is used in a way that is unique to the source. Explanation. When you introduce facts that you have found in a source.
Q. Do you have to cite your source if you rewrite the sentence in your own words?
If you rewrite that perfect paragraph or sentence (aka you paraphrase or summarize it), remember that the ideas in the reworded version still came from the original author(s)…so you must cite the original source! Don’t forget to cite the source that the quote comes from!
Q. When you summarize a source you do not need to cite it?
A ten-paragraph article is summarized into one single paragraph. As for giving source credit, since the author’s name and title of the source are stated at the beginning of the summary paragraph, you don’t need an in-text citation.
Q. Are summarizing and paraphrasing the same?
Paraphrasing involves putting a passage from source material into your own words. Summarizing involves putting the main idea(s) into your own words, including only the main point(s). Once again, it is necessary to attribute summarized ideas to the original source.
Q. When would you want to directly quote a source over paraphrasing it?
Choose a direct quote when it is more likely to be accurate than would summarizing or paraphrasing, when what you’re quoting is the text you’re analyzing, when a direct quote is more concise that a summary or paraphrase would be and conciseness matters, when the author is a particular authority whose exact words would …
Q. Should I cite every sentence?
In order to make it clear that quoted or paraphrased information is not your own work, cite every quotation and every new instance of paraphrased information in your paragraphs. Occasionally, a long paraphrase may continue over several paragraphs.
Q. How many times do you need to cite the same source in a paragraph?
Including just one citation at the end of a paragraph is not sufficient unless the last sentence is the only information in the paragraph that came from the cited source. Cite sources often and correctly throughout a paragraph in order to avoid unintentional plagiarism.
Q. How many in-text citations is too many?
Two or three may be preferred for more controversial material or as a way of preventing linkrot for online sources, but more than three should generally be avoided; if four or more are needed, consider bundling (merging) the citations.
Q. Can I end a paragraph with a citation APA?
Therefore, putting one citation at the end of a paragraph paraphrase is NOT APA compliant. If paraphrasing multiple consecutive sentences from the same source, cite each sentence to avoid plagiarism.