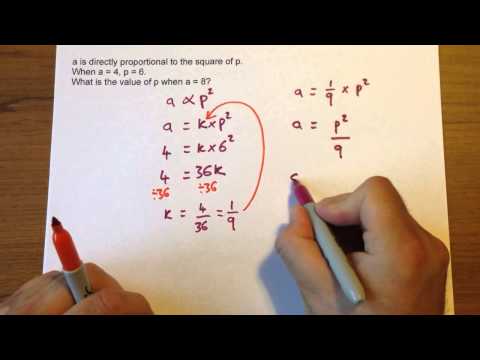Direct square proportion is the relationship between two things in which the quantity of one is directly proportional to the square of the other. In this relationship, the ratio of the first to the square of the second is a constant. In this type of proportion, the two quantities change by the same factor.
Q. What is the inverse square law formula?
Intuitive explanation of the inverse square law. Written by Willy McAllister. In Coulomb’s Law, the distance between charges appears in the equation as 1 / r 2 1/r^2 1/r21, slash, r, squared. That makes Coulomb’s Law an example of an inverse square law.
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the inverse square law formula?
- Q. What is another name for the direct square law?
- Q. How does kVp affect IR exposure?
- Q. What is the effect of a grid on contrast?
- Q. What is the purpose of a grid?
- Q. What is the purpose of moving grid?
- Q. Does collimation reduce scatter?
- Q. What is the biggest source of scatter when taking radiographs?
- Q. What increases scatter?
- Q. How is Bucky factor calculated?
- Q. What is a Bucky factor?
- Q. What is a Bucky used for?
- Q. What is Bucky factor in radiology?
- Q. Why is it called a Bucky?
- Q. What is chest Bucky?
- Q. What is a Potter Bucky diaphragm?
- Q. Which part of a radiographic table is called a Bucky?
- Q. What is moving grid?
- Q. What is focused grid?
- Q. What is Grid and its types?
Q. What is another name for the direct square law?
Direct Square Law / Density Maintenance Formula: This is similar to the Inverse square law formula for maintenance of radiation intensity .
Q. How does kVp affect IR exposure?
The kVp affects the exposure to the IR because it alters the amount and penetrating ability of the x-ray beam. When the kVp is increased at the control panel, a larger potential difference occurs in the x-ray tube, giving more electrons the kinetic energy to produce x-rays and increasing the kinetic energy overall.
Q. What is the effect of a grid on contrast?
As radiographers, we know that the whole purpose of using grids in radiography is to reduce scatter radiation, thereby increasing radiographic contrast. Thus, using grids with higher ratios and higher frequencies cleans up more scatter radiation, which increases contrast more than low-ratio and low-frequency grids.
Q. What is the purpose of a grid?
A grid can be used to organize graphic elements in relation to a page, in relation to other graphic elements on the page, or relation to other parts of the same graphic element or shape.
Q. What is the purpose of moving grid?
in radiology, a device consisting essentially of a series of narrow lead strips closely spaced on their edges and separated by spacers of low density material; used to reduce the amount of scattered radiation reaching the x-ray film.
Q. Does collimation reduce scatter?
Collimation and Contrast Because collimation decreases the x-ray beam field size, less scatter radiation is produced within the patient, and less scatter radiation reaches the IR.
Q. What is the biggest source of scatter when taking radiographs?
Scatter radiation is generated in the patient when an x-ray beam strikes the patient. The maximum scatter radiation occurs perpendicular to the x-ray beam. In other words, if the x-ray unit is above the patient, the highest scatter radiation at a set distance from the patient will be out to the side of the patient.
Q. What increases scatter?
The thicker or larger the body part is, the greater are the scatter and the fog. When there is a greater quantity of tissue in the path of the x-ray beam, there will be greater absorption of the x-ray beam and more interactions that produce scatter radiation.
Q. How is Bucky factor calculated?
Bucky factor = 1 / Grid penetration.
Q. What is a Bucky factor?
Characteristics. The Bucky factor is the ratio of radiation on the grid to the transmitted radiation. It indicates the increase in patient dose due to the use of a grid. It is typically two to six. However, this leads to increased x-ray tube loading and radiation exposure to the patient.
Q. What is a Bucky used for?
A bucky is typically used for table or wall mounted x-ray systems and holds the x-ray cassette and grid. A bucky, is a device found underneath the exam table, a drawer like device that the cassette and grid is slid into before shooting x-ray.
Q. What is Bucky factor in radiology?
The Bucky factor is the ratio of radiation on the anti-scatter grid to the transmitted radiation. Hence, the Bucky factor reflects the increased radiation dose required from anti-scatter grid use, as any increase in mAs proportionally increases dose.
Q. Why is it called a Bucky?
When Joe Simon created his initial sketch of Captain America for Marvel Comics precursor Timely Comics in 1940, he included a young sidekick. “The boy companion was simply named Bucky, after my friend Bucky Pierson, a star on our high school basketball team”, Simon said in his autobiography.
Q. What is chest Bucky?
Chest X-ray bucky is an important part of human body photography. Chest X-ray in the posterior and anterior position is one of the most widely used routine X-ray examinations in clinical practice and one of the routine radiological quality control examinations.
Q. What is a Potter Bucky diaphragm?
A section of the resultant Bucky-Potter Diaphragm is shown. It was placed between the patient and the X-ray film. Parallel lead strips move across inside the wooden casing during an exposure. They block scattered rays travelling at other angles.
Q. Which part of a radiographic table is called a Bucky?
Spot film shows increased image quality because of the reduction of scattered radiation fog. Is called a Bucky, and the moving grid during the exposure blurs the image of the grid lines so that the grid image is not visible on the film. What does a stationary gird do?
Q. What is moving grid?
MOVING GRID A grid which is set into motion (one way or oscillating) just before an X-ray exposure starts. The intention is to remove or reduce the shadows produced by the lead strips in the grid. The moving grid was invented by Hollis E. Potter in 1920, see Potter Bucky grid. See also stationary grid.
Q. What is focused grid?
Q. What is Grid and its types?
Let’s look at five kinds of layout grids; manuscript, column, baseline, modular and hierarchical. Manuscript Grids are used in documents, ebooks, pdfs and presentations with lots of text. Column Grids are used for magazines to organize content in columns so it is easier to read.